
Risk sentiment under the influence of negative headlines - according to Fed officials, the cut could be started this year
• GLOBAL CAPITAL MARKETS OVERVIEW:
The Dow Jones Index and the Standard & Poor's 500 Index fell for Tuesday's third consecutive trading day. People still worry that the spread of the Coronavirus Delta variant will significantly impact economic recovery. New mask authorizations, travel restrictions, event cancellations, and delayed office reopening are all affecting growth. At the same time, traders are increasingly betting that the Fed's reduction plan may be postponed because the labor market recovery has slowed sharply. The U.S. employment report shows that the U.S. economy has added the fewest jobs in seven months. In addition, the Nasdaq index fell more than 0.6%, mainly dragged down by giants such as Apple and Facebook. The Toronto Stock Exchange's Standard & Poor's/TSX Composite Index fell 69 points, or 0.3%, to 20,738 on Wednesday, falling from a record high hit on Monday to the second trading day after the Bank of China maintained interest rates and quantitative easing. Stabilizing and strengthening the Canadian economy still needs monetary policy support. Concerns that the fourth wave of new coronavirus infections and continued supply bottlenecks may affect economic recovery undermine market sentiment. Nevertheless, energy stocks are still supported by rising oil prices, and WTI crude oil has ended its three consecutive days of decline. On Wednesday, due to growing concerns about the pace of economic recovery, the FTSE MIB reduced its early losses and closed at a two-week low of 25877 points, a drop of 0.8%. At the same time, on the eve of the European Central Bank’s monetary policy meeting, market participants were generally cautious after the Central Bank of China ruled out the possibility of increasing stimulus measures to boost economic growth. In terms of data, Italian retail sales in July fell 0.4% from June, indicating that retail activity was the slowest since January last year, mainly due to the non-food sector. In terms of earnings, Exor fell 0.9% after announcing its 2021 half-year results, with a consolidated profit of 838 million euros, while a combined loss of 1.318 billion euros in the same period in 2020. After the Chinese auto giant Dongfeng divested 1.2% of the French-Italian auto group, Stellattis fell 2.9%. CAC 40 index fell 0.9% to close at 6669 points, a one-week low, as investors took conservative measures on the eve of the European Central Bank meeting after the Chinese central bank ruled out increased stimulus measures to boost the economy possibility of growth. At the same time, due to the risks posed by the pandemic, growth expectations remain cautious. The World Health Organization says the pandemic will become an endemic disease. Except for the industrial group Bouygues, French securities are primarily bearish. The group closed up 0.9% after confirming that it submitted a non-binding offer to Engie to acquire its subsidiary Equans. Stellatis fell 2.8% after the Chinese auto giant Dongfeng divested 1.2% of the French-Italian auto group. The FTSE 100 Index closed down 54 points, or 0.8%, to 7,096 points on Wednesday, the lowest level since August 20, because growth concerns are weighing on investors, who are waiting for the European Central Bank’s policy meeting Thursday. The central bank may announce plans to slow down large-scale bond purchases at the meeting. On the corporate side, British technology company Smiths Group will sell its medical unit to UICU medical for US$2.4 billion, while supermarket Morrisons is discussing an auction with its private equity acquirer and the British Takeover Commission. Negotiations on its future ownership issues. In other respects, investors continue to digest Prime Minister Boris Johnson's plan to raise taxes on workers, employers, and some investors to pay for social, medical expenses and the NHS. The Shanghai Composite Index closed flat and closed at a nearly seven-month high on the previous trading day. Traders digested the report on China’s macro leverage ratio (a measure of overall economic debt). It was 274.9% at the end of June, which decreased from the end of 2020. 4.5 percentage points. At the same time, the People’s Bank of China said today that there is still much room for monetary policy and that it will maintain a prudent monetary policy without taking flood-like stimulus measures. China’s official media, "People’s Daily" stated that China’s long-term economic policy remains unchanged. , The supervision of its industry will promote its healthy development. The Ministry of Education in Hong Kong, China, said Wednesday that private teachers would be banned from providing courses through instant messaging services or livestock platforms after the US stock market saw a 0.52% drop in early trading. The Nikkei 225 Index rose 265 points or 0.89% to close at 30,181 points, the highest closing point since March 18, rising for the eighth consecutive trading day after Japan’s second-quarter GDP data was revised upwards, confirming economic success Avoided recession. Compared to the previous quarter, Japan’s economy grew by 0.5% in the second quarter, while the preliminary data showed a 0.3% increase and a 1.1% decline in the first quarter after revision. The report was released after Prime Minister Naotoku Suga announced that he would not seek re-election to the party leadership. In a business report, PayPal Holdings Inc. said on Tuesday that it would acquire Paidy of Japan for US$2.7 billion in cash because the American payments company hopes to expand its business in Asia. At the same time, Mizuho Bank said today that the bank experienced a system failure for the seventh time this year. SoftBank Group closed up 4.64% after reaching a $7 billion share swap with Deutsche Telekom. At the same time, Nikon rose 4.18%, and Lotte Group rose 3.89%. The Australian Stock Exchange 200 Index fell 18 points, or 0.24%, to close at 7512. Dragged down by the rise in Australian coronavirus cases, New South Wales reported 1,480 new cases today, up from 1,220 the day before. The reason is that the authorities are speeding up vaccination while trying to contain the outbreak of the delta mutant virus. Reports of weaker commodity prices also weakened investor sentiment. The gold index fell by about 3.6%, its lowest level in six months after a strong US dollar and rising U.S. Treasury yields pushed the price of gold to below US$1,800 per ounce. Affected by weak iron ore and copper prices, mining stocks fell about 1%, continuing their decline for the third consecutive trading day. The technology index fell 0.9%, and heavyweight Afterpay fell 1.58%.
• REVIEWING ECONOMIC DATA:
Looking at the last economic data:
- US: U.S. consumer credit increased by $17 billion in July 2021, after an increase of $37.86 billion in the previous month, which was lower than market expectations of an increase of $25 billion. Revolving credit increased by US$5.56 billion, and non-revolving credit increased by US$11.45 billion.
- US: In September 2021, the US IBD/TIPP Economic Optimism Index fell 5.1 points to 48.5, the lowest level since September last year, and fell into a pessimistic range for the first time since December. The six-month outlook for the US economy fell 8.9 points to 41.1 points, the lowest since September 2020; the personal finance sub-index fell 2.8 points to 55. The federal policy sub-index fell 3.8 points to 49.1, the first negative value since February.
- US: According to data from the Mortgage Bankers Association, the number of mortgage applications in the United States fell by 1.9% in the week ending September 3, after a 2.4% drop in the previous week, and the index was pushed to the level since July. The lowest level. Housing refinancing applications fell by 2.8%, and housing purchase applications fell by 0.2%. The average interest rate on 30-year fixed mortgages remained unchanged at 3.03% for the second consecutive week. "The amount of refinancing has been slowing down, and given the lack of housing on the market, purchases continue to be lower than expected. Economic data sent a mixed-signal, employment growth slowed, but the unemployment rate fell further in August. We expect further improvement. Will cause the Fed to reduce MBS purchases at the end of August, MBA chief economist Mike Fratanoni said: "This will put a certain amount of upward pressure on mortgage interest rates. ".
- US: The number of job vacancies in the United States increased by 749,000 from the previous month and reached a new series of 10.934 million highs in July 2021, which was much higher than the market's expectation of 10 million, increasing signs of a tight labor supply. Job vacancies increased in several industries, among which medical and social assistance (increased by 294,000 people) advanced the most; finance and insurance (increased by 116,000 yuan), and accommodation and food services (increased by 115,000 yuan). The opening level in the northeast, south, and west regions has increased. At the same time, the number of employees fell by 160,000 to 6.667 million, while the total number of departures (including separations, layoffs, dismissals, and other departures) increased by 174,000 to 5.786 million.
- RU: Russia’s annual inflation rate rose from 6.5% last month to 6.7% in August 2021, higher than market expectations of 6.6%. This is the highest inflation rate since August 2016, supported by the prices of food (7.7%), non-food (8.0%), and services (3.8%). After rising 0.3% in July, monthly consumer prices rose 0.2%.
- CA: The Canadian Ivey Purchasing Managers Index jumped from 56.4 last month to 66 in August 2021, indicating that Canada's business conditions have improved significantly. The main upward pressure comes from the employment sub-index, as companies expand the labor force faster (from 62.1 in July to 66.9). In terms of prices, the inflation rate has dropped to its lowest level in eight months (from 77.1 to 69.7), as inventories have almost remained stable (from 60.4 to 60.3) and supplier delivery times have increased at a lower rate (from 31.1 drops to 34.2).
- CA: According to forecasts, the Bank of Canada will maintain its overnight interest rate target at 0.25% on September 9, 2021. After cutting $1 billion at the last meeting, the Bank of Canada will maintain its quantitative easing program at a target rate of $2 billion per week. Policymakers continue to expect the economy to strengthen in the second half of 2021, although the fourth wave of new coronavirus infections and continued supply bottlenecks may affect the recovery. In addition, the central bank believes that there is still considerable overcapacity in the Canadian economy, and recovery still requires extraordinary monetary policy support. Therefore, the Bank remains committed to keeping the policy interest rate at the effective lower limit until the economic weakness digested to sustain the 2% inflation target. According to the World Bank’s July forecast, this will happen in the second half of 2022.
- SW: In July 2021, Swedish household consumption increased by 0.7% from the previous month, after reducing it by 0.3% in the previous month. Expenditure growth in restaurants, cafes, hotels, and other accommodation services has accelerated (41% and 15%, respectively). In addition, spending on entertainment and culture, goods and services rebounded (0.6% vs. -2%); and housing and utilities (0.74% vs. -1.2%). At the same time, the consumption of food and beverages decreased (1.1% and 1.4%, respectively); clothing and footwear (down 1.2% and 2.7%, respectively); automobile transportation, retail, and service industries (down 0.7% and 1.1%, respectively); And furniture, furniture, household equipment and consumables (down 1.8% and 4.3%, respectively). Household consumption grows by 6.4% annually.
- SW: In July 2021, Swedish industrial output increased by 11.3% year-on-year, after a downward revision of 15.5% in the previous month. This is the sixth consecutive month that industrial activity has risen, although the expansion rate has slowed to its lowest level in four months. Manufacturing output continued to grow steadily (15.2% in June and 16.5% in June), and mining and quarrying activities contracted further (11.1%, 6.3%). On seasonally adjusted monthly data, industrial production rose 1.2%, down from an 8-month high of 1.9% in June.
- EU: In June 2021, France's current account deficit widened to 3.5 billion euros from 900 million euros last month, compared with the 1.4 billion euro gap expected by the market. The latest data shows that this is the biggest gap since September 2020. The goods deficit widened from 3.8 billion euros in June to 5.9 billion euros, while the services surplus narrowed from 3.3 billion euros to 2.8 billion euros. At the same time, the primary income surplus did not change much, at 3.6 billion euros, and the secondary income gap was flat at 4 billion euros.
- EU: In July 2021, Italian retail sales fell 0.4% month-on-month, after increasing 0.7% in the previous month. This was the most serious contraction in retail activity since January, as sales of non-food products declined (0.6% in June and 0.3% in June), while food sales remained the same as the previous month (down 1.0%). On an annual basis, retail sales rose 6.7% in June, after 7.9%.
- EU: In July 2021, France's trade deficit widened to 6.96 billion euros, while last month's revised value was 6.05 billion euros, which is the largest gap since August 2020. Due to the decline in sales of other industrial products (-5.6%), exports fell by 1.9%; in transportation equipment (down 4.8%); and in food industrial products (-2.1%). In addition, exports to most regions have fallen, especially the European Union (down 5.0%), Asia (-4.8%), and European countries outside the EU (-2.6%). At the same time, imports rose slightly by 0.1%, mainly mechanical equipment, electrical, electronic and computer equipment (1.2%); and natural hydrocarbons, other mining products, electricity, waste (5.3%), and transportation equipment declined (-6.8 %) offset most of the gains. Among the major trading partners, purchases from the European Union (0.5%), Asia (2.4%), and European countries outside the EU (4.4%) are higher.
- JP: The Japanese economy grew by 1.9% annually in the second quarter, while preliminary data showed that the Japanese economy grew by 1.1%. The market generally believed that the Japanese economy grew by 1.6%, which contracted 4.2% after the first quarter revision. Household consumption, business investment, and government spending have all rebounded. At the same time, as the virus inoculation has accelerated, the economy has recovered from the damage of the coronavirus, and exports and imports have further increased.
- JP: Japan’s current account surplus increased from 1,535.3 billion yen in the same month of the previous year to 1,910.8 billion yen in July 2021, while the market expected a surplus of 2,300 billion yen.
- JP: The Japanese economy grew by 0.5% month-on-month in the second quarter, while preliminary data was an expansion of 0.3% and a revised 1.1% contraction in the first quarter. Domestic demand contributed 0.8 percentage points to GDP growth.
• LOOKING AHEAD:
Today, investors will receive:
- USD: Unemployment Claims, Natural Gas Storage, Crude Oil Inventories, FOMC Member Daly Speaks, FOMC Member Evans Speaks, FOMC Member Bowman Speaks, 30-y Bond Auction, and FOMC Member Williams Speaks.
- EUR: German Trade Balance, Monetary Policy Statement, Main Refinancing Rate, and ECB Press Conference.
- CNY: CPI y/y, PPI y/y, M2 Money Supply y/y, and New Loans.
- JPY: M2 Money Stock y/y and Prelim Machine Tool Orders y/y.
- NZD: Manufacturing Sales q/q.
- GBP: RICS House Price Balance.
- AUD: RBA Deputy Gov Debelle Speaks.
- CAD: BOC Gov Macklem Speaks.
• KEY EQUITY & BOND MARKET DRIVERS:
- DAX 30 drops to a 5-week low of 15596.
- The Dow Jones Index rose above 35,000 points.
- The French stock market fell 77 points. Leading the decline were Renault (down 1.92%), BNP Paribas (down 1.79%) and Faurecia (down 1.61%).
- The Japanese stock market rose 257 points. Leading the gains were SoftBank (3.11%), Mazda Motors (2.26%), and Keisei Electric Railway (1.85%). The biggest losers were Donghe Zinc Industry (down 1.88%), Omron Corporation (down 1.66%), and Maruhi Co., Ltd. (down 1.49%).
- The yield on Germany’s benchmark 10-year government bond fell to -0.33% after hitting its highest level since mid-July on Tuesday. Investors became cautious before Thursday’s ECB meeting. The latest US employment data increased the workforce in the world’s largest economy. Signs of a slowdown in the market recovery. There are signs that the European Central Bank may begin to restrict emergency bond purchases. Earlier, Eurozone inflation soared to a 10-year high in August, with European Central Banks including Austria’s Robert Holzman and Bundesbank President Jens Weidman (Jens Weidman). The officials made strong comments. Robert Holzmann, a member of the European Central Bank Management Committee, said that because inflationary pressures may persist, the European Central Bank may tighten policy sooner than many people expected. German Central Bank President Jens Weidman warned that inflation might exceed the European Central Bank’s forecast because the temporary factors behind the recent surge in inflation may seep into potential price growth.
- As traders digested the latest news from the Reserve Bank of Australia’s September meeting, the Australian 10-year bond yield approached 1.30% in the second week of September, the highest level since mid-July. Policymakers confirmed their decision to reduce government bond purchases to A$4 billion per week but said they would maintain this rate until February, citing coronavirus-related risks. In general, the central bank will purchase more bonds in July than originally planned. New South Wales and Victoria are abandoning the zero new crown virus strategy in the flu pandemic. Instead, they are opening up because the vaccination rate has risen to a more comfortable level, in contrast to most parts of the country.
- The yield on the benchmark 10-year Treasury note fell slightly to 1.36% on Wednesday, after hitting a nearly two-month high of 1.38% on the previous trading day, as investors are still worried that the coronavirus delta variant will continue to spread and slow growth. In addition, the US economy only added 235,000 jobs in August, the lowest level in seven months. At the same time, the disappointing employment report dispelled expectations that the Fed will soon begin to scale back its bond purchase program.
• STOCK MARKET SECTORS:
- High: Utilities, Real Estate, Consumer Staples.
- Low: Materials, Energy, Information Technology.
• TOP CURRENCY MARKET DRIVERS:
- EUR: After the euro-dollar exchange rate rose above $1.19 for the first time since June 30 last week, the euro-dollar exchange rate fell to $1.18. Investors wait for the European Central Bank's policy meeting on Thursday to see if the bank will start to scale back its bond purchase program. Previous data showed that the eurozone inflation rate surged in August to the highest level in 10 years and included Austria's Robert Holzman and Bundesbank President Jens Weidman. A series of comments by European Central Bank hawks. Robert Holzmann, a member of the European Central Bank’s Management Committee, said that the European Central Bank should consider reducing emergency bond purchases. At the same time, the Bundesbank President Jens Weidmann warned that inflation could exceed Europe’s central bank forecasts that temporary factors behind the recent surge in inflation may seep into basic price growth.
- USD: The US dollar index was at 92.55 on Wednesday, the highest level since September 1, tracking the rise in US Treasury yields. The yield on the benchmark 10-year Treasury note rose to nearly 1.38% on Tuesday, the highest level since July 11, as people are increasingly worried about the spread of the coronavirus delta variant and its impact on economic recovery. After the disappointing non-farm payrolls report was released, investors postponed expectations of the Fed to reduce bond purchases. However, the European Central Bank is expected to debate cut stimulus measures later this week.
• CHART OF THE DAY:
Oil received unexpected support in the form of events in Libya. Reuters sources say protesters have blocked the Hariga and El Sider terminals. However, the fields that supply oil to these terminals continue to operate. In addition, in the United States, the recovery in oil refining is happening faster than the recovery in production in the Gulf of Mexico. By Tuesday evening, 79 platforms were still unmanned. The production volumes in the bay are about 20% of the potential. Thus, since last weekend, losses in supplies amount to 17-18 million bar. Hurricane Ida most likely led to a decrease in reserves. According to a Reuters poll, the market is expected to reduce oil reserves by 3.8 million barrels, gasoline by 3.6 million barrels, and distillates at 3.0 million bar. According to data from the American Petroleum Institute, in the week ending September 3, 2021, US crude oil inventories fell by 2.882 million barrels. The previous week fell by 4.045 million barrels, which is the sixth consecutive week of decline. In contrast, the market expects a drop of 3.832 million.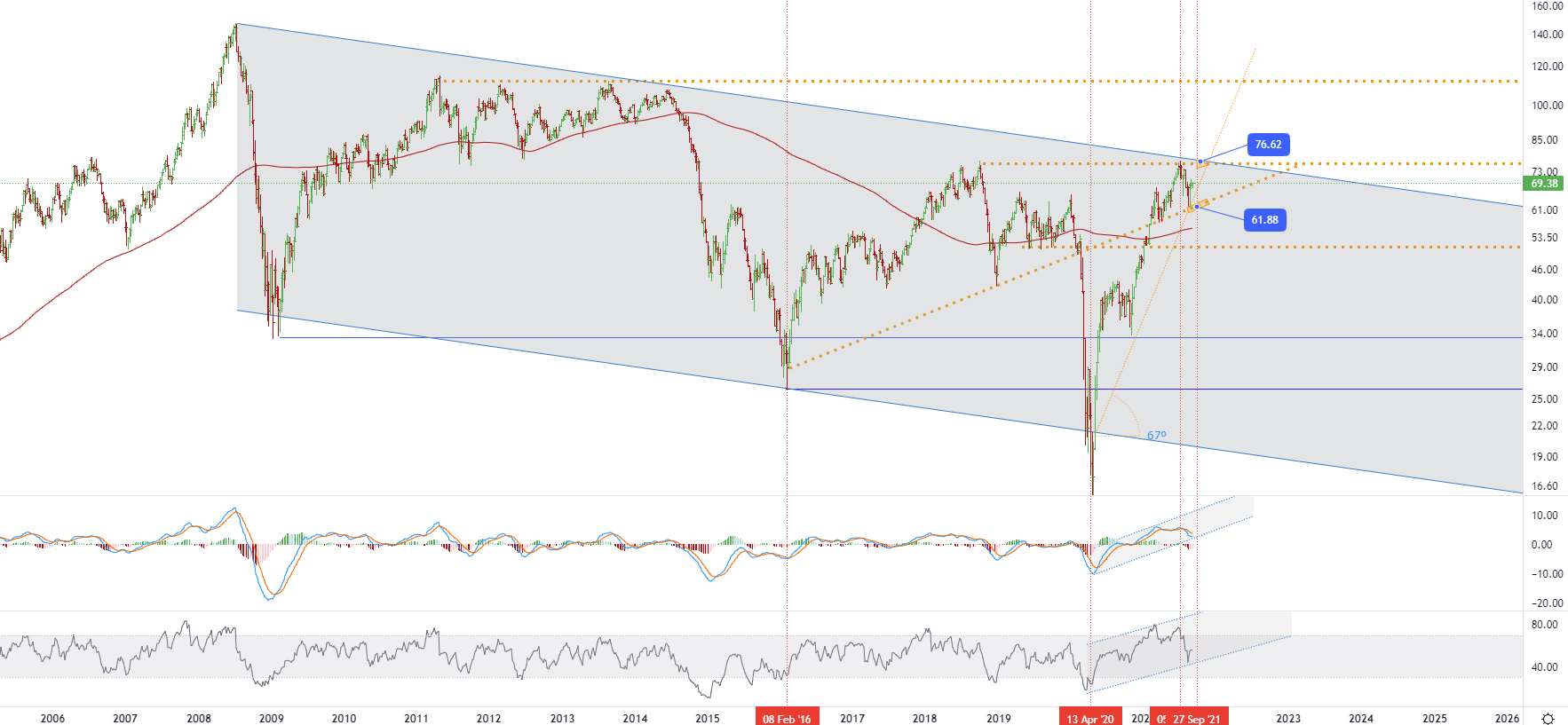 • Crude oil - W1, Resistance (target zone) around ~ 76.62, Support (consolidation) around ~ 61.88
• Crude oil - W1, Resistance (target zone) around ~ 76.62, Support (consolidation) around ~ 61.88
Demo account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account with virtual funds in a risk-free environment
Demo accountLive account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account in our transparent live model environment
Open an Account





