
Energy shares boost European equities, but recession fears cap gains
GLOBAL CAPITAL MARKETS OVERVIEW:
European stocks closed mixed on Monday, with Germany's DAX, Italy's FTSE MIB, and Spain's IBEX 35 falling below unchanged, while London's FTSE 100 and France's CAC rose. Energy, commodities, and healthcare were the best performers, with banks down more than 1% after the Financial Times reported on Sunday that the European Central Bank was looking for ways to stop banks from raising interest rates later this month. Earn billions of euros in extra profits from ultra-cheap loan schemes launched during the pandemic. Meanwhile, Bundesbank President Nagel warned the ECB against using monetary policy tools to limit risk premia while saying the focus should be on fighting inflation, which may require further rate hikes. The FTSE MIB index closed just below the 21,344 level on Monday, still near a 17-month low last week, as investors continued to assess recession risks amid the prospect of tighter monetary policy in the third quarter. Sharp losses in the banking and technology sectors offset a rebound in Milan's energy shares. Intesa Sanpaolo shares fell more than 2 percent, leading to losses in the financial industry after the Financial Times reported that the European Central Bank was taking steps to prevent banks from profiting excessively from high-interest rates. Meanwhile, STMicroelectronics led declines in the tech sector, falling nearly 2%, following the European chipmaker after JPMorgan downgraded Austria's as Osram. On the other hand, Eni and Tenaris rose 2.4% and 3.7%, respectively, amid a rebound in European oil companies. On Monday, the CAC 40 rose 0.4 percent to close at 5,954.65, extending gains for a second session, as higher oil prices boosted energy stocks while a pullback in commodity prices boosted consumer stocks. Total energy rose 4.55%, the biggest gainer in the index, followed by Alstom (up 1.51%) and Legrand (up 1.11%). In addition, consumer giants rose, led by Carrefour (+1.24%) and Danone (+0.79%). By contrast, most tech stocks fell, notably Capgemini (down 2.75%) and STMicroelectronics (down 1.84%). The MOEX-Russia index erased earlier gains to close at 2,205 on Monday, its lowest close in more than two months, as investors continued to assess the health of Russia's economy and business environment after prominent companies forwent dividend payments point. Shares in Gazprom fell 3.8%, extending losses since Thursday to nearly 40% as the company withholds dividend payments in fiscal 2021, which saw the giant record a record high income. The dividend withdrawal has fueled speculation about Russia's 2022 gas revenue as Russia continues to cut supplies to Europe and G7 nations discuss a price cap on Russian energy imports. On the other hand, the financial sector closed sharply higher, with VTB shares up 6% and Sberbank up more than 1%. Hongkong Hang Seng Index fell 0.1% to close at 21,830 on Monday, falling for a third straight session, as coronavirus cases in China rose as control measures eased, further fueling concerns about the region's economic recovery. On the corporate front, Ganfeng Lithium (down 3.3%) was the worst performer after the company said on Friday that it had received notice from China's top market regulator of its decision to indict A-share insider trading charges earlier this year and file a lawsuit against it. Meanwhile, from Monday, investors can use local securities or brokerage firms to trade eligible ETFs listed on the mainland and Hong Kong exchanges. China Shanghai Composite rose 0.53% to close at 3,405, while the Shenzhen Composite rose 1.29% to close at 13,026 on Monday, near its highest level in four months, buoyed by the newly launched ETF Connect between China and Hong Kong. This is expected to boost capital inflows into the mainland market. Investors also welcomed Beijing's recent pledge of 300 billion yuan in funding for infrastructure projects as authorities seek to stimulate China's economic recovery from the coronavirus. Meanwhile, investors' caution capped market gains amid a new round of mass testing in parts of eastern China due to the coronavirus outbreak. Healthcare, industrial, and tech stocks led gains, with solid gains in Jiangsu Hengrui (5.7%), Wuxi Aptech (6.1%), Tongwei (10%), Qinghai Salt Lake (2.8%), and Dongfang Monetary Information (1.8%) . The Nikkei 225 rose 0.84% to close at 26,154. In comparison, the broader Topix index rose 1.34% to close at 1,870 on Monday, ending a three-day decline, with utilities supporting a rebound as Japan continues to grapple with power shortages threatening power shortages. Unprecedented heat wave. Industry leaders TEPCO and Renova Corp rose 11% and 2%, respectively. . A fire has shut down a 500-megawatt unit at JERA, Japan's largest power generator, adding to fears of chronic power shortages. Other index heavyweights also rose, including SoftBank Group (3%), Toyota Motor (2.2%), Sony Group (2.1%), Mitsubishi Corporation (4%), and Xinzhao Holdings (2.9%). Meanwhile, shares of telecom giant KDDI fell 1.7% after the company suffered its biggest-ever system outage over the weekend, affecting nearly 40 million subscribers. The New Zealand dollar 50 indexes rose 109.18 points, or 1.02%, to close at 10,862.34 on Monday. It is the first daily gain in four years and retreated from a near two-week low hit on Friday as New Zealand and the European Union completed freedoms last week. Boosted by news of a trade deal that could boost the flow of goods and services by 30%. Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern said it had taken 14 years since the idea of a trade agreement was first proposed. Risk appetite was also boosted by reports that investors in China and Hong Kong began trading exchange-traded funds (ETFs) in each other's markets today. In the U.S., stocks closed higher on Friday in light trading ahead of a holiday-extended weekend, with gains mostly in utilities and retail. Traders are awaiting the latest Fed minutes and the June wage report later this week. I led the gains today, up 8.3%, followed by New Zealand King Salmon Investments (6.2%), Evolution Education (5.6%), and Marlborough Wine Estates (5.6%). Australia S&P/ASX 200 index rose 1.1% to close at 6611 on Monday after three straight losses, as investors bought depressed stocks ahead of expectations of a rate hike from the Reserve Bank of Australia. The Reserve Bank of Australia is expected to raise interest rates by another half a percentage on Tuesday to curb soaring inflation. Inflation accelerated to a 20-year high of 5.1% in the first quarter and is expected to approach 7% by the end of 2022. Tech stocks led gains, with solid gains from Xero (2.3%), Block Inc (5.1%), and Seek Ltd (2.1%). Other index heavyweights also rose, including CSL Ltd (2.1%), Macquarie Group (1.8%), Woodside Energy (2.7%), Newcrest Mining (2.3%), and Telstra (1.3%). Meanwhile, shares of Magellan Financial fell 9.9% as sales chief Frank Casarotti left the company.
REVIEWING ECONOMIC DATA:
Looking at the last economic data:
- CA: The S&P Global Canada Manufacturing PMI fell to 54.6 in June 2022 from 56.8 the previous month. The latest data showed factory activity expanded for the 24th month but at the slowest pace since January 2021. Production rose at the weakest pace in two years, while new orders grew only modestly amid persistent inflationary pressures and material shortages. Also, employment and purchasing activity growth slowed, while exports fell for the first time in four months. On the price front, input prices rose markedly and were the fastest in the history of a range of goods and services, including metals, fuels, energy, resins, and transportation. Finally, business sentiment fell to a 17-month low amid concerns over the global economy and the lingering impact of COVID-19.
- AU: Annual producer inflation in the eurozone fell to 36.3% in May 2022 from a record 37.2% in April, below market expectations of 36.7%. Prices for energy (94.4% vs. 99% in April) and intermediate goods (25% vs. 25.2%) slowed. On the other hand, the costs of consumer durables (9.1% vs. 8.6%), non-durables (12.3% vs. 11.9%), and capital goods (9.1% vs. 8.6%) rose further. Excluding energy, producer prices rose 16%, up from 15.6% in April.
- GE: Germany's trade surplus narrowed sharply to 500 million euros in May 2022, its lowest level since December 1992, imports surged 33.6% year-on-year to 129.8 billion euros, energy prices surged, and export growth was even weaker, reaching 129.8 billion euros. 131.1 billion euros. Exports to Russia amounted to 1.1 billion euros. On a seasonally adjusted basis, total shipments fell 0.5%, while imports rose 2.7%. Sales to Russia rose 29.4% in May after falling 9.9% in April. Most goods were exported to EU countries (down 2.8%), the UK (down 0.5%), while exports to the US (5.7%) and China (0.5%). Imports from the United States (9.7%) and the euro area (2.5%) rose, while imports from China (1.6%) fell.
- HK: The People's Bank of China said on Monday it had upgraded the currency swap mechanism with Hong Kong to a permanent agreement and expanded the scale from 500 billion yuan ($119.4 billion) to 800 billion yuan. The agreement, signed by the People's Bank of China and the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA), is the PBOC's first long-term swap agreement, according to its website. The bank said the upgraded agreement could provide long-term liquidity support for the Hong Kong market, help stabilize market expectations, and promote the development of Hong Kong's offshore renminbi market. The deal came as Hong Kong celebrated the 25th anniversary of its handover.
- AU: Private residential approvals in Australia fell 2.7 percent month-on-month to 9687 in May 2022, after a downwardly revised 0.2 percent growth rate in the previous month, the third decline since the start of the year. Approvals fell in New South Wales (down 11.1%), South Australia (down 4.1%), Queensland (down 1.3%), and Victoria (down 0.9%), while Western Australia (up 4.9%). Private housing permits were down 29.5 percent in the year to May.
- AU: The seasonally adjusted total housing estimate approved in Australia unexpectedly rose 9.9% month-on-month to 16,390 units in May 2022, easily beating the consensus forecast for a 1.8% decline and turning down from a revised 3.9% decline a month earlier 1.8%. This was the first rise in building permits since February, largely due to a sharp rebound in approvals for private sector housing, excluding housing (32% vs. 8.1% in April). Meanwhile, support for private sector housing fell further (-2.7% and -0.2%, respectively). Across Australia, housing approvals increased in Western Australia (38.7%), Tasmania (26.8%), Queensland (20.9%), and New South Wales (4.7%), while in South Australia (down 21.3%) and Victoria (down 6.6%). However, building permits fell by 20.9% per year as approvals for private and private sector housing, excluding housing, fell.
- AU: Job advertisements in Australia rose 1.4% month-on-month in June 2022 to the highest level since 2008 at 243,523, up from 0.4% in May. The latest newspapers highlighted that demand for labor showed no signs of stalling and suggested that the unemployment rate could fall to new lows in the coming months. "Unmet labor demand suggests that underutilization will continue to decline and remain low even if demand growth is dampened by higher inflation and rising interest rates," said ANZ senior economist Kathryn Birch. "The labor market is very tight, which is a key reason why we expect the economy to be resilient in the face of this," she added. Compared with January 2020, before the first outbreak of the epidemic, the annual increase in job advertisements was 18.4% and 59%, respectively.
LOOKING AHEAD:
Today, investors will receive:
- USD: Factory Orders m/m.
- EUR: French Industrial Production m/m, Spanish Services PMI, Italian Services PMI, French Final Services PMI, German Final Services PMI, and Final Services PMI.
- GBP: Final Services PMI, Housing Equity Withdrawal q/q, BOE Financial Stability Report, FPC Meeting Minutes, FPC Statement, BOE Gov Bailey Speaks, 30-y Bond Auction, and MPC Member Tenreyro Speaks.
- JPY: Average Cash Earnings y/y, and 10-y Bond Auction.
- NZD: NZIER Business Confidence: ANZ Commodity Prices m/m, and GDT Price Index.
- AUD: AIG Construction Index, Retail Sales m/m, Cash Rate, and RBA Rate Statement.
- CNY: Caixin Services PMI.
- CAD: Building Permits m/m
KEY EQUITY & BOND MARKET DRIVERS:
- RU: The 10-year Russian OFZ yield was above 9.1%, rebounding from a six-month low of 8.7% in late June amid a sharp drop in Russian assets. Despite record 2021 earnings, state-backed giant Gazprom canceled its 2021 dividend payment, denting confidence in Russia's economy and business environment, boosting expectations that as Russia cuts off supplies to Europe, the country's gas revenue could fall sharply. Meanwhile, investors further priced in a Russian sovereign debt default as Western institutions blocked interest payments to foreign holders of dollar-denominated European bonds. While its short-term impact on OFZ markets is limited, a technical default is expected to significantly affect Russia’s future access to credit and its costs. On the monetary policy front, the ruble remains firm as consumer prices fall, and the CBR is expected to cut the benchmark rate further.
- CA: Canada’s 10-year government bond yield fell below 3.2 percent in early July, its lowest level in four weeks, as fears of an economic slowdown boosted demand for safer assets such as government debt. Preliminary data showed Canada’s economy contracted 0.2% in May, the first drop in monthly GDP since May 2021, due to lower output from the energy and metal mining industries. On the monetary policy front, markets are pricing a 75 basis point hike in overnight interest rates at the Bank of Canada's July meeting, which would be the largest in 24 years. The Bank of China has raised interest rates by 1.25 basis points since March to curb inflation. Inflation is at its highest level in 39 years, while the latest unemployment figures are at record lows.
- FR: Yields on French 10-year oats rebounded to 1.9% from a one-month low of 1.7% on July 1 and were in line with gains in European government bond yields as investors hit another eurozone inflation hit. After the record, it put pressure on expectations of the European Central Bank to tighten policy. At the central bank's annual forum, President Lagarde said rates could rise faster in the third quarter if the outlook for inflation remains high after policy tightening began in July. Investors also continued to await details on the ECB's new tools to avoid a split among its member states and how to narrow bond yield spreads in higher-indebted countries. At the same time, the French government's budget deficit for January-May 2022 was reduced compared with the previous year.
- AU: Australia's 10-year government bond yield fell to a four-week low of 3.55% as fears of a possible global recession sent investors flocking to the safety of government bonds ahead of tomorrow's domestic monetary policy decision. After keeping rates near record lows, the RBA raised the critical rate, or cash rate, by a combined 75 basis points to 0.85 percent in May and June. Markets expect a 50-basis point hike in the cash rate this month, with the RBA governor hitting back at a sharp 75 basis point hike amid signs of consumer fatigue. Weekly card spending data from Australia's significant banks slowed in June after months of positive growth, while private consumer surveys also pointed to a pullback in spending.
- IT: Italy's 10-year BTP bond yield rose above 3.3%, rebounding slightly from a one-month low of 3.1% hit on July 1 and extending volatility in European debt instruments as investors weighed in on ECB policy tightening. Continue to assess recession fears as promised. Annual inflation in the eurozone hit a record high in June, CPI data showed, adding to speculation that the European Central Bank will speed up its interest rate hikes after a tightening cycle begins this month. Investors, meanwhile, were closely watching Italy's political backdrop as Prime Minister Draghi began talks with Conte after 5 Star Movement leader said his party could quit the government. The spread between the 10-year BTP and the Bundesbank held steady at 2 points, reflecting no increase in views on Italian debt risk.
- GE: The yield on 10-year German Bunds rose above 1.3%, rebounding from a one-month low of 1.16% since July 1, as investors stopped investing in safer assets. Investors continue to assess heightened recession risks as inflation mounts and the prospect of tighter monetary policy from the European Central Bank. The latest CPI data showed annual inflation in the eurozone hit a record high of 8.6%, with higher-than-expected figures in France, Italy, and Spain offsetting slower price growth in Germany. At the European Central Bank's annual forum, President Lagarde said the central bank would tighten the pace of drawing in the third quarter if the inflation outlook remained elevated. Fears of an economic slowdown intensified as demand fell sharply in the eurozone for the first time since 2020. In addition, June manufacturing PMI data showed a contraction in production and new orders for the first time since 2020.
- EU: European stock futures were higher on Monday, with the Dax and Stoxx 50 futures contracts up nearly 0.6%, but trade was expected to be light as U.S. markets were closed for the July 4 public holiday and no major earnings were released. On the data front, the latest data showed German exports fell in May, while PPI unemployment figures for the eurozone and Spain are also due. Meanwhile, investors will continue to watch for any signs of recession and monetary tightening, with comments from ECB policymakers, including President Christine Lagarde, and the minutes of the ECB's last monetary policy meeting this week.
STOCK MARKET SECTORS:
- High: Utilities, Real Estate, Consumer Staples, Consumer Discretionary, Financials
- Low: n/a
TOP CURRENCY & COMMODITIES MARKET DRIVERS:
- CAD: In early July, the Canadian dollar rose to the 1.285/dollar mark, the highest level in more than three weeks, supported by the Bank of Canada's tightening policy and expectations of higher crude oil prices. The Bank of China is expected to continue raising its benchmark interest rate in the third quarter to rein in inflation that soared to a 39-year high in June, while unemployment hit a record low. At its last meeting, the central bank decided to raise interest rates to 1.5% for the third time. Meanwhile, the lunatic was supported by a rebound in crude oil prices after fears of a deep recession dented demand for energy in the second half of June. However, the prospect that the Fed could also significantly tighten its funding rate in the third quarter prevented further gains. The Canadian dollar is one of the strongest currencies in the G10, depreciating less than 1% against the U.S. dollar.
- AUD: The Aussie held at around $0.68, hovering near its lowest level in two years, as the commodity currency came under pressure from the Federal Reserve's aggressive tightening program and the risk of a global recession rose. There are also signs that the Australian economy is cooling, house prices are falling, and consumer confidence is mired in a quagmire. The Australian dollar weakened despite expectations that the Reserve Bank of Australia will raise interest rates by another half a basis point at its July meeting, after a more-than-expected 50 basis point hike in June. Markets are betting that the central bank will raise interest rates to 3.25% by the end of the year. RBA governor Philip Lowe recently said there would be further tightening as interest rates remain "very low," He expects inflation to hit 7 percent by the end of the year. Still, he underestimated the cost of an outsized 75 basis point hike.
- NZD: The New Zealand dollar held at around $0.62, hovering near its lowest level in two years, as the risk of a global recession rose as commodity currencies came under pressure from the Federal Reserve's aggressive tightening program. Recent figures also show that 63 percent of New Zealand businesses expect economic conditions to worsen in the year ahead, mainly due to supply disruptions and surging cost pressures, underscoring risks to the country's economic trajectory. That challenges the Reserve Bank of New Zealand, which is expected to stick to its aggressive tightening policy to lower inflation, even if it means there is a risk of a recession. Markets are pricing in another 50-basis point hike in July, taking rates to 2.50% and around 4% by the end of the year.
- USD: The dollar index steadied at around 105.1 in holiday-thin trading on Monday, hovering near its highest level since December 2002, as the Federal Reserve led a wave of aggressive monetary tightening around the world in response to rising prices. Last week, Fed policymakers cemented expectations for further policy tightening, heralding another 75-basis point rate hike in July. Meanwhile, tighter financial conditions in significant economies have sparked fears of a global recession, prompting investors to divest from riskier assets and invest in the safety of the U.S. dollar. Data on Friday also showed U.S. manufacturing activity slowed more than expected in June. Investors can now look to the minutes of the last central bank meeting and the monthly jobs report for clues on where U.S. monetary policy may be headed.
CHART OF THE DAY:
The Dax failed to hold on to early gains, falling 0.4% about an hour before Monday's close, while the Stoxx 600 gained 0.6%, but trade was thin as U.S. markets were closed for the July 4 holiday. Energy, commodities, and healthcare were the best performers. At the same time, banks fell more than 1% after the Financial Times reported on Sunday that the European Central Bank was looking for a way to stop banks once it started raising interest rates later this month. Earn billions of euros in extra profits from ultra-low loan schemes launched during the pandemic. Meanwhile, Bundesbank President Nagel warned the ECB against using monetary policy tools to limit risk premia while saying the focus should be on fighting inflation, which may require further rate hikes.
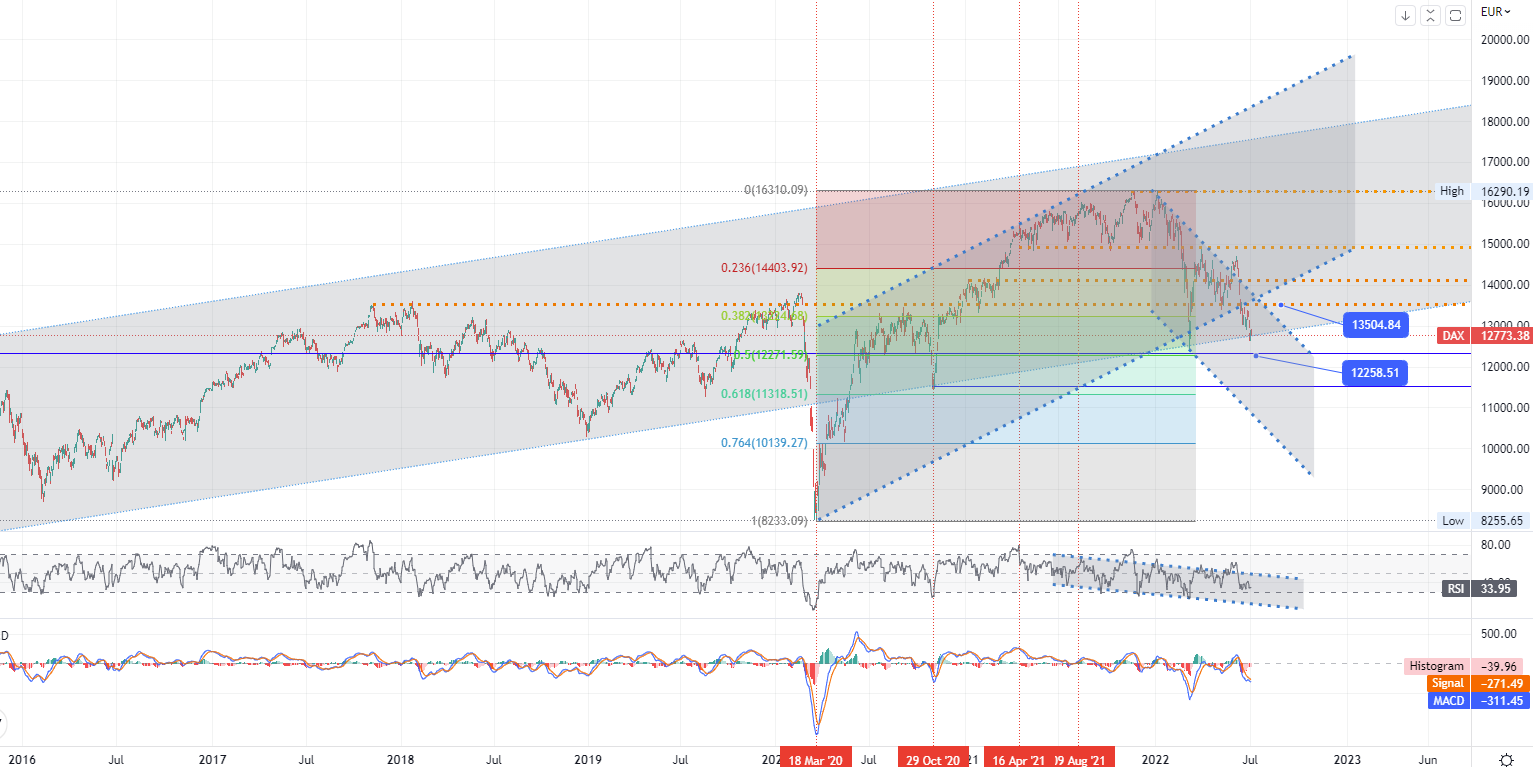
- German DAX index - D1, Resistance around ~ 135504, Support (target zone) around ~ 12258
Demo account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account with virtual funds in a risk-free environment
Demo accountLive account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account in our transparent live model environment
Open an Account





