
Global growth concerns after weaker-than-expected data out of China and a sharp decline in the August Empire State Manufacturing Index
GLOBAL CAPITAL MARKETS OVERVIEW:
All three major U.S. stock indexes resumed their gains on Monday, with investors ignoring dismal economic data from China as they awaited a slew of earnings results from retailers. China's industrial output, retail sales, and fixed-asset investment all fell short of analysts' expectations, raising concerns that a slowdown in the world's second-largest economy could disrupt supply chains and undermine global growth. The country's central bank also unexpectedly cut interest rates, reflecting a bleak economic outlook. Still, investors remained optimistic about the U.S. economy, with lower-than-expected headline and core inflation prompting lower expectations for the scale of Fed monetary tightening while easing fears of a looming recession. This week's earnings from Home Depot, Walmart, and Target followed a busy week of retail earnings. European shares rose for a fourth session on Monday, with the Stoxx 600 gaining around 0.3% to close above 440, as gains in the utility sector offset losses in the energy sector. China released a slew of economic data that included disappointing industrial output, retail sales, and fixed-asset investment, rekindling concerns that a slowdown in the world's second-largest economy could disrupt supply chains and dampen global growth concerns but the market remains volatile. Telecom Italia jumped more than 5 percent on the corporate front to lead the Stoxx 600 in headlines, indicating that Italy's far-right Fraternity Party may take the phone company private. Domestically, the benchmark DAX 40 gained 0.2% to around 13,817. On Monday, the CAC 40 rose 0.3 percent to close at 6,570, its highest level since April 22 and in line with its European peers, even as weak data from China weighed on investor risk appetite. Trading volumes were lower as France celebrated National Day. Shares in Air France-KLM (3.3%) were the best performers, with a Total down 2.4% and oil prices down nearly 5%. London stocks ended little on Monday, with the benchmark FTSE 100 hovering near a more than two-month high of 7,500, with gains in utilities offsetting losses in materials and energy stocks. A slew of economic data from China, including disappointing industrial output, retail sales, and fixed-asset investment, sparked fears of a slowdown in the world's second-largest economy, which could disrupt supply chains and the globe. increase. Regarding individual share price movements, RS Group rose more than 5%, the biggest gainer in the FTSE 100, while GSK and Rio Tinto fell 3% and 2%, respectively. The ruble-based MOEX-Russia index rose 0.8 percent to close at 2,165 on Monday, its highest in two weeks, as investors continued to study market dynamics on Russia's main commodity exports, digesting the latest GDP data after Friday's close. Russia's economy contracted by 4% in the second quarter but beat the Central Bank of Russia's forecast of 4.3%. Still, the central bank expects the impact of Western sanctions to be hit harder in the third quarter, as the economy is expected to contract by 7%. Miners and metallurgists offset early losses to lead the trade, with Rusal and MMK up 5.5% and 3.6%, respectively. On the other hand, heavyweight energy stocks largely underperformed the broader index as poor industrial activity data from top importer China weighed on demand expectations. Lukoil and Transneft closed below levels, while Tatneft's shares fell 2.3% ahead of the board's decision to pay a dividend. Canada's S&P/TSX composite index fell sharply to 20,050 on Monday, retreating from a two-month high hit on Friday, as a slew of worrying economic data brought recession fears to investors' attention. Industrial production in China largely missed analysts' expectations, sending crude prices plunging more than 5 percent and weighing on Toronto's heavyweight energy sector. Canadian Natural Resources, Suncor, and Sinoway Energy recorded more than 5% losses. Falling bullion and base metal prices also weighed on miners, with Nutrien losing more than 2 percent. On the data front, Canada's June wholesale sales growth was revised lower, while the contraction in manufacturing sales was also revised smaller. Hong Kong stocks were under pressure on Monday, with the benchmark Hang Seng Index retreating from its highest level in a week to bottom at 20,050, with industrial, energy, and materials stocks falling. A flurry of economic data from China, including disappointing industrial production and retail sales, further stoked fears of a global slowdown. Meanwhile, the People's Bank of China unexpectedly cut a key policy rate for the first time since January to restore demand for credit and support an economy battered by the coronavirus pandemic. On the corporate front, Hong Kong stocks of several Chinese companies, including China Life Insurance and China Petroleum and Chemical, were buoyed by concerns over U.S. delisting risks and renewed cross-strait tensions. under heavy pressure. New Zealand NZX 50 rose 58.51 points, or 0.5%, to close at a near 15-week high of 11,789.03 on Monday, reversing gains from the previous session after reports of easing inflation and a better-than-expected earnings report. All benchmarks for U.S. stocks hit their highest in at least three months on Friday. In China, the People's Bank of China unexpectedly cut key lending rates after weak economic data in July. The country's industrial production rose 3.8% year-on-year, lower than the market consensus of 4.6%; retail sales rose 2.7%, also lower than the 5% expected. Meanwhile, fixed-asset investment grew less than expected in the year's first seven months. Traders are now awaiting the outcome of Wednesday's Royal Bank of New Zealand monetary policy meeting. The Fed's board is widely expected to raise policy rates by another 50 basis points as policymakers intensify their efforts to combat soaring inflation. Gainers included Bremworth Limited (7.6%), Vital Limited (6.5%), NZME Limited (5%), and Accordant Group Limited (5%). China Shanghai Composite was down 0.2% at around 3,270. At the same time, Shenzhen shares were mixed on Monday, up 0.1% at 12,435 after China's central bank unexpectedly cut its key lending rate after a batch of economic data missed expectations, underscoring the need for further policy support. The People's Bank of China cut its one-year policy loan rate by ten basis points to 2.75% and the seven-day reverse repo rate by the same amount to 2%, defying expectations for unchanged rates. Meanwhile, China's industrial output rose 3.8% year-on-year in July, below a forecast of 4.6% and slowing from a 3.9% increase in June. The country's retail sales rose 2.7% in July from a year earlier, well below forecasts of 5%, after rising 3.1% in June. High-growth new energy and technology stocks mostly rose, while financials, consumer-related, and healthcare stocks fell. Japan Nikkei 225 rose 1 percent to close above 28,800 on Monday. In comparison, the broader Topix index rose 0.5 percent to close at 1,983, with both benchmarks hitting multi-month highs as easing U.S. inflationary pressures lifted markets Sentiment, driving a new round of gains in global stock markets. Investors also assessed Japan's economic growth at an annualized rate of 2.2% in the second quarter of 2022, below analysts' forecast of 2.5%. Growth-oriented tech and consumer stocks led gains, with SoftBank Group (4.8%), Tokyo Electron (1%), Laser Technology (1.1%), Sony Group (1.2%), and Nintendo (1.4%) gaining strongly. The shares of healthcare company Daiichi Sankyo also rose 15% after winning a legal battle with U.S. drugmaker Seagen over a deal between the two companies to use the latter's drug technology. Australia S&P/ASX 200 rose 0.6% to 7074 on Monday, recouping losses from the previous session, led by technology and clean energy-related stocks. Australian shares also followed Wall Street higher on Friday as signs of easing U.S. inflationary pressures boosted investor sentiment. Nearmap Ltd led the gains in tech stocks, surging 25 percent after securing a $1.06 billion takeover offer from a US private equity firm. Other gainers in the sector included Xero Ltd (2.8%), Block Inc (1.5%), and Megaport (4.3%). Names related to clean energy also rose, with strong gains from Core Lithium (9.2%), Lake Resources (4.7%), and Pilbara Minerals (1.4%). Meanwhile, on disappointing earnings reports, retail banking companies Bendigo and Adelaide Bank and oil and gas company Beach Energy fell 8 percent and 11 percent, respectively.
REVIEWING ECONOMIC DATA:
Looking at the last economic data:
- US: In August 2022, the U.S. NAHB Housing Market Index fell for the eighth straight month to 49, the lowest reading since May 2020 and well below the consensus forecast of 55. “The Fed’s tightening monetary policy and rising construction costs have contributed to a housing recession. Total single-family housing starts will decline in 2022, the first decline since 2011. However, with inflation showing signs of approaching its peak Increasingly, long-term rates have stabilized, which will provide some stability on the demand side of the market in the coming months," said NAHB chief economist Robert Dietz. The current sales sub-index fell 7 points to 57; buyer traffic fell from 37 to 32, and sales expectations for the next six months fell 2 points to 49.
- US: In August 2022, the Empire State Manufacturing Index fell to -31.1, the lowest level since May 2020 and the second-largest monthly decline on record for the index (11.1 in July). Business activity in New York State fell sharply, with new orders (-29.6 vs. +6.2) and shipments (-24.1 vs. 25.3) falling sharply, with outstanding orders falling further (-12.7 vs. -5.2). Meanwhile, delivery times remained stable for the first time in nearly two years (-0.9 to 8.7), and inventories edged up (6.4 to 14.8). Labor market indicators showed a slight increase in employment (7.4 to 18) but a drop in average weekly hours worked (11.1 to 4.3). The price paid decreased (55.5 to 64.3), and the price received index remained stable (32.7 to 31.1). Looking ahead, companies do not expect much improvement in operating conditions over the next six months (2.1 vs. -6.2).
- CA: Wholesale sales in Canada rose 0.1% in June 2022 from the previous month, down from a preliminary estimate of 0.5% after a revised 0.9% gain last month. Sales of miscellaneous goods (3.5%) and motor vehicles and motor vehicle parts and accessories (3.1%) declined, with sales of personal and household goods falling the most (-3.5%).
- CA: In June 2022, Canadian manufacturing sales fell 0.8% month-on-month, slightly less than a preliminary estimate of 1%, after falling 1.1% in the previous month. It was the second monthly decline in manufacturing sales since September 2021, with sales falling in 8 of 21 industries. Oil and coal products fell notably (-7.8%), the first decline in five months, as recession fears weighed on energy prices. Sales of wood products also fell sharply (-7.2%) due to lower sales of sawmills and wood preservation products. On the other hand, auto sales (11.8%) capped a steep decline in manufacturing turnover as a rise in assembly production in Ontario overwhelmed woes in the supply of semiconductor chips. Manufacturing sales rose 18.8% year over year.
- JP: In June 2022, Japanese industrial production rose 9.2% month-on-month, compared with a flash figure of 8.9%, reversing the final decline of 7.5% a month earlier. It was the first increase in industrial output since March and the fastest pace on record, helped by an upturn in production after China eased Covid-19 control measures. Automotive (14.1% vs. -8.3% in May), electrical machinery, information and communication electronics (11.7% vs. -11.1 %), and electronic parts and equipment (11.6% vs. -4.2%) were the main sectors driving the rebound. On an annual basis, industrial output fell 2.8% in June and 3.1% in May, the fourth consecutive monthly decline.
- JP: Japan's economy grew at an annualized rate of 2.2% in the second quarter of 2022, its third consecutive quarter of growth, compared with market expectations of 2.5%. This comes after a surge in Covid-19 cases hit spending, while some reports said the latest GDP data had reached levels seen before the outbreak began to spread globally, with a revised 0.1% growth rate in the first quarter. Both private consumption and government spending accelerated, while capital spending rebounded sharply. In addition, public investment rose after falling in the previous fifth quarter. The contribution of net exports to GDP is positive as exports increase, and imports fall.
- CN: China's surveyed urban unemployment rate fell slowly from 5.5% in June to 5.4% in July 2022. It was the lowest unemployment rate since January as the government continued its efforts to restore momentum to the economic recovery by further easing Covid-19 restrictions. This year, the government aims to keep the unemployment rate at around 5.5%. The unemployment rate for 25-59-year-olds increased to 4.3% in July from 4.5% in June, while the employment rate for 16-24-year-olds rose to 19.9% from 19.3% the previous month. Meanwhile, the surveyed unemployment rate in 31 large cities and towns fell from 5.8% to 5.6%. Corporate employees' average weekly working time climbed to 48.0 hours from 47.7 hours in June. Considering the first seven months of this year, 7.83 million new jobs were created nationwide. After adding 12.69 million jobs a year ago, Beijing has set a goal of adding 11 million new urban jobs in 2022.
- CN: Average new home prices in 70 major Chinese cities fell 0.9% year on year in July 2022, after falling 0.5% a month earlier. It was the third straight month of declines in new home prices and the biggest drop since September 2015, when the Covid-19 outbreak in some cities sent the real estate sector into a slump. Among China's largest cities, prices fell further in Tianjin (-3.5% vs. -2.4% in June), while Beijing (5.5% vs. 5.8%) and Chongqing (3.1% vs. 3.4%) saw slower increases. Meanwhile, home prices accelerated in Shenzhen (3.2% vs. 0.2%), Shanghai (3.5% vs. 3.4%) and Guangzhou (0.4% vs. 0.3%). Every month, new home prices were flat for the second month in a row.
- CN: In July 2022, China's retail industry grew by 2.7% year-on-year, below market expectations of 5% and 3.1% a month earlier. Still, it was the second straight month of growth in the retail sector.
- CN: In the first seven months of this year, China's fixed asset investment increased by 5.7% year-on-year to 32.0 trillion yuan, compared with a market forecast of 6.2% and a 6.1% increase in the first six months of this year. Among sub-sectors, investment slowed in all sectors: primary (2.4% vs. 4.0%), secondary (10.4% vs. 10.9%), and tertiary (3.7% vs. 4.0%).
- CN: In July 2022, China's industrial production rose 3.8% year-on-year, lower than the market consensus of 4.6%, after increasing 3.9% in June. The latest reading was the third straight month of growth in industrial output as the economy moved further out of the strict Covid-19 restrictions.
- CN: The People's Bank of China (PBoC) unexpectedly cut its key policy rate for the first time since January as it ramped up support for an economy struggling to recover from a coronavirus lockdown and a housing downturn. On Monday, the central bank cut the one-year medium-term lending rate by ten basis points to 2.75%. The seven-day reverse repo rate, also a policy rate, fell to 2% from 2.1%.
- CN: Average new home prices in 70 major Chinese cities fell 0.9% year on year in July 2022, after falling 0.5% a month earlier. It was the third straight month of declines in new home prices and the biggest drop since September 2015, when the Covid-19 outbreak in some cities sent the real estate sector into a slump. Among China's largest cities, prices fell further in Tianjin (-3.5% vs. -2.4% in June), while Beijing (5.5% vs. 5.8%) and Chongqing (3.1% vs. 3.4%) saw slower increases. Meanwhile, home prices accelerated in Shenzhen (3.2% vs. 0.2%), Shanghai (3.5% vs. 3.4%) and Guangzhou (0.4% vs. 0.3%). On a monthly basis, new home prices were flat for the second month.
- NZ: New Zealand's Services Performance Index (PSI) fell to 51.2 in July 2022 from a downwardly revised 54.7 in June. The data showed that growth in the services sector was the slowest in five months, suggesting that a strong rebound following the orange setting of the COVID-19 traffic light system in mid-April may have lost steam. Activity/sales (54.4 to 55.8 in June), new orders/business (52.5 to 60.5) and inventories (53.1 to 54) and employment contraction (49.2 to 52.7) slowed.
LOOKING AHEAD:
Today, investors will receive:
- CAD: Housing Starts, CPI m/m, Common CPI y/y, Median CPI y/y, Trimmed CPI y/y, Core CPI m/m, and Foreign Securities Purchases.
- USD: Building Permits, Housing Start, Capacity Utilization Rate, and Industrial Production m/m.
- NZD: GDT Price Index.
- EUR: Trade Balance, ZEW Economic Sentiment, and German ZEW Economic Sentiment.
- GBP: Average Earnings Index 3m/y, Claimant Count Change, and Unemployment Rate.
- AUD: Monetary Policy Meeting Minutes.
- JPY: Tertiary Industry Activity m/m.
KEY EQUITY & BOND MARKET DRIVERS:
- IT: Italian 10-year BTP yields fell below 3% in mid-August, tracking a rise in global demand for safe debt instruments, and hovered near a two-month low of 2.9% hit earlier this month as macroeconomic concerns continued. The data added to recession fears. Weak industrial activity in China is the latest sign of a slowdown in the global economy, exacerbating a contraction in Purchasing Managers' Index (PMI) data and a drop in retail sales in Europe. Meanwhile, investors continued to assess the support the ECB's TPI provides to credit risk in highly indebted economies. On the political front, investors are closely watching polls supporting the right-wing coalition in next month's snap elections, as any changes in ongoing reforms could garner more than 200 billion euros in recovery funding. The spread between 10-year British gilts and German bunds was 210 basis points, slightly higher than last week, indicating a somewhat more elevated view of Italian debt risk.
- UK: Britain's 10-year gilt fell to 2% in the third week of August, tracking a broad decline in bond yields as investors fled to safety after weak Chinese data in July sparked further fears of an economic slowdown. Meanwhile, the Office for National Statistics will release UK inflation, unemployment, and retail sales data this week, providing other updates on labor market recovery and price pressures, providing further clues to the size of the Bank of England's September rate hike. According to Reuters, money markets are now pricing an 85% chance of a half-basis-point rate hike at the September central bank meeting, bringing the odds of a rate hike by the end of the year close to 125 basis points in total.
- GE: German 10-year bond yields hovered around 0.95%, down slightly from a three-week high of 1%, and tracked global government debt as a slew of worrying economic data from China underscored fears of a worldwide slowdown. Domestically, Germany's Federal Network Agency said the country needs to cut its natural gas use by 20 percent to avoid winter rationing. Emergency measures to cut energy use have led to a drop in economic activity, fueling recession fears in Europe, with recent PMI data showing private sector activity contracted in July and retail sales unexpectedly falling in June. On the monetary policy front, markets expect the ECB to raise interest rates by another 50 basis points in September, extending the central bank's July decision by the same amount.
- RU: Russia’s 10-year bond yield fell to 9.1% in mid-August, still well below levels seen before Russia invaded Ukraine, as deteriorating economic conditions in Russia boosted demand for fixed-coupon assets. Russia's economy contracted by 4% annually in the second quarter. Still, the central bank expects GDP to fall by 7% in the third quarter, as Western sanctions will take a bigger toll on the economy. Meanwhile, since February 24, authorities have opened up trading in debt instruments for "friendly" countries for the first time. Meanwhile, the Kremlin approved a decree to spend half of its $210 billion emergency fund on state bond purchases, which it has never done before, making it the main funding source for Russia's budget this year. Meanwhile, Moscow has made debt deals for foreigners from "friendly" countries for the first time since February 24.
- US: Yields on the 10-year U.S. Treasury note bottomed at around 2.80%, retreating further from a multi-week peak of 2.91, as investors turned to the safety of bonds amid lingering fears of a global economic slowdown. A slew of financial data from China, including disappointing industrial production and retail sales, further raised concerns about the health of the world's second-largest economy. On top of that, several Fed policymakers noted that despite signs that inflation may peak, a dovish turn is unlikely, adding to fears of a Fed-induced recession.
STOCK MARKET SECTORS:
- High: Utilities, Consumer Staples, Real Estate, Communication Services, Information Technology, Consumer Discretionary.
- Low: Energy, Materials.
TOP CURRENCY & COMMODITIES MARKET DRIVERS:
- EUR: The euro retreated to around $1.02 in the third week of August as concerns over an economic slowdown, particularly in Europe and China, and hawkish rhetoric from some Fed officials boosted the greenback. The euro has traded near parity since early July as there are growing signs that the eurozone economy is heading for recession; while inflation continues to hit record highs, the energy crisis is far from over, and the ECB will continue to raise borrowing costs. Germany's top network regulator, Germany, must cut its gas use by a fifth to avoid a severe gas shortage this winter, according to the Financial Times. The country is about to enter the third phase of its contingency plan, which includes rationing gas to industry. Meanwhile, the European Central Bank is still set to raise rates by 50 basis points in September.
- GBP: Sterling fell to $1.2 in the third week of August, boosted by a stronger dollar, turning to safety as traders await key U.K. economic data this week after weak Chinese data. The Office for National Statistics will release data on inflation, unemployment, and retail sales, providing further updates on labor market recovery and price pressures, providing additional clues on the size of the Bank of England's September rate hike. According to Reuters, money markets are now pricing an 85% chance of a half-basis-point rate hike at the September central bank meeting, bringing the odds of a rate hike by the end of the year close to 125 basis points in total. Meanwhile, Bank of England governor Andrew Bailey has criticized his approach to inflation after Liz Truss, the front-runner to become the next prime minister, criticized his approach to inflation, The Telegraph reports. "Open mind" to the central bank's mandate.
- USD: The U.S. dollar index consolidated around 106 as investors reassessed the outlook for U.S. monetary policy following a series of hawkish comments from Fed officials, driven by a strong showing last week. Several policymakers noted that despite signs that inflation may peak, a dovish turn is unlikely. More speeches this week and the minutes of the Federal Open Market Committee meeting released on Wednesday are now highly expected to provide clues on the direction of the central bank's interest rates. On top of this, a slew of economic data from China, including disappointing industrial production and retail sales, has further stoked fears of a global slowdown. The U.S. dollar strengthened, with buying activity most evident in riskier currencies such as the Australian and New Zealand dollars.
- CNY: The offshore yuan weakened by more than 6.75 against the dollar, hitting its weakest level in nearly two weeks, as China's central bank unexpectedly slashed key lending rates in response to downbeat data highlighting the country's economic woes. The People's Bank of China cut its one-year policy loan rate by ten basis points to 2.75% and the seven-day reverse repo rate by the same amount to 2%, defying expectations for unchanged rates. Meanwhile, China's industrial output rose 3.8% in July from a year earlier, below expectations for a 4.6% increase and slowing from a 3.9% increase in June. The country's retail sales also rose 2.7% in July, well below analysts' expectations for a 5% increase, after rising 3.1% in June. The Chinese economy has been on a difficult road to recovery as the country continues to grapple with recurring Covid-19 outbreaks, risks to the real estate sector, and tensions with the United States over Taiwan.
- NZD: The New Zealand dollar retreated to $0.64 from a two-month high hit last week, weighed down by weak economic data from key trading partner China and hawkish comments from Federal Reserve policymakers. The New Zealand dollar has risen sharply since mid-July on speculation that other major central banks will catch up with the Fed's tightening cycle, but comments from Fed officials that they are ready to raise interest rates further to tame inflation prompted markets to reassess those expectations. Meanwhile, the Reserve Bank of New Zealand is widely expected to raise policy rates by another 50 basis points when it meets on Wednesday, and markets will focus on the central bank's latest forecast as it grapples with inflation. At the same time, there is a growing risk of recession.
- AUD: The Australian dollar retreated to below $0.71 from a two-month high hit last week, weighed down by weak economic data from key trading partner China and hawkish rhetoric from Fed policymakers. The Australian dollar has rallied sharply since mid-July amid speculation other major central banks will catch up with the Fed's tightening cycle, but comments from Fed officials that they are ready to raise interest rates further to curb inflation prompted markets to reassess those expectations. In July, the Reserve Bank of Australia raised its policy rate for a fourth straight month but cut its guidance for future rate hikes amid expectations of a slowing economy. RBA governor Philip Lowe said the process of normalizing monetary conditions had not followed a preset path, returning to earlier assertions that the central bank intended to cut interest rates to a "neutral" level of at least 2.5 percent.
CHART OF THE DAY:
All three major U.S. stock indexes resumed their gains on Monday, with investors ignoring dismal economic data from China as they awaited a slew of earnings results from retailers. China's industrial output, retail sales, and fixed-asset investment all fell short of analysts' expectations, raising concerns that a slowdown in the world's second-largest economy could disrupt supply chains and undermine global growth. The country's central bank also unexpectedly cut interest rates, reflecting a bleak economic outlook. Still, investors remained optimistic about the U.S. economy, with lower-than-expected headline and core inflation prompting lower expectations for the scale of Fed monetary tightening while easing fears of a looming recession. This week's earnings from Home Depot, Walmart, and Target followed a busy week of retail payments.
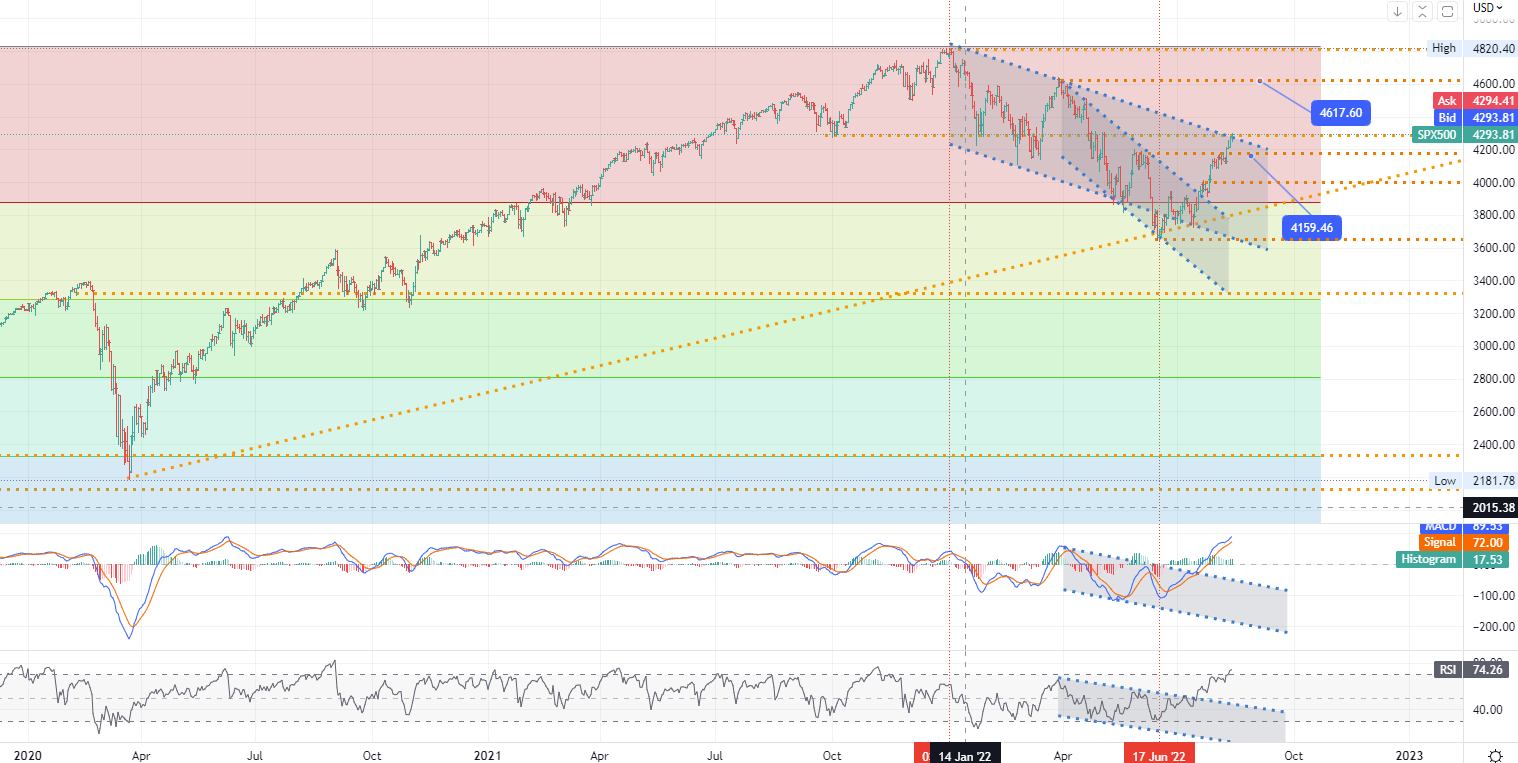
- US SP 500 index - D1, Resistance around ~ 4617, Support (target zone) around ~ 4159.
Demo account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account with virtual funds in a risk-free environment
Demo accountLive account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account in our transparent live model environment
Open an Account





