
The major indexes closed slightly lower in a fatigued session. Gold picks up $1800, yields sell-off following US30-y auction
• GLOBAL CAPITAL MARKETS OVERVIEW:
European stock markets were mixed at the end of the turbulent trading day on Thursday. The Frankfurt DAX 30 index rose 0.1% after closing at a more than one-month low on Wednesday to close at 15,630 points. The Paris CAC 40 index and the Milan FTSE MIB index rose 0.2 %. At the same time, the London FTSE 100 Index and the Madrid Index fell 1% and 0.4%, respectively. The European Central Bank announced that it would reduce bond purchases for the rest of this year but did not signal the next policy actions, including how to cancel the 1.85 trillion euros pandemic emergency purchase plan (PEPP). In addition, the central bank raised its growth and inflation expectations for this year. In other respects, concerns about the slowdown in global growth caused by the coronavirus outbreak continue to weigh on market sentiment. The FTSE 100 index closed at 7022 points on Thursday, a 1% drop, the lowest level since July 28, as concerns about slowing economic growth hit commodity and financial stocks. In addition, EasyJet’s share price plummeted by more than 10% after British Airways stated that it rejected the takeover offer and would raise US$1.7 billion from shareholders to fund its flu pandemic recovery and expansion of operations. On the political front, Prime Minister Boris Johnson successfully passed a new tax increase plan to provide health care and social security funding. The plan increases the national insurance tax for employers and employees by 1.25% and an additional 1.25% dividend tax. In other respects, the European Central Bank announced that it would moderately reduce the speed of net asset purchases following PEPP regulations for the remainder of this year, which is consistent with popular expectations. Still, it did not provide details on the timetable and speed of the reduction. The Dow Jones Index rose more than 100 points on Thursday, and the Standard & Poor's Index rose 0.2%, trying to recover from a three-day decline after the number of first-time jobless claims in the past week fell by more than an expected 310,000. Nonetheless, investors remain cautious about the economic slowdown due to the spread of the coronavirus delta variant and the uncertainty of the Fed’s dwindling timeline. In addition, Nasdaq has also been boosted by large technology companies, including Apple, Facebook, and Amazon. At the same time, as China has stepped up its regulatory crackdown on online games, Chinese stocks traded in the United States, including Alibaba and NetEase, have fallen. The Standard & Poor's/Toronto Stock Exchange composite index rose slightly on Thursday, financial and technology stocks rose, and energy and industrial stocks fell. Concerns about the slow economic rebound and the increase in new coronavirus cases have also affected risk appetite. At the same time, the latest polls show that the Conservative Party continues to lead the Liberal Party in this month's federal election because the candidates are preparing for the third and final debate tonight, which is the only one conducted in English. Debate. The Shanghai Composite Index rose 18 points, or 0.49%, to close at 3693 points, the highest closing point since February 19. Resource stocks climbed to a six-year high. Previous data showed that soaring raw material prices drove it. China’s factory door inflation reached an 11-year high in August. Traders are also optimistic that Beijing will introduce more fiscal stimulus measures to support China's economic recovery. The new crown pneumonia epidemic has recently weakened China's economic recovery. At the same time, the People's Bank of China pointed out that the room for monetary policy is still relatively large, and domestic liquidity supply and demand will remain balanced in the coming months. In terms of data, China’s annual inflation rate in August unexpectedly reached 0.8%, the lowest level in five months. In Hong Kong, the stock market fell 2.57% at the second meeting, and Beijing’s new blow to gaming and the strong job opportunities announced in the United States in July this year increased. The Nikkei 225 index fell 173 points or 0.57% on Thursday to close at 30,008 points. It was the first drop in nine trading days and also reduced the sharp drop in early trading. Previously, there were reports that foreign investors purchased 664.2 billion yen worth of Net stocks. This is the largest weekly net buying since May 14, when the economy is expected to rebound after the sudden resignation of Prime Minister Naoto Kan last Friday. As the medical system is still tense about the influenza pandemic, Japan will formally decide to extend the state of emergency until September 30 later in the day. In the United States, several Fed policymakers said on Wednesday that the Fed would continue to reduce asset purchases this year following the release of strong job vacancies data in July. SoftBank Group shares fell 1.93%, and after reaching a $7 billion exchange deal with Deutsche Telekom on Wednesday, the group's share price soared. The fast retail industry also fell by 0.65%. The ASX 200 index fell 142.5 points, or 1.9%, to close at 7369.5 points, the lowest closing point since July 21. Concerns about the imminent reduction of central bank stimulus measures have been escalating. Several Fed policymakers said on Wednesday that in July, After the release of strong job vacancies data, the Fed will still reduce asset purchases this year. In the most recent data, the US consumer credit growth in July was lower than the market consensus, while the economic optimism index in September fell to its lowest level in a year. In terms of COVID-19, there are 1405 cases of the new virus in New South Wales today, compared with 1,480 cases a day ago, as the authorities shifted their focus to increasing vaccination rates rather than implementing a zero-coronavirus strategy. At the same time, according to Reuters, Sydney’s cafes, restaurants, and bars will reopen in late October after months of strict lockdown. Virgin Currency UK fell 7.93%, and Orocobro Ltd fell 6.32%.
• REVIEWING ECONOMIC DATA:
Looking at the last economic data:
- US: In the week ending September 4, 2021, the number of Americans newly applying for unemployment benefits fell to 310,000, lower than the 335,000 predicted by the market. This is a new pandemic low, just before the end of federal unemployment benefits across the country on September 6. The previous week’s level was raised by 5,000 to 345,000, and the 4-week moving average that eliminated weekly fluctuations fell to 339.5 thousand, which is also a new pandemic low. The number of continuing claims fell to 2.783 million, compared with the forecast of 2.744 million. Recent data continues to show that, with the help of business reopening and the start of the school year, despite the continued resurgence of COVID-19 and labor shortages that pose some risks, the world's largest economy is still recovering.
- US: The number of people applying for unemployment benefits for the first time last week may fall to 335,000, which is the lowest level since the new crown epidemic hit the US labor market in March 2020, which is before the end of federal unemployment benefits nationwide on September 6. The latest data should continue to show that with the help of business reopening and the start of the school year, the world’s largest economy will continue to recover, despite the continued resurgence of COVID-19 and labor shortages that pose some risks. At the same time, ongoing claims may fall to a new low of 2.74 million during the pandemic.
- EU: As the coronavirus crisis subsides, the European Central Bank (ECB) is expected to scale back its emergency stimulus plan on Thursday. Still, it may assure the market that this is not the beginning of a gradual withdrawal of easing policies and that it will remain committed to keeping inflation at a target level. . Policymakers may announce a further decline at the beginning of next year. The plan will cut the fourth quarter bond purchases from around 80 billion euros in July to 60 to 70 billion euros per month through PEPP before the end of March. . Before making this decision, a series of ECB hawks made comments in the past few weeks, suggesting that due to inflationary pressures, the ECB may tighten policy sooner than expected. Officials will pay attention to the strong economic growth in the Eurozone, declining unemployment and rising consumer prices, as well as the slowing of the global recovery amid the lingering threat of the coronavirus pandemic.
- EU: Three days after the euro fell back from its two-month high of $1.191 last week, it stabilized at about $1.182 on Thursday. Investors are awaiting the outcome of the European Central Bank’s policy meeting to determine whether the bank will begin to scale back its bond purchase program. Previous data showed that the Eurozone inflation rate surged in August to the highest level in 10 years. European Central Banks, including Austria's Robert Holzman and Bundesbank President Jens Hawks, commented on Weidman. Robert Holzmann, a member of the European Central Bank’s Governing Council, said that because inflationary pressures may persist, the European Central Bank may tighten policy sooner than many people expected. Weidmann) warned that inflation may exceed the European Central Bank’s forecast because the temporary factors behind the recent surge in inflation may seep into potential price growth.
- EU: Germany’s current account surplus shrank from 20.2 billion euros in the same period last year to 17.6 billion euros in July 2021. The goods surplus fell slightly to 17.6 billion euros from 19.8 billion euros a year ago, while the service shortage fell to 2.4 billion euros from 2.6 billion euros. At the same time, the primary income surplus increased from 6.8 billion euros to 8.2 billion euros, while the secondary income deficit increased from 3.7 billion euros to 5.7 billion euros.
- EU: In July 2021, Germany's trade surplus was 18.1 billion euros, compared with 19.2 billion euros in the same period last year. Exports increased by 12.4% to 115 billion euros, exports to the EU increased by 17.1%, exports to the United Kingdom increased by 7.2%, exports to the United States increased by 15.7%, and exports to China fell by 4.3%. Imports increased by 16.6% to 96.9 billion euros, of which purchases from the European Union (18.7%), the United Kingdom (15.6%), China (3.9%), and the United States (4.1%) increased. Compared with February 2020, in the month before restrictions were imposed due to the German coronavirus pandemic, exports increased by 1.6%, and imports increased by 5.9%.
- CN: In August 2021, food prices in China fell 4.1% year-on-year, after falling 3.7% in the previous month. This marked the third consecutive month of decline in food costs and the fastest decline in the third consecutive month. The price of pork fell even faster after a sharp increase due to the African swine flu outbreak in 2019 (July:- 43.5%, a drop of -44.9%). In addition, the price of fresh vegetables continued to fall (-1.5% vs. 4%). At the same time, the prices of edible oil (6.8% vs. 7.2%), dairy products (1.8% vs. 2%), eggs (11.9% vs. 15.6%), and fresh fruits (5% vs. 5.2%) have increased at a moderate rate.
- CN: In August 2021, Chinese producer prices rose 9.5% year-on-year, higher than market expectations and the 9% increase in July. This is the eighth consecutive month that factory door prices have risen, and since August 2008, in the context of rising commodity prices, despite Beijing's efforts to cool it down, the increase has been even greater.
- CN: In August 2021, China’s annual inflation rate unexpectedly reached 0.8%, while the market consensus and July data was 1%. This is the lowest figure in five months because non-food costs have fallen, food costs have fallen even more, and pork prices have fallen even faster.
- NZ: In the second quarter of 2021, New Zealand’s manufacturing sales increased by 18.8% year on year and accelerated from a year-on-year growth of 4.3%, the largest increase in history. On a seasonally adjusted quarterly basis, total manufacturing sales fell 0.1%. The biggest industry changes were metal products (up 3.4%), beverages and tobacco products (up 4.5%), and petroleum and coal products (down 8.8%).
- RU: Russia’s annual inflation rate rose from 6.5% last month to 6.7% in August 2021, higher than market expectations of 6.6%. This is the highest inflation rate since August 2016, supported by the prices of food (7.7%), non-food (8.0%), and services (3.8%). After rising 0.3% in July, monthly consumer prices rose 0.2%.
• LOOKING AHEAD:
Today, investors will receive:
- GBP: Construction Output m/m, GDP m/m, Goods Trade Balance, Index of Services 3m/3m, Industrial Production m/m, and Manufacturing Production m/m.
- EUR: German Final CPI m/m, Eurogroup Meetings, ECB President Lagarde Speaks, French Industrial Production m/m, and Italian Industrial Production m/m.
- NZD: Visitor Arrivals m/m.
- CNY: M2 Money Supply y/y and New Loans.
- CAD: Employment Change, Unemployment Rate, and Capacity Utilization Rate.
- USD: PPI m/m, Core PPI m/m, and Final Wholesale Inventories m/m.
- GBP: NIESR GDP Estimate.
• KEY EQUITY & BOND MARKET DRIVERS:
- The Dow Jones Index rose above 35,000 points.
- Italy 40 drops to a 4-week low of 25704.
- Australia 200 fell to a 5-week low of 7429 points.
- The yield on Germany’s benchmark 10-year government bond fell slightly to -0.33%, still close to the nearly two-month high of -0.31% hit earlier this week after the European Central Bank said on Thursday that it would be in the fourth quarter as expected. Moderately slowed down large-scale emergency bond purchases but did not signal the end of the emergency stimulus.
- The European Central Bank (ECB) kept interest rates at a record low but announced that it would begin net asset purchases under PEPP in the fourth quarter at a slightly lower rate than the previous two quarters. The central bank reiterated that the PEPP envelope will remain at 1.85 trillion euros, at least until the end of March 2022, in any case, until it judges that the coronavirus crisis phase is over.
- The yield on the benchmark 10-year U.S. Treasury bond fell slightly to 1.33% on Thursday. After hitting a nearly two-month high of 1.38% earlier this week, there is widespread risk aversion. As the Coronavirus Delta variant continues to spread, investors remain concerned about slowing growth and bet that the Fed will postpone its gradual reduction plan. The US economy only added 2.35 million jobs in August, which is the lowest level in seven months, and wage growth increases. At the same time, the Fed's Beige Book showed that the US economy "slightly declined" in August. At the same time, there is strong demand for auctions of $38 billion in 10-year Treasury bonds. The Treasury Department will also issue $24 billion in 30-year bonds on Thursday.
• STOCK MARKET SECTORS:
- High: Financials, Energy, Materials.
- Low: Real Estate, Health Care, Consumer Staples.
• TOP CURRENCY MARKET DRIVERS:
- OIL: According to data from the EIA Oil State Report, in the week ending September 3, US crude oil inventories fell by 1.529 million barrels, which was the fifth consecutive decline, and the market forecast was 4.612 million barrels. At the same time, gasoline inventories fell by 7.215 million barrels, exceeding the expected 3.39 million barrels.
- CAD: On Thursday, as traders looked beyond the Bank of Canada monetary policy meeting, the global economic growth woes took the forefront, and the Canadian dollar to US dollar exchange rate barely changed near the two-week low of 1.27. As demand in strategic areas in Asia continues to be suppressed by the epidemic, the fall in the price of oil, Canada’s main export product, has also put the lunatic asylum in trouble. Nevertheless, the central bank decided on Wednesday to maintain the monetary policy unchanged, citing excess capacity. Looking ahead, policymakers pointed out that despite the lingering risks of the epidemic and supply chain, the economy is moving towards a more stable expansion in the second half of 2021.
- USD: The US dollar index fell back to 92.5 on Thursday, after hitting a two-week high of 92.8 in the previous trading day, as investors digested different monetary policies regarding stimulus. After the disappointing non-agricultural employment report was released, traders began to suppress when the Fed reduced bond purchase expectations. However, Bank of Dallas Governor Robert Kaplan said that he would support the gradual reduction in bond purchases announced in September and may begin in October based on current prospects. In addition, Bank of New York Governor John Williams said it "may be appropriate" to reduce bond purchases before the end of the year gradually. At the same time, the European Central Bank said it would slow down the pace of asset purchases. Still, it did not change the overall scope of the stimulus plan, saying that it will be maintained at least until the end of March 2022 or the end of the coronavirus crisis.
- USD: The pound rose to $1.382 on Thursday, ending a three-day decline after the British Parliament supported Prime Minister Boris Johnson's plan to raise taxes to the highest level on record to cover social, medical expenses and the NHS. According to the proposal, the national insurance payroll tax rate paid by workers and employers will be increased by 1.25 percentage points. The same increase will also apply to shareholder dividend tax. In terms of monetary policy, Andrew Bailey, Governor of the Bank of England, said that in the next two to three years, the Bank of England may be forced to raise interest rates in response to inflationary pressures, even though the UK’s economic recovery from the new crown epidemic is slowing. ; Policymaker Michael Saunders said that if the economy continues to grow and inflation becomes more difficult, the central bank may need to raise interest rates next year.
• CHART OF THE DAY:
The euro rose slightly to $1.185 on Thursday, after the European Central Bank stated that it would slow down the large-scale bond purchase program from the fourth quarter, but reiterated that the total purchases will remain at 1.85 trillion euros until March 2022 or after (if necessary), which shows that the European Central Bank has not considered canceling stimulus measures. In addition, data from last week showed that inflation in the eurozone soared to a 10-year high in August.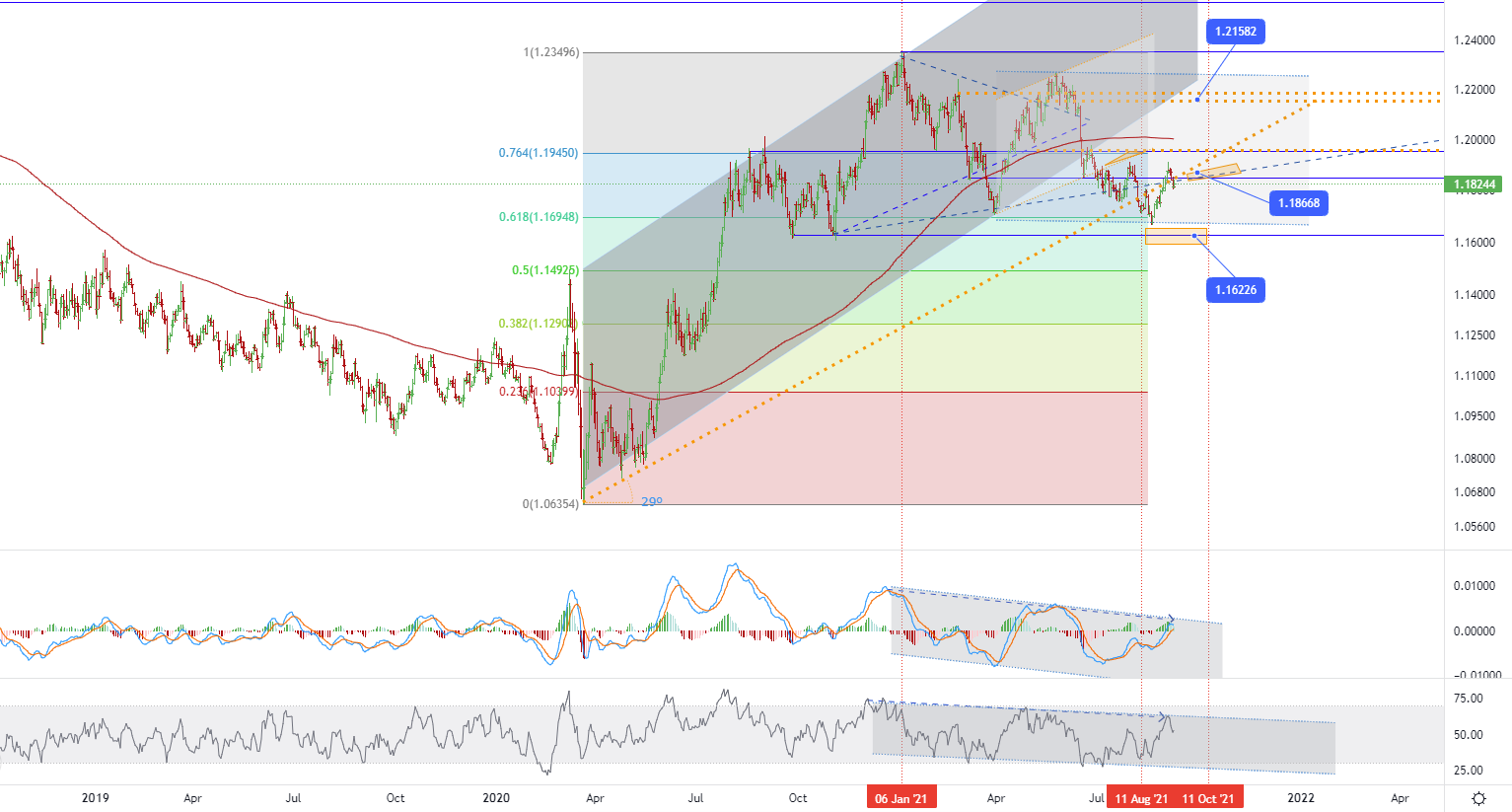
• EURUSD - D1, Resistance around ~ 1.21582, Support (target zone) around ~ 1.18668 and 1.16226
Demo account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account with virtual funds in a risk-free environment
Demo accountLive account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account in our transparent live model environment
Open an Account





