
Market recovery - driven by positive results, relatively encouraging economics, and lower interest rates
• GLOBAL CAPITAL MARKETS OVERVIEW:
The Wall Street stock market rebounded by more than 1.5%. After the decline began in the third quarter, investors' attention turned to solid economic growth and strong earnings prospects, regaining momentum. Following JPMorgan Chase and BlackRock, Citigroup, Wells Fargo, Bank of America, Morgan Stanley, and UnitedHealth have exceeded market expectations. The benchmark US 10-year Treasury bond yield fell below 1.52%, benefiting from large technology stocks such as Microsoft, Apple, Facebook, and Alphabet. At the same time, new economic data provided additional support, the number of first-time jobless claims fell to a new pandemic low, and the rise in producer inflation was lower than expected. The Dow Jones index rose 534.75 points, or 1.6%, to 34,912.56 points; the S&P 500 index rose 1.7% to 4438.26 points, the largest increase since March; the Nasdaq index rose 1.7% to 14,823.43 points. The S&P/TSX Composite Index closed above 20,800 on Thursday, the highest level in more than five weeks. Energy stocks rose 1.5%, affected by rising oil and gas prices, while materials stocks rose 0.9%, affected by rising gold prices. Technology stocks followed Nasdaq up 1.1%. The medical, financial, and industrial sectors rose further. On the political front, the United States announced that its Canadian land border would be reopened to vaccinated travelers in November, ending restrictions on non-essential land travel since March 2020. European stock markets rose on Thursday. The Frankfurt DAX index rose more than 1% to a two-week high of 15,463 points. Earlier better than expected earnings reports stimulated investors' risk appetite, although inflation risks continued to linger. Strong bank earnings exceeded analysts' expectations and boosted global stock markets. In terms of data, the producer prices paid to American producers rose the least in September, while China's factory-door inflation rate rose at a record rate. At the same time, traders also digested the latest minutes of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meeting on the Fed's September meeting. The meeting confirmed that the Fed would gradually reduce asset purchases as early as November. On Thursday, driven by the banking and energy sectors, the FTSE MIB index rose 1.2% to close at 26277 points, the highest since August 18. Although the latest data show that US inventories have increased, crude oil prices are hovering at multi-year highs as demand soars. The trading price of WTI crude oil is close to US$81 per barrel, and the trading price of benchmark Brent crude oil is close to US$84 per barrel. At the same time, the quarterly earnings results of US financial giants continued to exceed market expectations. At the same time, as investors reached a consensus that the central bank would limit the rise in inflation, concerns about rising inflation began to weaken. In addition, the minutes of the Fed's meeting yesterday showed that the Fed should begin to tighten monetary policy from mid-November to mid-December. CAC 40 index rose more than 1% to close at 6,690 points, the highest level since September 23. Strong earnings season hopes supported it. At the same time, the prospect of rising inflation and monetary policy tightening continued to worry investors. In a single stock, the French advertising group Publicis shares rose 2.7%. The group announced better-than-expected organic growth in the third quarter and improved its outlook for 2021 on the grounds of the global shift to digital media and e-commerce. The Shanghai Composite Index fell 0.1% to close at 3558 points, while the Shenzhen Composite Index fell 0.08% to close at 14,341 points. With record factory-gate inflation, investors are cautious about the direction of China's monetary policy. Due to rising commodity prices, China's producer price index rose 10.7% year-on-year in September from 9.5% in August. Investors worry that accelerating inflation and lower-than-expected loan growth in September have limited the possible scope of monetary policy easing. China's real estate index fell 3.88%, the medical sub-index fell 2.27%, and the financial and consumer goods sectors fell about 1%. The Nikkei 225 index rose 1.46% to close at 28551 points, while the broader Topix index rose 0.67% on Thursday. Technology heavyweights rose after a dovish statement from the Bank of Japan board members. Asahi Noguchi, a member of the Bank of Japan's board of directors, said in a speech on Thursday that Japan will not choose to reduce monetary stimulus in response to rising inflation because the country has not yet achieved its 2% price stability target. Electronics giants Tokyo Electronics (5.18%), Screen Holdings (4.33%), and Advantest (3.8%) led gains in technology heavyweights tracking their Nasdaq peers, while shipping and refinery companies continued to fall. The S&P/ASX 200 index rose above 7,350 points before losing momentum, but it still rose 0.54% to close at 7,312 points on Thursday, ahead of the rise in US technology stocks and gold and copper prices. Technology stocks rose, led by Afterpay (4.48%) and Xero (5.28%). Australian mining stocks also performed strongly. BHP Billiton (0.56%), Fortescue Metals (2.29%), Rio Tinto (1.15%), and South32 (4.93%) pushed up the index against the backdrop of rising gold and copper prices, despite recent coal prices. The prices of iron ore and iron ore have fallen. Data shows that due to the prolonged blockade in New South Wales, Victoria, and the Australian Capital Territory, the unemployment rate rose slightly in September, and the employment rate fell. The NZX 50 index rebounded to about 12,100 points and then recovered most of the gains. On Thursday, it rose only 0.18% to close at 12,049 points. The New Zealand government announced the largest increase in new coronary pneumonia cases in six weeks. All detected cases have occurred in Auckland, which increases the possibility of other lockdowns in the country's largest city after the lockdown was lifted on Monday. A2 Milk Company (4.64%) continued to rise in the face of legal proceedings. Oakland International Group (1.77%) rebounded after the news that passenger traffic increased by 68% year-on-year in August, supporting the market's rise.
• REVIEWING ECONOMIC DATA:
Looking at the last economic data:
- US: On Thursday, Citigroup, Wells Fargo, Bank of America, Morgan Stanley, and UnitedHealth exceeded market expectations after JP Morgan Chase and BlackRock, and the three major US stock indexes rose about 1%. The earnings season kicked off yesterday, and traders tried to assess the impact of recent inflationary pressures and supply constraints on companies. In addition, investors continue to digest the minutes of the recent Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meeting, which shows that the Fed may start to scale down as early as mid-November.
- US: In September 2021, the producer price for final demand in the United States rose 0.5% month-on-month, the smallest increase so far this year, and was lower than the 0.6% market forecast. The nearly 80% increase in PPI can be traced to a 1.3% increase in final demand commodity prices, the most significant increase since May, mainly due to gasoline (3.9%). The cost of beef and veal, residential electricity, fresh and dried vegetables, natural gas fuel, and significant basic organic chemicals has also risen. The final demand service price rose by 0.2%, the ninth consecutive increase. Trade services (0.9%), namely fuel and lubricant retail profit margins (11.6%), led the growth. At the same time, the annual producer inflation rate continued to accelerate to 8.6%, setting a new record since November 2010.
- US: In the week ending October 9th, the number of new Americans applying for unemployment benefits fell to 293,000, which is the lowest level since the outbreak hit the US economy in March 2020 and well below market expectations of 319,000. With the rebound in demand for workers and the slowdown in dismissals, layoffs, and departures, the labor market continues to recover steadily. Nevertheless, there are still signs that many people are still on the margins of the workforce due to lingering concerns about the coronavirus. The number of new applicants is still higher than the weekly average before the virus outbreak in 2019. The labor force participation rate in September was also lower than the level in February 2020.
- US: After Wells Fargo, Bank of America, Morgan Stanley, and UnitedHealth exceeded market expectations after JP Morgan Chase and BlackRock, US stock index futures rose sharply on Thursday, and the Dow Jones index contract rose more than 200 points. The earnings season kicked off yesterday, and traders tried to assess the impact of recent inflationary pressures and supply constraints on companies. In addition, investors continue to digest the minutes of the current Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meeting, which shows that the Fed may start to scale down as early as mid-November.
- US: The number of first-time jobless claims last week may have fallen to 319,000, close to the pandemic low of 311,000 reached in early September, as the labor market continues to recover steadily amid a rebound in worker demand, layoffs, layoffs, and a slowdown in turnover. Nevertheless, there are still signs that many people are still on the side of the labor force due to lingering concerns about the coronavirus, and the number of new applicants is much higher than the average weekly rate before the virus outbreak in 2019. Labor participation in September The speed is also lower than the February 2020 level. The number of people who continue to claim unemployment benefits may have dropped to a new low of 2.675 million in early October. These people are still receiving regular state unemployment benefits.
- RU: In the second week of October, the Russian ruble continued to rise against the US dollar, reaching 71.4, the highest level since July 2020. Energy prices rose. The Bank of Russia is expected to raise interest rates later this month to curb inflation. Policymakers wish to raise interest rates by 50 basis points when they meet on October 22, while Brent crude oil will reach a three-year high of more than $84 per barrel due to increased demand and supply disruptions.
- SW: Sweden's annual inflation rate rose from 2.1% in August to 2.5% in September 2021, but it was lower than market expectations of 2.7%. This is the highest level since November 2011, mainly due to housing and utility prices (5.1% vs. 3.8% in August), namely electricity and transportation (6.2% vs. 6.4%), including fuel. Additional promotion pressure comes from education (2.5% vs. 2%); restaurants and hotels (2.4% vs. 2.6%); miscellaneous goods and services (2% vs. 1.4%), and food and non-alcoholic beverages (0.9% vs. 0.3%). Measured at a fixed interest rate, consumer prices rose by 2.8% year-on-year in September, the fastest rate since October 2008, lower than market expectations of 3% but higher than the central bank's target of 2%. On a monthly basis, CPI and CPIF both rose 0.5%.
- JP: In August 2021, Japanese industrial production fell 3.6% month-on-month, after falling 1.5% in the previous month to only 3.2%. This marked the second consecutive month of shrinking industrial output, and the number of delta strains of COVID-19 cases across the country continued to rise. The automobile industry (-15.2% in July and -3.3% in July), the electrical machinery industry (8.6%, and -4.6% in July), the information and communication electronic equipment industry (11.5%, and -4.9% in July), and Production machinery (3.2%, -1.6% in July). On an annual basis, the industrial output value increased by 8.8% in August and 11.6% in July.
- CN: On October 14, 2021, the People's Bank of China provided a total of 10 billion yuan in a seven-day reverse repurchase at an interest rate of 2.2%. One hundred billion yuan expired on the same day, and the central bank had a net outflow of 90 billion yuan that day. The central bank stated that this move aims to maintain reasonable and sufficient liquidity, which means that before the end of the week-long holiday on October 7th, about 100 billion yuan will be injected every day to meet the growing demand for liquidity, and normalization will be introduced.
- CN: China's stock market fluctuated in early trading on Thursday after the release of September inflation data. The Shanghai Composite Index fell 0.15%, and the Shenzhen stock market rose 0.2%. China's producer price index soared 10.7% year-on-year, higher than the expected increase in raw material prices, while the consumer price index rose 0.7% year-on-year, lower than the 0.9% forecast. Shipping and energy-related stocks dragged down the market, while gold-related and economic reopening stocks in the aviation, entertainment, and tourism industries rose in early trading. Elsewhere, Hong Kong markets are closed on Thursdays.
- CN: In September 2021, food prices in China fell by 5.2% year-on-year, after falling 4.1% in the previous month. This marked the fourth consecutive month of decline in food costs and the fastest drop for the fourth straight month. The price of pork fell even quicker after a sharp increase due to the African swine flu outbreak in 2019 (August:- 44.9%, a decrease of -46.9%). In addition, the price of fresh vegetables has fallen faster (-2.5% and -1.5%, respectively), while the cost of fresh fruits has fallen by 0.8% after rising by 5% in August. At the same time, the prices of edible oil (6.5% vs. 6.8%), dairy products (1.6% vs. 1.8%), and eggs (12.6% vs. 11.9%) have risen at a moderate rate.
• LOOKING AHEAD:
Today, investors will receive:
- USD: Core Retail Sales m/m, Retail Sales m/m, Empire State Manufacturing Index, Import Prices m/m, Prelim UoM Consumer Sentiment, Business Inventories m/m, Prelim UoM Inflation Expectations, IMF Meetings, FOMC Member Williams Speaks, and Federal Budget Balance.
- EUR: French Final CPI m/m, Italian Trade Balance, and Trade Balance.
- NZD: BusinessNZ Manufacturing Index.
- JPY: Tertiary Industry Activity m/m.
- CAD: Wholesale Sales m/m.
• KEY EQUITY & BOND MARKET DRIVERS:
- MOEX rises to an all-time high of 4285.
- The Japanese stock market rose 412 points. Donghe Zinc (4.06%), Tokyo Electronics (2.73%), and Dalibang Screen (2.62%) contributed to this growth.
- The benchmark US 10-year Treasury bond yield was about 1.54% on Thursday, rising to a nearly 4-month high of 1.596% the day before, as investors digested higher-than-expected CPI data and the minutes of the Federal Open Market Committee meeting. In September, the inflation rate in the United States was higher than expected, indicating that the economy is facing rising price pressures and further aroused people's concerns that soaring commodity prices will drag down growth and push up inflation. At the same time, the minutes of the Fed's meeting showed that, as expected, the process of shrinking may begin in mid-November.
- In September 2021, food prices in China fell by 5.2% year-on-year, after falling 4.1% in the previous month. This marked the fourth consecutive month of decline in food costs and the fastest drop for the fourth straight month. The price of pork fell even quicker after a sharp increase due to the African swine flu outbreak in 2019 (August:- 44.9%, a decrease of -46.9%). In addition, the price of fresh vegetables has fallen faster (-2.5% and -1.5%, respectively), while the cost of fresh fruits has fallen by 0.8% after rising by 5% in August. At the same time, the prices of edible oil (6.5% vs. 6.8%), dairy products (1.6% vs. 1.8%), and eggs (12.6% vs. 11.9%) have risen at a moderate rate.
- The minutes of the last meeting of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) showed that the Fed did not decide to continue to purchase assets reasonably in September, but policymakers generally believe that if the economic recovery remains typically on the right track, the gradual reduction will end around the middle of next year. Thus, the process may be appropriate. Participants pointed out that if it is decided at the next meeting to start reducing purchases, reducing purchases can start from the monthly purchasing calendar starting in mid-November or mid-December. Policymakers also considered an illustrative path of reduction, including a monthly reduction in the rate of asset purchases, a reduction of US$10 billion in Treasury bonds, and a reduction of US$5 billion in institutional mortgage-backed securities (MBS).
- Avis Budget (CAR) shares fell 2.8%: Morgan Stanley downgraded its rating to below market.
- Bank of America (BAC) shares jumped 2.1% after a solid quarterly report.
- Commercial Metals (CMC) Shares Down 4.6% After Weak Quarterly Report.
- Helbiz (HLBZ) shares up 16% after partnering with the National Football League.
- IronSource (IS) shares up 7.5% after Credit Suisse's rating upgrade and security target.
- Lyft (LYFT) Shares Down 2.8% After RBC Capital Raises Target.
- NetApp (NTAP) Shares Up 2.1% After Citi Upgraded To Buy.
- Shopify (SHOP) shares up 1.8%: TD Securities kicks off research coverage of the paper with a HOLD rating and a $ 1,500 target.
- US Bancorp (USB) shares lost 3.7% after releasing the quarterly report.
• STOCK MARKET SECTORS:
- High: Information Technology, Materials, Industrials.
- Low: Consumer Discretionary.
• TOP CURRENCY & COMMODITIES MARKET DRIVERS:
- OIL: According to data from the EIA Oil State Report, in the week ending October 8, US crude oil inventories soared by 6.088 million barrels, much higher than the market forecast of 702,000 barrels. This is the third consecutive week of gains and the biggest gain since the week that ended on March 5. At the same time, gasoline inventories fell by 1.958 million barrels, while the market expected a drop of 0.83 million barrels.
- CAD: In mid-October, thanks to rising commodity prices and a broad rebound in risk appetite, the Canadian dollar's gains against the US dollar continued to below 1.24, the highest level since July 6. The price of crude oil futures, Canada's main export commodity, climbed to US$81 per barrel, as the shortage of natural gas in Europe and Asia supported the oil demand. At the same time, OPEC+ member countries insisted on plans to increase supply gradually. At the same time, the optimistic employment data reinforces the reason for reducing the Bank of Canada bond purchase program again before the end of this month.
- RMB: China's offshore renminbi rose to 6.43 against the US dollar, the highest level since September 15. Investors welcomed China's robust trade data, showing that imports and exports continued to grow at a steady rate in September, both hitting record highs. At the same time, after a meeting between senior Chinese and American officials over the weekend, expectations that the United States may partially cancel trade tariffs rose, supporting market sentiment. In other respects, as the Federal Reserve (Federal Reserve) will gradually reduce its massive stimulus plan next month, the US dollar is still close to a one-year high.
• CHART OF THE DAY:
The US dollar index fell back to 94.1 on Wednesday. It briefly touched an 11-month high of 94.5 in early trading. Investors digested recent inflation data and the minutes of the Federal Open Market Committee meeting. The latest CPI data shows that inflationary pressures remained high in September, raising concerns that inflation will stay at multi-year highs longer than expected. At the same time, the minutes of the Federal Open Market Committee meeting show that the Fed is likely to begin to scale down in mid-November.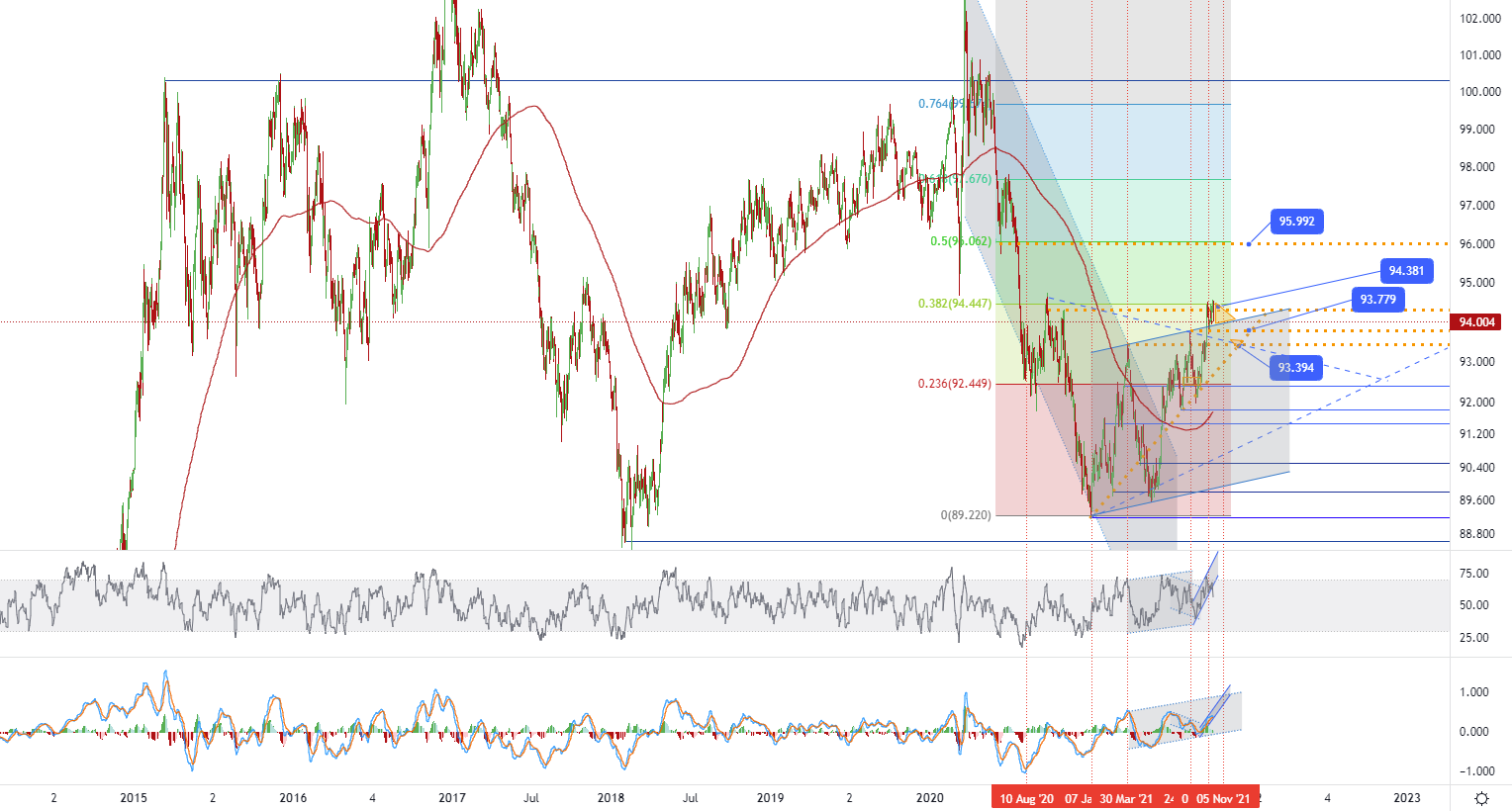 • U.S. Dollar index (DXY) - D1, Resistance around ~ 94.38 & 95.99, Support around ~ 93.77 & 93.39.
• U.S. Dollar index (DXY) - D1, Resistance around ~ 94.38 & 95.99, Support around ~ 93.77 & 93.39.
Demo account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account with virtual funds in a risk-free environment
Demo accountLive account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account in our transparent live model environment
Open an Account





