
Feeling the market is due for a pullback after the recent rally.
GLOBAL CAPITAL MARKETS OVERVIEW:
The Dow rose more than 200 points on Tuesday, the S&P 500 rose 0.3%, and the Nasdaq traded near the flat line as investors digested a slew of earnings posted by major retailers. Walmart jumped nearly 6% as the discount retail giant reported second-quarter profit and revenue that beat Wall Street expectations while raising its full-year earnings outlook. Home Depot also reported quarterly earnings that beat analysts' expectations. Such upbeat results have boosted shares of other retail brands, including Target, Best Buy, and Bath & Body Works. On the negative side of the ledger, ZipRecruiter surprised investors by dropping more than 7% after releasing third-quarter revenue guidance. On the data front, the U.S. housing market softened in July, with building permits and housing starts both falling more than expected. European shares rose for a fifth straight session on Monday, with the Stoxx 600 gaining around 0.2% to close around 445 for the first time in more than two months, as gains in utilities, materials, and energy offset losses at real estate companies. A string of upbeat earnings results was enough to boost risk appetite. Mining company BHP Billiton posted a lucrative profit, while food company Delivery Hero expects gross merchandise value to rise 7% between the second and third quarters. Jewelry maker Pandora reiterated its annual forecast. On the data front, Germany's ZEW Economic Confidence Index fell from -53.8 in July to -55.3 in August 2022, the lowest level since October 2008, heralding difficult times for Europe's largest economy. Domestically, the benchmark DAX 40 added 0.7 to near the 13,910 level. On Tuesday, the CAC 40 rose 0.3 percent to close at 6,593, its highest since April 21, extending its fifth straight session of gains. ArcelorMittal and Thales were among the top gainers, up 3% and 2.6%, respectively. Sanofi (up 1.7%) and Michelin (up 1.6%), while Malaysia Airlines signed a preliminary agreement to acquire 20 Airbus A330 NEOs to replace its aging wide-body A330 fleet. Afterward, Airbus (Airbus) rose 1.6%. The sentiment was also supported by expectations that Chinese policymakers will roll out more stimulus and corporate earnings. The FTSE MIB index edged to 23,000 on the first trading day of the week, enough to hit a fresh two-month high, as investors continued to assess how a recent spate of worrying economic data could affect guidance from major central banks. China's poor industrial production and retail sales data for July showed a slow economic recovery after a strict coronavirus lockdown. They prompted the People's Bank of China to cut lending rates in an emergency. In Milan, a surge in European gas prices underpinned sharp gains in the utility sector, offsetting losses in heavyweight banks and healthcare stocks. Snam, A2A, and Italgas closed above 2%, while Enel closed at 1.1%. Amplifon, on the other hand, fell nearly 6% and led losses, tracking Swiss rival Sonova's slump after its outlook was downgraded. The FTSE 100 rose 0.4% to close at 7,536 on Tuesday, its highest since June 8, as upbeat corporate updates were more than enough to offset concerns about the country's economic outlook. Mining company BHP Billiton posted a lucrative profit, and online food delivery company Delivery Hero expects gross merchandise value to grow 7% between the second and third quarters. Meanwhile, retailer Ted Baker surged after announcing it had agreed to a final £211m cash offer from Authentic Brands Group LLC, owner of Juicy Womenswear, Reebok, and David Beckham brands. More than 17% was in the spotlight, with cybersecurity firm Darktrace jumping more than 24% after it disclosed it was in preliminary discussions with private equity firm Thoma Bravo about a possible acquisition. On the data front, the U.K.’s unemployment rate was 3.8% in the second quarter, in line with expectations, while employment rose by 160,000 in the April-June period, well below expectations. On Tuesday, the ruble-based MOEX-Russia index rose 2 percent to close at 2,208, taking yesterday's gains to their highest level in more than two weeks, supported by heavyweight energy sectors, miners, and banks. Gazprom and Novatek rose 3.7% and 3.1%, respectively, as European gas prices surged due to soaring temperatures and poor logistics for transporting fossil fuels. The recent support for natural gas prices has exacerbated massive supply cuts at Gazprom, which has cited turbine problems as the reason for its supply woes, which have been viewed with suspicion by Western leaders. Meanwhile, Tatneft's shares rose 5 percent after its board recommended paying a dividend of 32.71 rubles per share. Elsewhere, investors continued to digest second-quarter GDP data and central bank forecasts to gauge the extent of the economic downturn following Russia's invasion of Ukraine. The latest figures show that GDP fell by 4% annually in the second quarter, while CBR forecast a 7% drop in the third quarter. The Canada S&P/TSX Composite edged higher on Tuesday, hovering at a two-month high of 20,200, recovering from a stagnant session in the previous session, with gains in the heavyweight energy sector offsetting losses in the tech sector. Investors digested new consumer price data for July, the first drop in inflation in more than a year, raising hopes that inflation may have peaked, supported by a sharp drop in gasoline prices. Energy stocks rebounded from yesterday's sell-off, up more than 1% on average, while mining and metallurgical stocks also rose. At the same time, lower consumer prices have supported green deals in consumer staples. Hong Kong stocks fell for a second session on Tuesday, dragged down by the energy, technology, and materials sectors, with the benchmark Hang Seng Index closing below 20,000. In corporate news, fast-food operator Yum China Holdings Inc. has filed for an initial listing in Hong Kong as the company looks to avoid taking its shares from the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) amid tighter regulations on Chinese companies. risk of delisting. Regarding individual share price movements, Meituan fell more than 9% and was the biggest loser on the Hang Seng Index, while Xiaomi fell nearly 4% and was the second biggest loser. New Zealand NZX 50 rose 58.12 points, or 0.49%, to close at 11,847, up from the previous session but still near a 15-week high, buoyed by gains in U.S. stocks on Monday, as sentiment for U.S. Optimism about a slowdown in inflation has grown, which could slow the pace of Fed rate hikes. In China, the People's Bank of China abruptly cut key lending rates on Monday to stimulate demand after the country's economy unexpectedly slowed in July. Market participants now expect the outcome of the Wednesday of the Royal Bank of New Zealand monetary policy meeting. The Fed's committee is expected to raise interest rates by half a percentage point for the fourth time. Still, most economists see rates below policymakers' expectations after the most aggressive tightening in 20 years to tame soaring inflation. Common shares of Vital Limited rose 9.1%, while Sky Network Television, Marin Global Ltd, and Ebers Group Ltd rose 4%, 3.4%, and 3%, respectively. China Shanghai Composite rose 0.2 percent to close above 3,280, while the Shenzhen Composite added 0.3 percent to 12,498, its highest level in nearly three weeks, helped by gains in Chinese growth stocks. A day earlier, the People's Bank of China (PBoC) surprised markets by cutting key lending rates to boost demand and combat economic weakness. This was underscored by lower-than-expected industrial production and retail activity in July. High-growth new energy and consumer stocks led to gains, led by Contemporary Amperex (2.9%), Solar Power (4%), Lange Green Energy (2.1%), BYD Corporation (1.1%), and Chongqing Changan (2.2%) Significant increase. Meanwhile, CNBC reported that southwest China's Sichuan province imposed industrial power rationing amid its worst heatwave in 60 years, and metal producers closed factories or limited output on Monday. Japan Nikkei 225 was flat near 28,870, while the broader Topix index fell 0.2% to 1,980 on Tuesday, taking a breather from a strong rebound, dragged down by energy and shipping stocks losses. Weak economic data from China and the United States also raised fears of a potential global recession, weighing on investor sentiment. Energy and oil stocks fell sharply, with industry leaders Inpex Corp and Eneos Holdings down 1.9% and 1.1%, respectively. Shipping companies also fell on a gloomy outlook for the industry, with Japan's Yusen (down 3.2%), Mitsui Shipping Co (up 3.5%), and Kawasaki Kishimori (down 2.6%) taking heavy losses. Meanwhile, select companies such as W-Scope Corp (8.1%), Renova Inc (6.5%), and M3 Inc (5.4%) also saw notable gains. Australia S&P/ASX 200 index rose 0.7% to around 7115 on Tuesday, its highest level in over two months after iron ore mining giant BHP Billiton reported a 26% rise in annual profit and declared a record dividend led the gains. Shares in Australia's largest miner rose 4% to hit a more than one-month high. Other index heavyweights also rose, including CSL Ltd (1.1%), Commonwealth Bank (1%), and Telstra (1.6%). Elsewhere, Tassar Group rose 5.3% after it accepted a larger takeover offer of A$5.23 a share from Canadian aquaculture company Cooke Inc., boosting the Australian salmon producer's enterprise value to reach A$1.7 billion. Meanwhile, Challenger Ltd fell 12% on a disappointing earnings report, while James Hardie fell 2% after cutting its annual profit forecast.
REVIEWING ECONOMIC DATA:
Looking at the last economic data:
- US: U.S. manufacturing production rose 0.7% in July 2022, rebounding from a downwardly revised 0.4% drop last month and beating expectations for a 0.2% increase. Durable manufacturing was up 1.1%, automotive was up 6.6%, while fabricated metal products, aerospace, and miscellaneous transportation equipment were all up more than 1%. Nondurable manufacturing edged up 0.1 percent, with gains in apparel and leather, chemicals, plastics, and rubber offsetting losses in other sectors. Manufacturing capacity utilization rose 0.5 percentage points to 79.8 percent, 1.6 percentage points higher than the long-term average.
- US: U.S. industrial production rose 0.6% in July 2022 from the previous month, beating market expectations of 0.3% and moving higher from a revised stagnation in June. Manufacturing output rose 0.7%, rebounding from a 0.4% drop in the previous month, with durable and non-durable manufacturing up 1.1% and 0.1%, respectively. In durable goods manufacturing, motor vehicle production rose 6.6 percent, while fabricated metal, aerospace, and miscellaneous transportation equipment rose more than 1 percent. In non-durable manufacturing, higher output was concentrated in apparel, leather, and chemicals. Elsewhere, the mining index rose 0.7%, easing from a 2% gain the previous month. Capacity utilization rose 0.4 percentage points to 80.3 percent in July, 0.7 percentage points above the long-term average.
- US: In July 2022, U.S. housing starts fell 9.6% month-on-month to an annualized rate of 1.446 million units, the lowest level since February 2021 and far below the market's forecast of 1.54 million units. The real estate sector has been cooling on the back of soaring material prices and rising mortgage rates. Single-family housing starts fell 10.1% to 916,000 units, the lowest level since June 2020; starts for five or more buildings fell 10% to 514,000 units. Operating rates were lower in the Midwest (33.8% to 139,000), the South (18.7% to 710,000), and the West (2.7% to 367,000) but rose in the Northeast (65.5% to 230,000). The June figure was revised up slightly to 1.599 million units from the previously reported 1.559 million units.
- US: U.S. building permits, which represent future construction, fell at an annualized rate of 1.1% to 1.674 million in July 2022, the lowest level since last September, compared with a forecast of 1.65 million. Single-family dwelling authorizations fell 4.3% to 928,000, while approvals for five or more dwellings rose 2.5% to 693,000. Building permits fell in the West and South (-12%) and (-0.1%) but grew in the Northeast (9.3%) and Midwest (8.1%).
- CA: Foreign investors sold C$17.5 billion in Canadian securities in June 2022 after receiving an upwardly revised C$2.8 billion a month earlier. It was the first foreign divestment of Canadian securities since July 2020 and the largest since December 2018, mostly by selling shares. Foreign investors reduced their exposure to Canadian equities by C$12.6 billion in June after divesting C$1.2 billion in the previous month, mostly in the banking sector. Non-resident investors also reduced their holdings of Canadian debt securities by $5 billion, the first divestment since March 2021, mostly by the government ($15.7 billion) and federal government businesses ($8.6 billion). Meanwhile, Canadian investors reduced their holdings of foreign securities by C$12.3 billion in June, the fourth monthly withdrawal in 2022, largely due to the sale of U.S. equities and U.S. money market instruments.
- CA: Annual inflation in Canada was 7.6% in July 2022, down from a 39-year high of 8.1% set last month, in line with market estimates. Transportation costs rose at a much slower pace (14.4% vs. 16.8% in June) due to the sharp drop in gasoline prices (35.6% vs. 54.6%). In addition, inflation was lower for housing (7% vs. 7.1%), home operations, furniture and equipment (5% vs. 5.6%), and clothing and footwear (1.4% vs. 2.7%). Meanwhile, inflation continued to rise for food (9.2% vs. 8.8%), as did grocery (9.9% vs. 9.4%), while entertainment costs stagnated (6.2%). Excluding gasoline, the CPI rose 6.6% annually. On a monthly basis, consumer prices rose 0.1%, the slowest gain since December 2021.
- CA: According to the Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation (CHMC), housing starts in Canada increased by 1.1 percent in July 2022 from a month earlier to 275,329 units, beating market expectations of 262,100 units. Urban starts fell 0.8% to 254,371 units, single-detached city starts fell 2.3% to 58,384 units, and multi-unit city starts fell 0.3% to 195,987 units. The rural operating rate is estimated at 20,958 units on a seasonally adjusted basis.
- EU: In June 2022, the euro area recorded a trade deficit of 24.6 billion euros, the eighth consecutive shortfall, higher than the market's forecast for a deficit of 20 billion euros and in line with a surplus of 17.3 billion euros in the same period last year. Imports surged 43.5% to 276.8 billion euros, mainly due to soaring energy costs, while exports rose more slowly to 210 billion euros or 20.1%. In the first half of this year, the EU trade gap was 20.7 billion euros, compared with a surplus of 83.2 billion euros in the same period last year. Purchases surged 48.9% to 1.438 billion euros, with imports of energy and chemicals up 151.1% and 45.8%, respectively. During the period, exports rose by 17.9% to 1,237.3 billion euros, energy by 93.9%, and chemicals by 26.4%. The trade deficits of Russia (from 24.6 billion euros to 90.6 billion euros) and China (from 98.0 billion to 189.5 billion euros) widened sharply.
- EU: The Eurozone ZEW Economic Sentiment Index slipped to -54.9 in August 2022 from -51.1 the previous month, compared with market estimates of -57. It was the lowest reading since November 2011, as the economic outlook is expected to deteriorate further as Europe's energy crisis continues and the European Central Bank's rate hike cycle. Meanwhile, an indicator of current economic conditions rose 2.4 points to -42, while inflation expectations rose 2.1 points to -23.5.
- UK: The UK unemployment rate for the second quarter of 2022 was as expected at 3.8%, 0.1 percentage points higher than in the previous three months (January-March 2022) but 0.2 percentage points lower than before the coronavirus pandemic. The number of people unemployed for up to 12 months rose in the most recent three-month period, with the number of people unemployed for six to 12 months rising for the first time since February-April 2021. This increase was partly offset by a decrease in people who lost their jobs over 12 months. The unemployment rate was also at 3.8% from May three months. Employment rose by 160,000 between April and June, missing market expectations of 256,000. Layoffs remained very low, but the number of job openings fell for the first time since mid-2020. Regular pay growth, excluding bonuses, rose to 4.7% from 4.3%, but excluding extras, it failed to 5.1% from 6.4%.
- UK: Average weekly earnings (including bonuses) in the UK rose 5.1% year-on-year to £611 in the three months to June 2022, down from an upwardly revised 6.4% in the three months to May but above market forecasts of 4.5%. Regular compensation, excluding bonuses, rose 4.7% after a 4.4% increase in the first quarter, beating expectations for a 4.5% increase. Adjusted for inflation, gross wages fell by 2.5% and regular wages by 3.0%, the biggest drop on record, as living standards fell further in the UK. Considering only June, average real earnings excluding bonuses fell 2.8% year over year, the eighth straight month of declines, following a 2.6% decline in May.
- AU: Headline inflation in Australia is expected to rise further in the second half of 2022, although underlying inflation is expected to increase further, peaking at around 6% by the end of the year, minutes from the Reserve Bank of Australia’s August policy meeting showed. Meanwhile, the economy's resilience remains most evident in the labor market, with members noting that the unemployment rate is expected to fall further in the coming months. "The Federal Reserve Committee is expected to take further steps in normalizing monetary conditions, but it is not on a preset path," it added. "It's trying to do that in a way that keeps the economy steady. The road to that balance is narrow, and there's a lot of uncertainty." The central bank raised interest rates by 50 basis points to 1.85 at its August meeting %, the fourth-rate hike in recent months and the most aggressive tightening since the early 1990s.
LOOKING AHEAD:
Today, investors will receive:
- USD: Core Retail Sales m/m, Retail Sales m/m, FOMC Member Bowman Speaks, Business Inventories m/m, Crude Oil Inventories, FOMC Meeting Minutes, and FOMC Member Bowman Speaks.
- EUR: Flash Employment Change q/q, and Flash GDP q/q.
- GBP: CPI y/y, Core CPI y/y, PPI Output m/m, RPI y/y, and HPI y/y.
- NZD: Official Cash Rate, RBNZ Monetary Policy Statement, RBNZ Rate Statement, and RBNZ Press Conference.
- AUD: MI Leading Index m/m, and Wage Price Index q/q.
- JPY: Core Machinery Orders m/m, and Trade Balance.
- NZD: PPI Input q/q, and PPI Output q/q.
KEY EQUITY & BOND MARKET DRIVERS:
- US: The 10-year U.S. Treasury yield consolidated above 2.8% as investors awaited minutes from the Federal Reserve meeting to assess the economy's health and the pace of rate hikes. While some recent inflation reports suggest price growth may be slowing, the job market remains very tight, making it challenging to deal with the realities of the U.S. economy. Meanwhile, the Federal Reserve has reassured the market that a dovish pivot is unlikely. However, it has avoided giving exact numbers on the size of its next rate hike in September.
- CA: Canada's 10-year government bond yield rose above 2.8 percent in mid-August, its highest level in three weeks, as investors continued to assess the Bank of Canada's guidance following the release of new consumer price data. While headline inflation eased in July from a 39-year peak in the previous month, the central bank's measure of core consumer prices continued its accelerating trend. Rising costs, excluding energy costs, have prompted bets that the central bank is inclined to maintain its hawkish stance. At its last meeting, the Bank of China surprised markets by raising its benchmark interest rate by 100 basis points in July while signaling further tightening to rein in inflation well above its 2 percent target.
- UK: Britain's 10-year gilt rose to more than 2.1%, its highest level in more than three weeks, as recent data showed Britain's labor market remained tight but began to cool, with the Bank of England forecasting a 50-basis-point streak in borrowing costs. The unemployment rate was 3.8% in the second quarter, and employment rose by 160,000, missing market expectations of 256,000. The number of job openings fell for the first time since mid-2020 in the three months to July, and regular pay growth excluding bonuses, adjusted for inflation, fell by 3%, the largest since records began in 2001. Earlier this month, the Bank of England raised borrowing costs by 50 basis points, the most since 1995, and money markets are pricing in about an 83 percent chance of another rate hike at its September meeting. Investors are awaiting inflation data, which is expected to show consumer prices rose 9.8% year-on-year in July and the Bank of England expects to peak at 11% in October, the highest level since 1980.
- US: U.S. stock futures, which track the broader market, fell on Tuesday, with all three major indexes starting to weaken as investors digested a slew of earnings from big retailers. ZipRecruiter fell nearly 5% in pre-IPO trading after the company surprised investors by releasing third-quarter revenue guidance. On the other hand, Walmart jumped 4% as the discount retail giant reported fiscal second-quarter profit and revenue that beat Wall Street's expectations while raising its full-year profit forecast. Meanwhile, the U.S. housing market softened in July, with building permits and housing starts both falling more than expected. In regular trading Monday, the Dow rose 0.5%, the S&P 500 gained 0.4%, and the Nasdaq Composite gained 0.6%.
- CN: China's 10-year bond yield fell to a 26-month low of 2.659% on growing concerns over China's economic outlook, coronavirus containment, the ongoing housing crisis, and monetary policy divergence between the People's Bank of China and the Federal Reserve. That pushes up U.S. Treasury yields and makes Chinese bonds less attractive to investors. According to estimates from the Fund for International Investment, China's debt outflows were around $3 billion in July, which would be the sixth month of foreign debt outflows.
STOCK MARKET SECTORS:
- High: Consumer Staples, Materials, Financials, Industrials, Consumer Discretionary.
- Low: Information technology, Communication Services, Health Care, Real Estate, Energy.
TOP CURRENCY & COMMODITIES MARKET DRIVERS:
- CAD: The Canadian dollar appreciated more than $1.29 in mid-August as new consumer price data backed investor bets that Canadian banks should continue raising lending rates aggressively. While headline inflation eased for the first time in more than a year, the average of the three core figures used by the central bank accelerated to 5.3% from 5.2% the previous month. At its last meeting, the Bank of China surprised markets by raising interest rates by 100 basis points, the most since 1998, and signaled further tightening to curb inflation well above its target.
- USD: The U.S. dollar index rose to 107, a level not seen in three weeks, as subdued economic data from major economies sparked fresh fears of a global recession and boosted safe-haven demand for the greenback. On top of that, the Fed has been reassuring the market that a dovish turn is unlikely despite signs that inflation may peak. More speeches this week and the minutes of the Federal Open Market Committee meeting released on Wednesday are now highly expected to provide clues on the direction of the central bank's interest rates. The U.S. dollar strengthened across the board, with risk-on currencies such as the Australian and New Zealand dollars again seeing the most visible buying activity.
- JPY: The yen fell more than 134 yen against the dollar, moving further away from a one-month high of 130.4 yen set on Aug. 2, as investors sought the greenback's safety after disappointing Chinese and U.S. data rekindled fears of a global recession. At home, the latest data showed that Japan's economy expanded by 0.5% in the second quarter of this year, below market expectations of 0.6%. In addition, Japan's GDP grew at an annualized rate of 2.2%, compared to market estimates of 2.5%. On the monetary policy front, the Bank of Japan kept interest rates ultra-low at its July meeting, when other major central banks are racing to raise rates to curb soaring inflation. For the Bank of Japan, inflation is sustainable, not a priority, because while it is slightly above its 2 percent target, it remains low compared to other major economies.
- EUR: The euro fell below $1.015, near the key $1 parity level, after more data pointed to a recession in the European region. The latest data showed German investor morale unexpectedly fell to -55.3 in August, the lowest level since October 2008. Since the beginning of July, fears have grown that the eurozone economy is headed for a recession, while inflation is near parity as energy prices continue to hit record highs. The ECB continues to raise borrowing costs. Germany's top network regulator said that Germany must cut its gas use by a fifth to avoid a severe gas shortage this winter. Germany's top network regulator said that Germany must cut its gas use by a fifth to avoid a severe gas shortage this winter. The country is approaching the third phase of the emergency plan, which includes rationing natural gas in the industrial sector. Meanwhile, the European Central Bank is still set to raise rates by 50 basis points in September.
- GBP: Sterling fell to $1.2, near a two-year low of $1.18 hit on July 14, on growing concerns about the outlook for Britain's economy, with BoE inflation hitting 11.1% in October and Britain expected to enter a recession in the fourth quarter, and continued for five quarters. The latest figures show that the labor market is cooling, notably the number of job vacancies falling for the first time since August 2020, and wages excluding bonuses, adjusted for inflation, fell by 3%, the biggest drop since records began in 2001. Investors are now awaiting inflation and retail sales data later this week. Money markets are now pricing an 83% chance of a 0.5 basis point rate hike at the September central bank meeting, with the odds of a rate hike totaling 125 basis points by the end of the year. Meanwhile, Bank of England governor Andrew Bailey has criticized his approach to inflation after Liz Truss, the front-runner to become the next prime minister, criticised his approach to inflation, The Telegraph reports. "Open mind" to the central bank's mandate.
CHART OF THE DAY:
Japan Nikkei 225 was flat near 28,870, while the broader Topix index fell 0.2% to 1,980 on Tuesday, taking a breather from a strong rebound, dragged down by energy and shipping stocks losses. Weak economic data from China and the United States also raised fears of a potential global recession, weighing on investor sentiment. Energy and oil stocks fell sharply, with industry leaders Inpex Corp and Eneos Holdings down 1.9% and 1.1%, respectively. Shipping companies also fell on a gloomy outlook for the industry, with Japan's Yusen (down 3.2%), Mitsui Shipping Co (up 3.5%), and Kawasaki Kishimori (down 2.6%) taking heavy losses. Meanwhile, select companies such as W-Scope Corp (8.1%), Renova Inc (6.5%), and M3 Inc (5.4%) also saw notable gains.
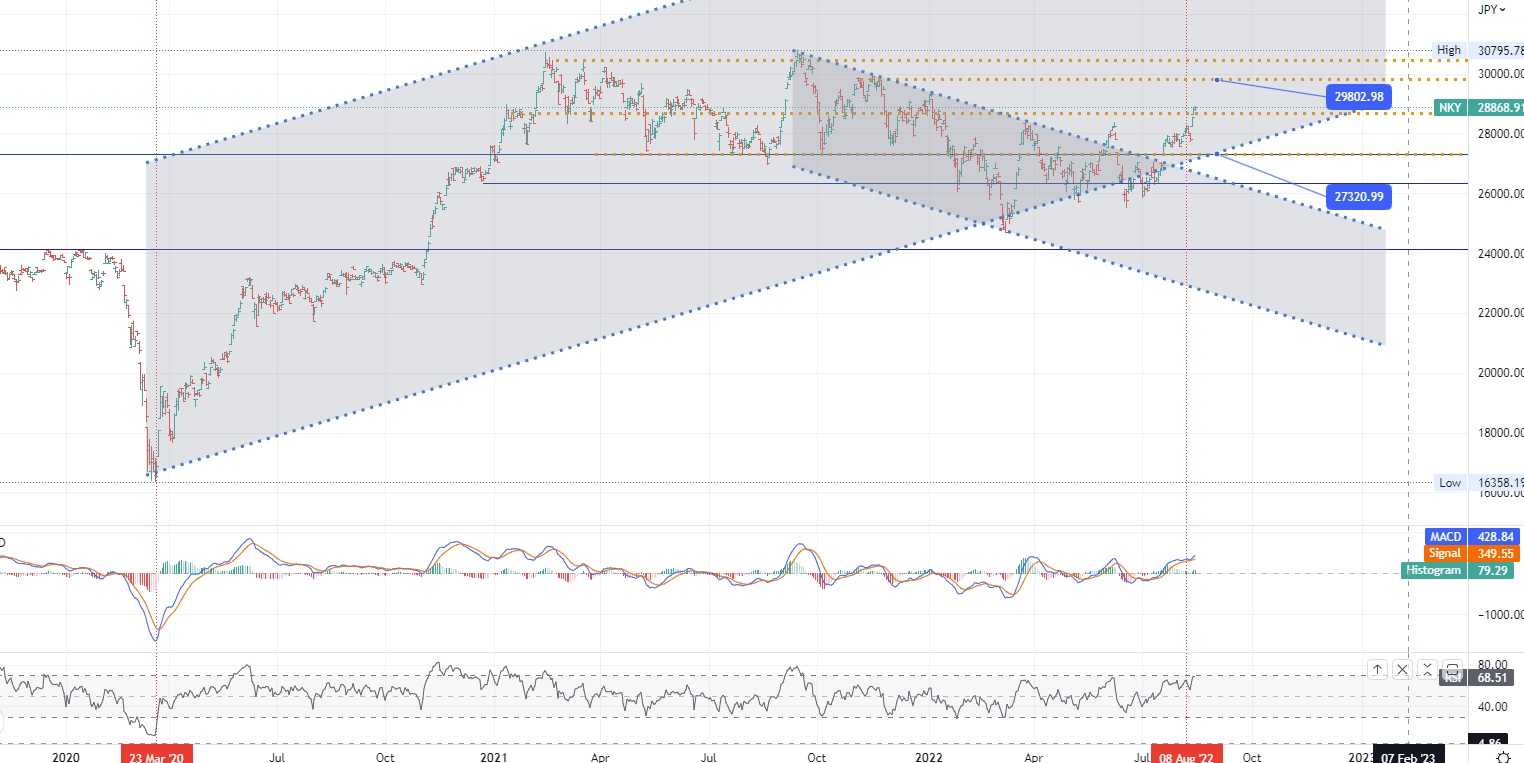
- Japan Nikkei 225 index - D1, Resistance around ~ 29802, Support around ~ 27320.
Demo account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account with virtual funds in a risk-free environment
Demo accountLive account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account in our transparent live model environment
Open an Account





