
The world equity market is under pressure as economic concerns rise - gold slips as yields, dollar gains
• GLOBAL CAPITAL MARKETS OVERVIEW:
European stock markets fell on Tuesday, falling back from a 1% rise in the previous trading day. Previous data showed that the morale of German investors fell to 26.5 in August, far below market expectations of 30. In addition, the prospect of a slowdown in global growth due to the coronavirus outbreak has weighed on market sentiment. Market participants await the European Central Bank policy meeting on Thursday, where policymakers discuss the PEPP asset purchase plan. On the company side, after US defense company TransDigm ruled out the possibility of acquiring a British competitor for US$8 billion, Meggitt’s share price fell more than 12.1%. The CAC 40 index fell during the session and closed at 6726 points on Tuesday, a decrease of 0.3%, the same as its European counterparts, as signs of a slowdown in the recovery triggered some cautious sentiment on the eve of the ECB's monetary policy meeting. Among French securities, heavyweight luxury goods stocks closed higher, with LVMH (up 0.7%), Kering (up 0.9%), and Hermes (up 1.1%). Economic data in the main market, China, was optimistic. At the same time, the stock price of steel company ArcelorMittal failed to maintain strong momentum, rising only 0.2% after the Guinea coup caused steel prices to rebound. At the bottom of the index, Danone fell 2.6% after Bank of America analysts lowered its target price to €55%, thereby lowering their recommendation on the food group from "neutral" to "underperforming." The FTSE 100 Index fell 38 points, or 0.5%, to 7,149 points on Tuesday, reversing the 0.7% gain of the previous trading day, dragged down by healthcare stocks and brokerages. In addition, the “i” newspaper reported that the British government had made plans that if the hospitalization rate remains high, it may overburden the NHS. The country is about to enter the “prolonged peak” of infection. It will be “fired” in October. Prime Minister Boris Johnson also proposed raising taxes for workers, employers, and some investors to pay for social, medical expenses and the national health system. In terms of economic data, due to the weakening of most of the stamp duty holiday, house price growth in the UK slowed to a five-month low in August. In a single stock, Meggitt’s share price fell more than 12.1% after the US defense company TransDigm ruled out the possibility of acquiring this British competitor for $8 billion. On the other hand, DS Smith rose nearly 3% after raising its price target. The Standard & Poor's/Toronto Stock Exchange Composite Index edged higher, hitting a new high of 20,897.57 on the first trading day of the week, as investors were optimistic that the central bank would insist on loose monetary policy to continue to promote economic recovery. Financial, healthcare, and energy stocks rose sharply, while industrial stocks traded near the horizontal line. At the same time, since investors did not make major changes to monetary policy after cutting the stimulus plan in July, the focus of investors' attention will be on the Bank of Canada's interest rate decision tomorrow. The US stock market fell flat and began a week of shortened holidays. Investors worried about the spread of the Coronavirus Delta variant and the economic slowdown. At the same time, after the disappointing employment report was released last week, bets that the Fed may postpone the reduction of its stimulus plan increased. Traders are currently waiting for data on Thursday’s initial jobless claims and Friday’s producer price data for further updates on the U.S. economic recovery. On Tuesday, the Shanghai Composite Index rose 55 points or 1.51% to close at 3677 points, the highest closing point since February 19, due to news that China’s exports and imports both hit record highs in August and the trade surplus reached 7 Traders are optimistic about the highest level this month. Reports that China will further open its capital markets to foreign investors have boosted market sentiment. At the same time, the People's Bank of China recently stated that it would continue to improve monetary policy control and prudent macroeconomic policies. In Hong Kong, the stock market rose 0.84% and hovered close to a one-month high. Hong Kong leader Carrie Lam said that some residents from China and Macau would be allowed to enter the city without the quarantine on September 15 and relax. Strict border restrictions to contain the pandemic. The Nikkei index rose 256 points, or 0.86%, to close at 29,916 points, the highest closing point since April 4, as people hope that the new prime minister can accelerate Japan’s economic recovery. The index has risen for seven consecutive trading days, the longest winning streak since Joe Biden won the US presidential election in early November. According to reports, Fumio Kishida, a strong competitor to succeed cedar, has called for a more than 30 trillion yen stimulus plan. According to reports, a Japanese group suggested that if further progress is made in vaccination, some restrictions may be relaxed in the fall. . In the most recent data, Japan’s average cash income in July increased by 1% year-on-year, surpassing the generally believed 0.8% increase, and rising for the fifth consecutive month. After the SoftBank Group reached a strategic share swap with Deutsche Telekom, its share price rose 9.86%. At the same time, Murata manufacturing and robot manufacturer Keynes rose 5.5% and 4.91%, respectively, after announcing that they would join the index when the benchmark index is adjusted next month. The Australian Stock Exchange 200 index rose slightly by 2 points on Tuesday and was almost flat after falling in early trading. Earlier news reported that the number of daily infections of new coronary pneumonia in Sydney fell for the third consecutive day due to a surge in vaccination rates triggered by the epidemic. At the same time, officials promised that urban residents would gain more freedom once the vaccination rate first reaches 70% and then reaches 80%. In terms of policy, the Reserve Bank of Australia today kept the cash rate unchanged at a historic low of 0.1%, and at the same time confirmed its plan to reduce the amount of government bond purchases to A$4 billion per week, and decided to do so at least by mid-February 2022 Do. In the region, China's exports and imports hit a record high in August, bringing the trade surplus to its highest value in seven months. Locally, Australia’s service industry activity saw its first decline in 11 months in August, and the country’s building permits fell the most in four months. Holy Grail Mining Co., Ltd. rose 6.34%, and Regis Resources Co., Ltd. fell 4.6%. The S&P/NZX index rose 22 points, or 0.17%, to close at 13,322 points, setting a high of more than seven and a half months and rising for eight consecutive trading days after New Zealand said it would be “very close” to purchasing more coronavirus vaccines. The transaction may be announced later this week. On Monday, New Zealand Prime Minister Jacinda Arden relaxed nationwide restrictions, except for Auckland, the largest city. Previously, daily cases fell from a peak of 85 on August 29 to 20 on Monday. At the same time, it is reported that the Reserve Bank of New Zealand is considering raising interest rates by 50 basis points, and future policy decisions will not be closely related to lock-in. Globally, hopes that U.S. interest rates will remain low and discussions on more stimulus measures in Japan and China drove the longest winning streak in three months in global stock markets on Monday. Evolve Education Group, and Harmoney Corporation rose 7.04% and 4.98%, respectively.
• REVIEWING ECONOMIC DATA:
Looking at the last economic data:
- TW: In August 2021, Taiwan’s wholesale price inflation slowed to 11.88% year-on-year and rose by 12.29% in July, the highest increase since 1981. The cost of quarrying and mining products slowed down (56.95% and 63.98% in July); and manufacturing products (10.02% and 10.55%, respectively). On the other hand, prices of agriculture, forestry, fisheries, and animals have risen faster (18.07% and 11.79%, respectively), and water, electricity, and gas supply (3.46% vs. 0.63%).
- TW: Taiwan’s annual inflation rate rose from a downward revision of 1.92% last month to 2.36% in August 2021, higher than market expectations of 1.9%. Prices of food (3.84% in July and 2.45% in July) and housing (1.25% and 0.7% in July) have accelerated, and education and entertainment (1.1% vs. 0.85%). In addition, public utility prices rebounded (1.9% vs -5%); and health (0.15% vs -0.17%). On the other hand, the cost of transportation and communications (6.51% vs. 6.95%) and clothing (2.04% vs. 2.07%) has fallen. Seasonally adjusted monthly data shows that consumer prices rose 0.31% after rising 0.08% in July.
- TW: Taiwan’s trade surplus narrowed from US$6.5 billion in the same month of the previous year to US$3.5 billion in August 2021, which was lower than market expectations of US$6.7 billion. Exports increased by 26.9% year-on-year, reaching a record 39.55 billion U.S. dollars, higher than market forecasts of 23.5% growth. Sales growth was mainly based on base metals and base metal products (50.3%); plastic and rubber products (up 42.7%); machinery (up 39.6%); electronic product parts (up 21.9%); and information, communications, and audiovisual Products (up 17.2%). At the same time, imports increased by 46.3%, reaching a record high of 36.1 billion U.S. dollars, which also exceeded the 29.4% growth expected by the market. Larger purchases of mineral products (101.7%); base metals and base metal products (up 76.2%), machinery (up 64.8%), chemicals (up 43%), and electronic product parts (up% 36.28).
- US: The Logistics Managers Index was almost unchanged in July 2021, at 74.5, which shows that the logistics industry has the third-highest growth in history driven by the indicators of the entire index. The warehousing price index hit a record high (88 to 85.4 in June), mainly due to insufficient capacity. Inventory levels continue to rise at an above-average rate (66.4 vs. 67.8) because companies abandon the JIT principle and order large quantities in advance to avoid shortages. In addition, transportation prices increased (91 vs. 87.3) because the transportation network felt the pressure of excess inventory.
- EU: In the second quarter of 2021, the quarterly economic growth rate of the Eurozone was revised to 2.2%. After two consecutive periods of contraction, with the help of rapid vaccination against the new crown pneumonia, the Eurozone economy reopened, activities and domestic demand recovered. As a result, the district's quarterly economic growth rate has steadily picked up. Household consumption increased by 3.7% (-2.1% in the first quarter), and fixed investment increased by 1.1% (-0.2% in the first quarter). In addition, public spending increased by 1.2% (-0.5% in the first quarter), while net trade did not contribute to GDP growth because export growth was almost the same as import growth. However, changes in inventories reduced GDP by 0.2%. On an annual basis, the US economy grew by 14.3%, a record high, reflecting the low base year due to the flu pandemic.
- EU: In September 2021, the Eurozone’s ZEW Economic Confidence Index fell further by 11.6 points to 31.1. This is the lowest level since April 2020 due to concerns about global material shortages and other supply chain issues, and concerns about a slowing recovery. At the same time, indicators of current economic conditions in the Eurozone rose by 7.9 points to 22.5, while inflation expectations fell by 22.1 points to 20.1 in September.
- EU: The German ZEW Economic Confidence Index fell from 40.4 in August to 26.5 in September 2021, which was lower than the 30 market forecast. The index fell for the fourth consecutive month to its lowest level since the outbreak of the coronavirus crisis in March 2020. However, the assessment of the German economic situation increased to 31.9 from 29.3 in August. Current data show that Germany's economic growth rate will only be slightly higher than the current level in the next six months. "In September 2021, expectations have fallen again significantly. Although financial market experts expect the economic situation to improve further in the next six months, the expected improvement has been significantly reduced. The global automotive industry chip shortage and the construction industry’s building materials have led to these industries. As a result, the profit of ZEW is expected to drop sharply,” commented Professor Achim Wambach, President of ZEW.
- CN: Foreign exchange reserves fell from US$3.236 trillion in July to US$3.232 trillion in August 2021, slightly higher than the forecast of US$3.227 trillion. At the same time, the value of gold reserves fell from 114.37 billion U.S. dollars to 111.69 billion U.S. dollars.
- CN: In August 2021, China’s trade surplus was 58.34 billion U.S. dollars, higher than the market consensus of 51.05 billion U.S. dollars, while the surplus in the same period last year was 57.25 billion U.S. dollars. At a time when commodity prices are soaring, this is the largest trade surplus since January. Exports increased by 25.6% year on year, and imports increased by 33.1%.
- CN: In August 2021, China's imports increased by 33.1% year-on-year, exceeding market expectations by 26.8%. A month ago, China's imports increased by 28.1%. This marked the eleventh consecutive month of expansion in inbound transportation in the context of increased domestic demand.
- CN: In August 2021, China’s exports increased by 25.6% year-on-year, much higher than market expectations of 17.1%, and accelerated from 19.3% growth in June. Nevertheless, port congestion, sporadic cases of new coronary pneumonia, and higher commodity prices are the 14th consecutive month of growth in outbound transportation.
- UK: In August 2021, the Halifax House Price Index rose by 7.1% year-on-year to a record 262,954 pounds. This was the smallest increase in house prices since March due to most of the impact of the stamp duty holiday Has faded. However, other important drivers of rising house prices should continue to provide some support. "Halifax managing director Russell Galley (Russell Galley) said: "We believe that structural factors have driven record levels of the buyer activity, such as the need for more space in a larger family work environment. . "In addition, the macroeconomic environment is becoming more and more positive, the job vacancy rate is at a record high, and consumer confidence has returned to pre-pandemic levels. In addition, the supply of properties for sale seems to be getting tighter, and job support programs are added. When it is lifted later this year, unless lock-in measures are re-implemented, or the unemployment rate rises sharply, these factors should continue to support housing prices in the short term," he added.
- JP: Flash data shows that Japan's index of leading economic indicators fell from the final 104.6 to 104.1 in July, which is the highest value in the past seven and a half years. The index measures economic conditions in the coming months, compiled using data such as employment opportunities and consumer confidence. This decline reflects the slowdown in the country’s economic recovery, as the delta variant cases continue to increase, forcing the government to extend and expand the state of emergency.
- JP: Preliminary data show that due to the continuous damage caused by the coronavirus, Japan's economic indicator index over the same period, which is composed of a series of data such as factory output, employment, and retail sales, fell from 94.6 in the last month a month ago to 94.5 in July 2021.
- JP: In July 2021, Japanese household spending actually increased by 0.7% year-on-year, which was lower than the market’s forecast of a growth rate of 2.9%, and after a 5.1% drop in the previous month. Food expenditure (1.9% versus -1.6% in June), clothing expenditure (2.7% versus -15.1%), transportation and communications expenditure (14.2% versus -5.8%), and cultural and entertainment expenditure (1.7% versus -0.2%) There was a rebound. In contrast, housing expenditures declined (1.7% and 1%, respectively), fuel, lighting, and water costs (5.9% and 5.8%, respectively), furniture and home furnishings (8.4% and 21.7%, respectively), medical care (respectively 8.4% and 21.7%) 7% and 2.7%) and education (9.9% and 12.1%, respectively). Household spending unexpectedly fell by 0.9% month-on-month, lower than the consensus increase of 1.1%. It fell by 3.2% in July.
- AU: As is widely expected, the Reserve Bank of Australia kept the cash rate at a record low of 0.1% at its September meeting.
- AU: The Australian Industry Group’s Australian Service Performance Index fell from 51.7 in July to 45.6 in August 2021, a drop of 6.1 points. The latest data shows that the service industry has contracted for the first month since September 2020.
• LOOKING AHEAD:
Today, investors will receive:
- JPY: Bank Lending y/y, Current Account, Final GDP Price Index y/y, Final GDP q/q, and Economy Watchers Sentiment.
- EUR: French Final Private Payrolls q/q, French Trade Balance, Italian Retail Sales m/m, and German 10-y Bond Auction.
- AUD: RBA Deputy Gov Debelle Speaks.
- CAD: BOC Rate Statement, Ivey PMI, and Overnight Rate.
- GBP: Monetary Policy Report Hearings.
- USD: JOLTS Job Openings, IBD/TIPP Economic Optimism, 10-y Bond Auction, FOMC Member Williams Speaks, Beige Book, and Consumer Credit m/m.
• KEY EQUITY & BOND MARKET DRIVERS:
- U.S. 10-year government bond yield rises to a 7-week high of 1.38%.
- The Chinese stock market rose 54 points. Leading the gains were Huayu Automobile (5.1%), SAIC Motor (3.46%), and Guangzhou Automobile (3.16%).
- The Japanese stock market rose 238 points. Pacific Metals (9.21%), Donghe Zinc (8.63%), and Japan Exchange Group (4.01%) led the gains. The biggest losers are Toyo Seiko Group (down 15.37%), Nikko Bo (down 10.65%), and Asahi Glass (down 0.88%).
- After the disappointing employment report was released last week, investors were worried about the spread of the Coronavirus Delta variant and the prospect of an economic slowdown. At the same time, they were betting that the possibility that the Fed might postpone the reduction of its stimulus plan increased, so U.S. futures were shortened during the holiday. There was almost no change at the beginning of the week. Investors are currently waiting for data on Thursday’s initial jobless claims and Friday’s producer price index to learn more about the latest developments in the US economic recovery.
- US stock futures rose slightly on Tuesday, supported by hopes that US interest rates will remain low for a long time. Investors are still evaluating a weaker-than-expected US employment report. The report shows that the U.S. economy added 2.35 million jobs in August, far below the 750,000 jobs expected, because the surge of new crown virus-19 infections may hinder company recruitment and workers from actively looking for jobs. The data also shows that wages have risen sharply, which has exacerbated concerns about inflation. Elsewhere, speeches about more stimulus measures taken by Japan and China have boosted global sentiment.
• STOCK MARKET SECTORS:
- High: Consumer Discretionary, Communication Services, Information Technology.
- Low: Real Estate, Industrials, Utilities, Consumer Staples.
• TOP CURRENCY MARKET DRIVERS:
- GBP: On Tuesday, British Prime Minister Boris Johnson announced plans to raise taxes for workers, employers, and some investors to cover social, medical expenses and the National Health Service (NHS). The pound fell to $1.38. Johnson announced that the government would increase the national insurance payroll tax rate paid by workers and employers by 1.25 percentage points. The same increase will also apply to shareholder dividend tax. This move angered some in his ruling party because it violated election promises, and business groups warned that the plan would hit the economy and lead to fewer jobs. In terms of monetary policy, Michael Saunders, a policymaker at the Bank of England, said that if the economy continues to grow and inflation becomes more difficult, the central bank may need to raise interest rates next year.
- USD: The U.S. dollar index rose slightly to 92.4 on Tuesday, from a one-month low at the beginning of the month, and is tracking the rise in US Treasury yields. After the disappointing non-farm payrolls report was released, investors postponed expectations of the Fed to reduce bond purchases. The European Central Bank is expected to debate cut stimulus measures later this week.
- CAD: On Tuesday, due to the fall in crude oil futures prices, the Canadian dollar/U.S. dollar exchange rate fell back to 1.26, not far from the three-week high reached last week. The price of Canada’s main export product, oil, traded near a two-week low of US$68 per barrel due to concerns about weak demand in major Asian regions. Nevertheless, before the Bank of Canada made its monetary policy decision on Wednesday, traders mostly held a wait-and-see attitude, expecting policymakers to keep interest rates unchanged.
- AUD: The Australian dollar fell slightly to $0.742 on Tuesday after the Reserve Bank of Australia insisted on scaling back its bond purchase program, but due to the coronavirus lockdown that hit the economy, the program was extended to at least mid-February. Some investors had expected it to postpone the reduction altogether. Nevertheless, the U.S. dollar is still close to its highest level since mid-July. The previously weaker than expected U.S. employment data has cast doubt on the Fed’s plan to reduce its asset purchase policy. Domestically, recent optimistic economic data and faster COVID-19 vaccination support market sentiment. Last week's data showed that supported by strong domestic demand. The Australian economy avoided a technical recession in the second quarter. In contrast, other economic news showed that as exports hit a record high, the trade surplus in July hit a record high.
• CHART OF THE DAY:
The US dollar index has been trading at around 92.2 this week, close to a level that has not been seen in a month. After the disappointing non-agricultural employment report was released, traders suppressed expectations of the Federal Reserve to begin to reduce bond purchases. The U.S. economy only added 235,000 jobs in August, lower than the 750,000 expected by the market. The surge of new crown virus-19 infections may hinder company recruitment and workers' active search for jobs. At the same time, the increase in average hourly income was stronger than expected, raising concerns about inflationary pressures. Traders will also look for clues about the European Central Bank’s stimulus cuts when the European Central Bank decides on monetary policy later this week.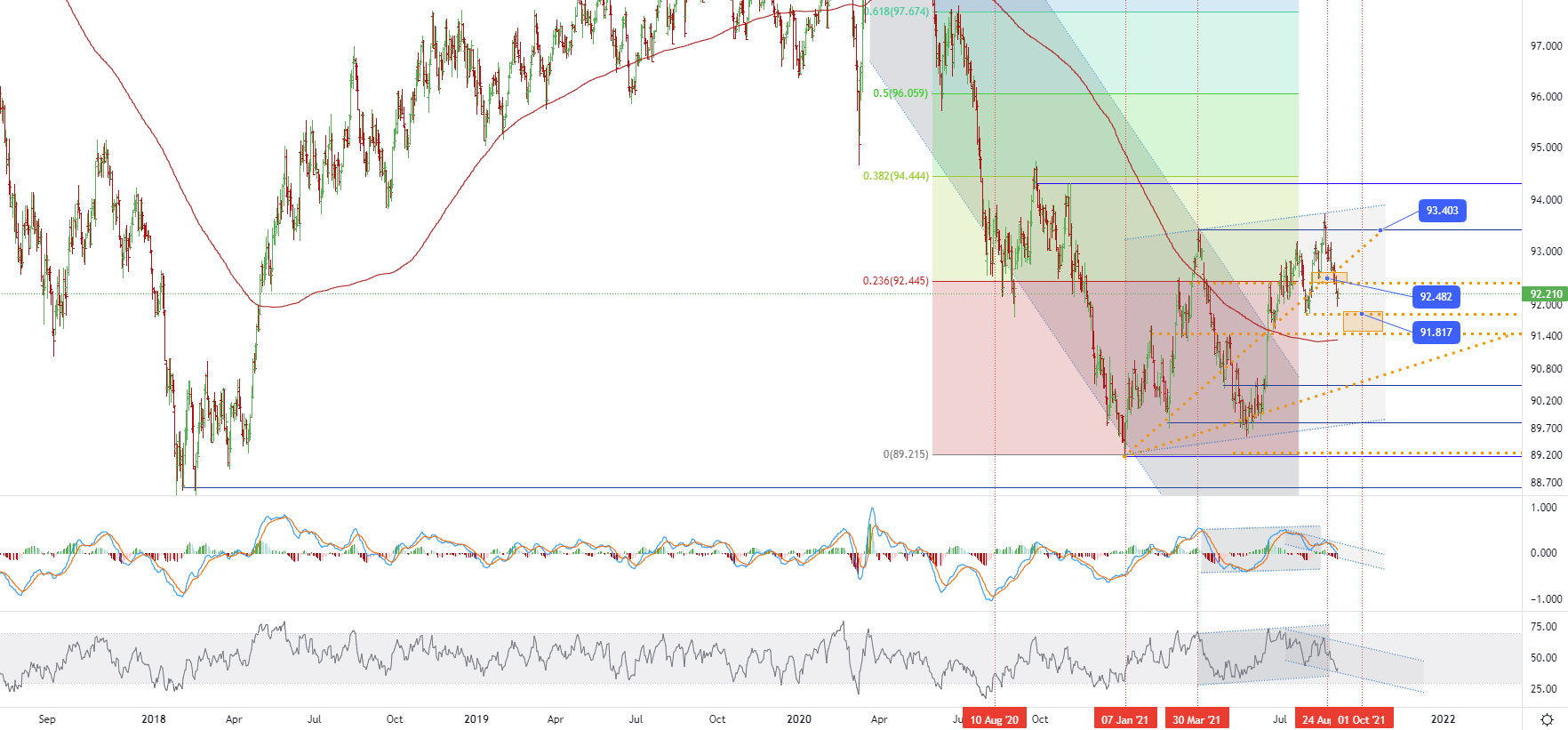 • US dollar index (DXY) - D1, Resistance around ~ 92.482 & 93.403, Support (target zone) around ~ 91.817
• US dollar index (DXY) - D1, Resistance around ~ 92.482 & 93.403, Support (target zone) around ~ 91.817
Demo account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account with virtual funds in a risk-free environment
Demo accountLive account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account in our transparent live model environment
Open an Account





