
U.S. indexes set intraday and closing record highs - mega-caps lead, cyclical stocks underperformed
• GLOBAL CAPITAL MARKETS OVERVIEW:
The three major U.S. stock indexes last week completed a roller-coaster finish within a record range. Investors dismissed concerns about the spread of the coronavirus delta infection variant. They turned to focus on the prospects of a strong global economic recovery and the continuation of central banks. Robust earnings reports from companies such as Twitter and American Express have also added to this optimism. In terms of data, the Markit Manufacturing PMI in July hit a record high of 63.1 again, easily exceeding market expectations, but price pressures and material shortages continued. Next week, when the Federal Reserve concludes its two-day meeting on Wednesday, everyone will focus on whether they are concerned about high inflation. Canada’s major stock markets closed higher last week, the S&P/TSX Composite Index closed at around 20,200, and high-growth technology stocks regained their foothold last week. In terms of economic data, preliminary data in June showed that retail sales increased by 4.4%, indicating that the Canadian retail industry has begun to recover after a two-month decline. On the company side, Westshore Terminals Investment Corp’s share price soared by nearly 30%, hitting a new index high. Before this, the company and BHP Billiton reached a conditional agreement on port services for the Canadian Jansen Potash Mine. European stock markets closed a roller coaster last week, with the benchmark DAX30 index closing above 15,600 points, as the prospect of economic recovery boosted cyclical stocks that had fallen behind earlier last week. The optimistic earnings report and another modest commitment from the European Central Bank (ECB) boosted sentiment across Europe to maintain a loose monetary policy for the foreseeable future. The European Central Bank will keep the pace of the quantitative easing program unchanged and maintain negative interest rates to support the eurozone economy until substantial progress is made in achieving the inflation target. In terms of economic data, following the recent reopening efforts, private sector activity in the eurozone has expanded by the most significant amount in 21 years. Driven by technology stocks, the FTSE 100 Index rebounded above 7000 points last Friday, ending last week's roller-coaster market. The prospects for global economic recovery are good, and central banks continue to provide support. In terms of data, retail sales in the UK increased by 0.5% in June, slightly higher than market expectations, and an increase of 9.5% compared to the level before the coronavirus pandemic in February 2020. Consumer morale rose to its highest level in 17 months in July, and the Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) survey showed a sharp slowdown in the growth of business activity in the UK. Last Friday, the Shanghai Composite Index fell 24 points to close at 3550 points, decreasing 0.7%. The previous trading day closed at a three-week high. Due to reports that floods in central China are threatening the commodity supply chain, traders are pessimistic. . The news that the number of first-time jobless claims in the United States unexpectedly rose to a two-month high in the last week also dragged down risk appetite; the Chicago Fed’s National Activity Index fell in June. In terms of policy, it is reported that the Central Bank of China will keep land and house prices stable because real estate loans have slowed after putting pressure on banks that support small businesses. Jiangsu Province in eastern China detected 12 new COVID-19 cases on Thursday, bringing the total to 23. This is the first localized outbreak since the flu pandemic last year. However, due to optimism that fiscal and monetary stimulus will continue to support economic recovery, the index rose 0.3% last week. Last Friday, the Australian Stock Exchange S&P/ASX 200 Index rose 9 points or 0.1% to close at a new high of 7394 points, reversing the early decline and rising 0.6% last week. Traders said when they followed the IMF on Thursday. The Federal Reserve is “very effective” in managing the COVID-19 crisis and supporting economic recovery, promising to exceed the 2% inflation target in the short term. The news that US second-hand home sales rose for the first time in five months in June also boosted market sentiment. On the 4th local time, British Prime Minister Scott Morrison apologized for the delay in the vaccination plan. At the same time, New South Wales today recorded the most significant one-day increase in new virus cases this year, prompting Sydney to tighten its lockdown. In business news, casino operator Star Entertainment Group withdrew its A$9 billion acquisition of rival Crown Resorts Ltd. Shares of Nickel Mines Co., Ltd. rose 6.5%, while Nuix Co., Ltd. rose 6%.
• REVIEWING ECONOMIC DATA:
Looking at the last economic data:
- US: Preliminary estimates show that the IHS-Markit U.S. composite PMI fell to 59.7 in July 2021, which is farther away from the record high in May. Production growth slowed to a four-month low, but overall remained strong as companies reported widespread capacity constraints. As a result, new business continued to grow steadily, and the growth rate of exports of goods and services was similar to that in June. In addition, due to labor shortages in the service industry, the rate of job creation has dropped to a four-month low. In terms of prices, the input cost inflation rate and sales price inflation rate in July was still at historical highs. Finally, due to increasing labor and material shortages, rising inflationary pressures, and fears about the flu pandemic, business confidence fell to a seven-month low.
- US: According to preliminary estimates, IHS Markit's U.S. service industry PMI fell from 64.6 last month to 59.8 in July 2021, far below market expectations of 64.8. The latest data show that due to labor shortages and difficulty in obtaining stocks, the growth rate of the service industry will slow further from the record high in May. New business growth was the lowest in five months, and some companies pointed out that customers were hesitant because of the sharp increase in sales prices. Similarly, the growth rate of new export orders has also slowed. Although companies have achieved steady growth in employment, the level of unfinished business in July rose further. In terms of prices, input costs and output costs continue to rise strongly. As a result, corporate confidence fell to a five-month low.
- US: The IHS Markit US Manufacturing PMI rose from 62.1 in June to 63.1 in July 2021, a record high. According to preliminary estimates, this number easily exceeded market expectations of 62. Supporting the overall growth is the rapid growth of new orders, as new customers and existing customers have increased their expenditures. Companies have also seen a substantial rise in demand from foreign customers. Despite further reports of material shortages, production is still growing at a slightly faster rate. Although the rate of job creation has accelerated to the highest level in three months, the backlog has risen to the second-fastest rate on record. At the same time, a delivery time has been significantly extended, and supply chain disruption is once again reflected in efforts to increase procurement activities and establish safety stocks. The strong global demand for inputs and the scarcity of materials has led to the fastest increase in cost burdens on record. Subsequently, the fee inflation rate accelerated to a new high.
- CA: In May 2021, Canadian retail sales fell 2.1% month-on-month, slightly lower than the market's forecast of 3% decline, because many retailers continue to face bankruptcy due to the third wave of the COVID-19 pandemic. The most significant declines were the distributors of building materials and garden equipment and supplies (-11.1%) and motor vehicles and parts (-2.4%). Sales at clothing and clothing accessories stores also fell (-11.2%), but sales at food and beverage stores rose by 0.8%.
- CN: In June 2021, Taiwan’s retail sales fell by 13.30% year-on-year, setting a record high. The previous month’s increase was 3.4%. This is the first contraction in retail activity since June 2020, and health authorities have extended lockdown measures to curb the surge in coronavirus infections. Sales of textiles and clothing further declined (-26.15% in May, down 53.90%); cultural and entertainment products (-38.38% vs. -20.09%); household appliances and commodities (-28.57% vs. -11.84%). The contraction in activities has also expanded to other categories, such as stores for automobiles, motorcycles, related parts and accessories (-22.95% vs. 6.26%); department stores (14.34% vs. 0.70%); and medicines, medical supplies, and cosmetics ( Respectively -11.09% and 10.12%). Retail sales fell 14.44% month-on-month and fell 5.23% in May.
- TW: Taiwan’s industrial production increased by 18.37% year-on-year in June 2021, after rising 16.88% in the previous month. This is the 17th consecutive month of expansion for the manufacturing industry and the most significant increase in industrial activity since January (17.69% in May, an increase of 20.20%). On the other hand, the output of mining and quarrying industries declined (-5.11% vs. 6.62%); water supply (-4.39% vs. -4.68%); electricity and natural gas supply (0.29% vs. 9.05%). As a result, industrial production increased by 2.57% on a seasonally adjusted monthly basis, which was little changed from the 2.54% increase in May.
- UK: Preliminary estimates show that the IHS-Markit/CIPS UK composite PMI fell from 62.2 last month to 57.7 in July 2021, which is far below market expectations of 61.7. The latest data show that the growth rate of business activity has slowed sharply, dropping to the lowest level since restrictions began to be loosened in March. New orders are growing at the weakest rate in five months. Some companies said that business and consumer confidence have declined due to the pandemic situation, while others continue to report export sales difficulties related to Brexit. Since March, employment growth has slowed to its lowest level, and survey respondents often cited the lack of candidates to fill vacancies and the unusually high number of employee turnovers. In terms of prices, input cost inflation hit a record high, and output costs rose steadily. Finally, business confidence fell to its lowest level since October 2020 because of concerns about the lasting impact of the flu pandemic.
- EU: Preliminary estimates show that the IHS-Markit Eurozone composite PMI rose from 59.5 last month to 60.6 in July 2021, higher than market expectations of 60.0. The latest data shows that as the Eurozone economy continues to reopen from the restrictions of COVID-19, private sector activity has seen its strongest growth since July 2000. The service industry output growth was the highest in 15 years, while the expansion of the manufacturing industry eased due to the deterioration of the supply line, but the overall growth remained strong. The growth rate of new orders in the manufacturing and service industries has reached the fastest level since May 2000, and the number of employees has also risen sharply. In terms of prices, input costs have risen at a near-record rate, while sales price inflation has eased from its peak in June. At the same time, concerns about delta variables have intensified, damaging business confidence and pushing market sentiment this year to a five-month low.
- EU: The IHS-Markit Eurozone manufacturing PMI fell from a record 63.4 in June to 62.6 in July 2021, compared to an expected 62.5. According to preliminary estimates, this is the lowest level since March. In many cases, the slowdown in growth is related to worsening supply lines and input shortages, although new orders are still increasing. In addition, the backlog of jobs has increased significantly, and employment growth has not changed much from the record in June. In terms of prices, input inflation has remained unchanged at historically high levels, and output costs have risen at a near-record rate.
- RU: In June 2021, Russian industrial production increased by 10.4% year-on-year, after the previous month’s revised increase of 12.3%, while the market expected an increase of 10.1%. Due to manufacturing (7.7% vs. 12.1% in May) and the slight increase in the output of electricity, natural gas, and steam, industrial output increased for the fourth consecutive month in June, although the growth rate has slowed compared to the previous month; Air conditioning (8.0% vs. 8.1%). On the other hand, the mining industry (15.8% vs. 12.6%) and the water supply industry (32.3% vs. 27.4%) have seen faster output growth. As a result, industrial production grew by 1.1% on a monthly basis, rebounding from a decline of 1.7% in May.
• LOOKING AHEAD:
Today, investors will receive:
- USD: New Home Sales.
- NZD: Trade Balance.
- JPY: Flash Manufacturing PMI, and BOJ Core CPI y/y.
- EUR: German Ifo Business Climate.
- GBP: MPC Member Vlieghe Speaks.
• KEY EQUITY & BOND MARKET DRIVERS:
- The DOW Index rises to a 10-week high of 35091 points.
- Stockholm rises to its highest point in 23 years at 2369.
- The French stock market rose 38 points. The driving force for the rise came from Valeo (7.24%), Airbus (3.10%), and ArcelorMittal (2.02%). The biggest losses came from Sanofi (-0.27%) and Dassault Systèmes (-0.21%).
- The Chinese stock market fell 24 points. Fuyao Glass Industry (-3.49%), Qingdao Haier (-3.19%), and Guangzhou Baiye (-3.03%) led to the decline. To offset the decline, the top gainers were Metallurgical (10.06%), Power Company (7.88%), and Great Wall Motors (6.19%).
- Most major Asian stock markets fell on Friday, adversely affected by the COVID-19 delta variables. There were reports that the number of first-time jobless claims in the United States each week unexpectedly rose to a two-month high. Hong Kong stocks (1.1%) and China (0.6%) caused losses, and there are reports that floods in central China threaten the commodity supply chain. However, supported by earnings optimism, the South Korean stock market rose slightly by 0.1%, rising for the second consecutive trading day. The asx200 index closed little changed, and the Japanese stock market was closed for national holidays.
- The Central Bank of Russia raised its benchmark policy rate by 100 basis points to 6.5% again at its July meeting. The reason was that inflation expectations were too high, and the balance of risks shifted to promote inflation, which may cause inflation to deviate from the 4% target for a more extended period. The central bank also pointed out that the Russian economy has reached the pre-pandemic level in the second quarter of 2021. Therefore, policymakers will also consider further increasing key interest rates at the upcoming meeting. According to the latest forecast by the central bank, the annual inflation rate in 2021 will reach 5.7%-6.2%, and will slow to 4.0%-4.5% in 2022, and will continue to remain at a level close to 4% in the future.
- US futures rose on Friday, rising for the fourth consecutive trading day, led by technology stocks, and investors' attention turned to strong company performance. American Express, Honeywell, and Kimberly Clark are scheduled to report before opening today. On Thursday, Twitter announced strong results, and Intel’s reported supply tightness offset optimistic earnings and revenue. Last week, the three major stock indexes were expected to record an uptrend, rebounding from the sell-off triggered by concerns about the mutation of the coronavirus delta and the slowdown in global economic growth earlier last week.
- The U.S. benchmark 10-year Treasury bond yield was about 1.28% last Friday and fell to 1.23% the previous trading day. A disappointing debt report raised further concerns about the strength of the economic recovery and auctioned 10-year inflation. Strong demand for hedge securities has produced record low yields. However, the market was volatile last week, with benchmark yields ranging from 1.317% to 1.128%. Investors weighed the impact of the spread of the new coronavirus delta variant on the global economy and mixed US economic data. In the absence of further catalysts, attention is now turning to the Fed's monetary policy decision next week. Earlier this month, Fed Chairman Powell stated that there is still a long way to go in achieving full employment and stable prices. He also hinted that the Fed is not even close to tightening its policies and that the inflation rate will be in the numbers. It stays high during the month before it slows down.
- Despite the sell-off on Monday, European stock market futures opened up again on Friday, ending the week's small gains. Investors welcomed a batch of solid corporate performance last week and signs of longer-term stimulus by the European Central Bank (ECB). In terms of economic data, the PMI surveys in the Eurozone, the United Kingdom, and the United States will reflect the global economic situation in July for the first time. In addition, investors will pay close attention to any signs of continued price pressures.
• STOCK MARKET SECTORS:
- High: Communication Services, Health Care, Consumer Staples, Utilities.
- Low: Energy.
• TOP CURRENCY MARKET DRIVERS:
- USD: The U.S. dollar index continued its upward momentum, approaching the 4-month high of 93.19 hits on Wednesday. Due to market concerns about the further spread of the Delta-COVID-19 variant, demand for safe-haven assets remains strong. In addition, although people are increasingly worried about the recovery of the US economy, compared with other countries, the growth rate of the US economy is still much stronger. From a deeper perspective, the Fed has substantially raised its inflation expectations for this year and raised interest rates earlier. As a result, the US dollar has strengthened since mid-June.
- CAD: The Canadian dollar was steady at 1.26 yuan/US dollar against the US dollar on Friday and rebounded earlier last week due to a recovery in risk appetite. Last week, concerns about the resurgence of the global coronavirus infection triggered global risk aversion, which caused the index to fall to a 5-month low. However, investors now seem to imply that due to the high vaccination rate In the country, the hospitalization rate and death rate for COVID-19 are still shallow, and this decline may be overdone. In terms of data, retail sales fell 2.1% month-on-month in May, slightly lower than the 3% drop expected by the market.
- RUB: After hitting a two-month low of $75.35 on July 8, the Russian ruble closed at $73.6 after the Central Bank of Russia raised interest rates by 100 basis points to 6.5% and allowed further interest rate hikes if necessary. According to the latest forecast by the central bank, the annual inflation rate in 2021 will reach 5.7%-6.2%, and will slow to 4.0%-4.5% in 2022, and will continue to remain at a level close to 4% in the future. At the same time, investors continue to monitor the surge of coronavirus cases at home and abroad, although oil prices have recovered from the decline earlier this week. The benchmark Brent crude oil traded at around US$73.5 per barrel after the previous sell-off pushed oil prices to a two-month low of less than US$68.
- EUR: The euro is still below $1.18 this weekend, hovering near its lowest point since early April. The market expects the European Central Bank to remain dovish for a while and worry about the spread of delta variants. On Thursday, the European Central Bank pledged to maintain interest rates at record lows for a more extended period to bring the inflation rate back to the 2% target. In addition, European Central Bank President Lagarde warned about the new coronavirus pandemic and its impact on economic recovery Influence. This news pushes interest rate hike expectations further into the future, as the European Central Bank predicts that the inflation rate will be below 2% at least until 2023.
- AUD: The Australian dollar traded at approximately US$0.74 in the third week of July, the lowest level since late November 2020. The US dollar generally strengthened. However, due to the rapid spread of delta variants and concerns about global economic growth, the Australian dollar turned to safety. British Prime Minister Scott Morrison apologized for the delay in the COVID-19 vaccination program, and Finance Minister Josh Frydenberg said the latest lockdown could cost about A$300 million a day. According to the latest data, preliminary estimates indicate that the contraction in Australia's service industry activity in July was the largest in 14 months, while factory growth slowed to a 4-month low.
• CHART OF THE DAY:
The FTSE MIB index closed up 320 points, or 1.1%, to 25,125 points on Friday. Although it fell 3.3% on Monday, it still rose 2% last week, which was in line with its European counterparts, thanks to the good earnings season and the European Central Bank. The guarantee of an ultra-loose stance. Driven by Intel’s optimistic earnings, STMicroelectronics shares rose 2.8%, becoming one of the best-performing stocks of the day. In Italy, starting on August 6, access to indoor services will require a digital COVID-19 certificate. In terms of the pandemic, the country’s infection and incidence rates have risen sharply, especially among young people. However, the number of COVID-19 hospitalizations is still deficient, and all regions should remain in the white zone.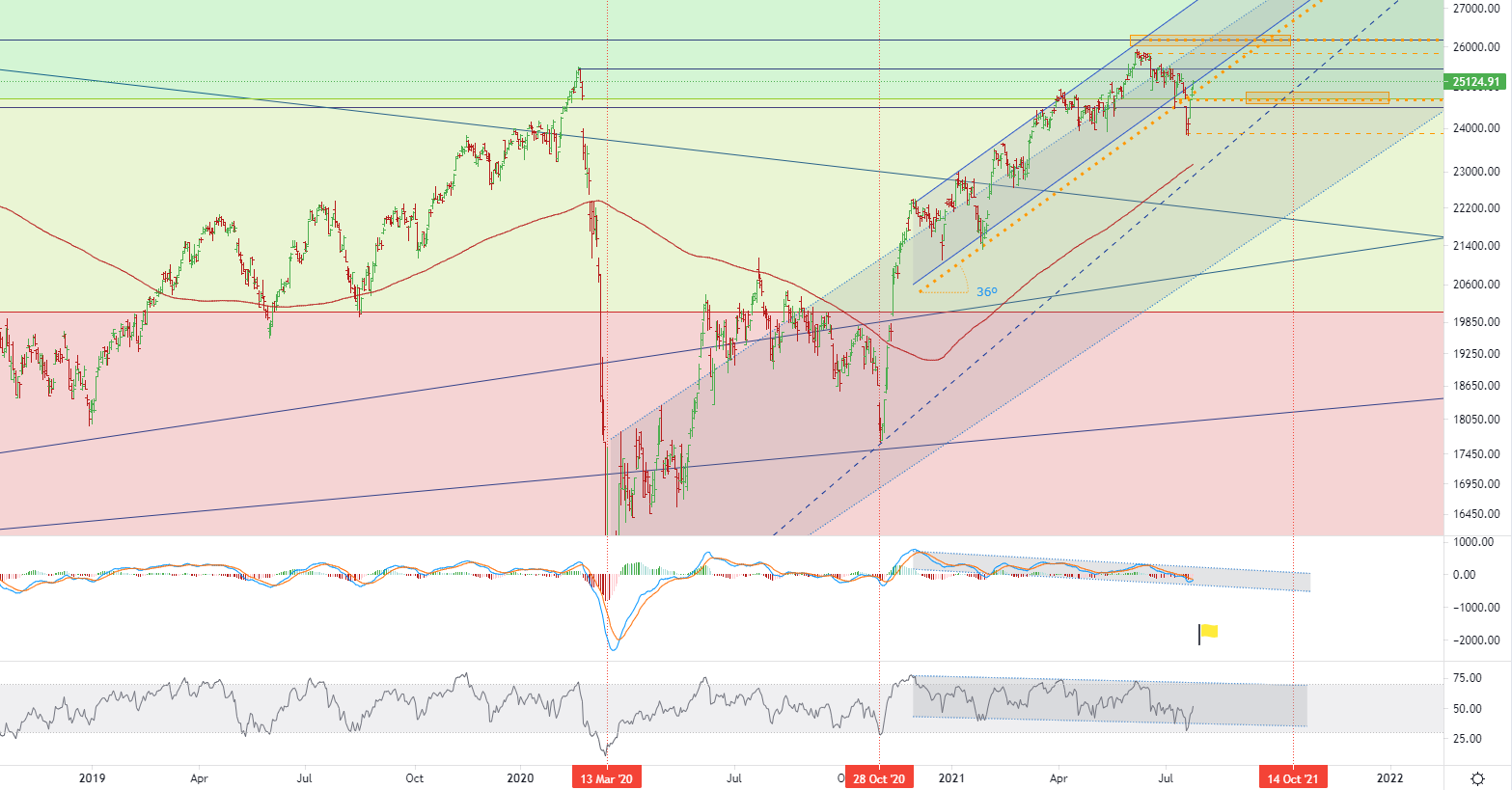 • Italian FTSE MIB index - D1, Resistance around ~ 26178, Support (target zone) around ~ 24800.
• Italian FTSE MIB index - D1, Resistance around ~ 26178, Support (target zone) around ~ 24800.
Demo account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account with virtual funds in a risk-free environment
Demo accountLive account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account in our transparent live model environment
Open an Account





