
S&P500 flat, growth stocks rallying - weak commodities, US10-yr yield trades below 1.50%
• CAPITAL MARKETS OVERVIEW:
European stock markets closed basically flat on Thursday, and the benchmark DAX index was hovering near record levels. Investors' optimism in the region’s economic recovery contrasted with the hard-line comments of the US Federal Reserve. The Federal Reserve hinted that it might raise interest rates as early as 2023, faster than initially thought. Chairman Jerome Powell said that it has also had preliminary discussions on the gradual reduction of bond purchases. This change in outlook has triggered a sell-off on Wall Street, especially those economically sensitive industries that rebounded recently. However, in Europe, this statement is a bit different. The European Central Bank took a wait-and-see attitude after its June meeting. European Central Bank President Lagarde said that monetary and fiscal stimulus measures should remain unchanged until the economy recovers further. The FTSE MIB index fell 54 points, or 0.2%, to close at a one-week low of 25,714 points. It was a mixed day for the European market. Investors have digested the tough signals sent by Fed officials. Fed officials are considering starting as early as 2023. The interest rate hike is at least one year ahead of the previous deadline. On the company side, Stellattis rose 0.3%. According to news, European car sales in May increased by 74% year-on-year to 892,000 units. The French-Italian automaker seized 22.4% of the market share. In terms of the flu pandemic, Italy will lift the mandatory curfew in most areas from next week, and the Italian government plans to abolish the mandatory wearing of masks by mid-July. The Canadian stock market was under pressure on Thursday. The S&P/TSX Composite Index fell from a record high to around 20150 points, and heavyweight commodity stocks dragged down the index. Dragged down by gold producers tracking price declines, the materials sector led the decline by nearly 4%, while heavyweight energy stocks also followed the decline in oil prices. In terms of data, the latest data from the ADP Canadian National Employment Report shows that from April to May, Canadian jobs increased by 101,600. Yamana Gold Inc. and First Majestic Silver Corp. fell 8% and 7.8%, respectively, and were the two companies that fell the most on the Toronto Stock Exchange. There was little change in the US stock market on Thursday, as investors digested the Fed’s tougher tone and higher-than-expected claims numbers. The number of people applying for unemployment benefits for the first time rose to 412,000, the first increase in 7 weeks. Compared with the expected 359,000, this shows that the labor market still has a long way to go before it can recover from the coronavirus. The Fed will reduce its support for the stimulus plan slowly and cautiously. Policymakers now expect two interest rate hikes by the end of 2023, and discussions about curtailing bond purchases may begin soon. In addition, the central bank’s latest forecast shows that despite the slowdown in price pressures in 2022, the inflation rate will continue to soar this year. On the corporate side, bank stocks such as JP Morgan Chase performed well, as the market hoped that interest rate hikes would boost bank profits, and DuPont was one of the top decliners in the Dow Jones Index. On Thursday, the Shanghai Composite Index rose 7.28 points or 0.21% to close at 3525.6 points, ending its three consecutive trading days of decline. Earlier reports stated that China’s national planner approved 5 fixed asset investments worth 74.9 billion yuan. Data released on Wednesday showed that the growth rate of Chinese factory output slowed for the third consecutive month in May, and the growth rate of retail sales and investment was also lower than market expectations. Traders paid little attention to this. On the global front, the Fed hinted on Wednesday that as the economy further recovers from the pandemic, the Fed may act sooner than originally planned and begin to withdraw its low-interest-rate policy. Policymakers said they would raise their benchmark interest rates twice before the end of 2023. According to Reuters, just as Didi is pushing for an IPO in the United States this year, Chinese market regulators have begun an antitrust investigation of Didi. At the same time, the Hang Seng Index rose 47.38 points to close at 28,484.22 points, an increase of 0.17%. The Nikkei 225 index fell 272.68 points on Thursday to close at 29018.33 points, a decrease of 0.93%, continuing the 0.51% decline of the previous trading day and further falling from the 5-week high due to the Federal Reserve (Federal Reserve) adjustment. It is tougher, and the time frame for raising interest rates has been advanced, and risk sentiment has deteriorated. In local news, the Japanese government will decide on Thursday to end the COVID-19 emergency covering Tokyo, Hokkaido, Osaka, and six other prefectures, while maintaining Okinawa for another three weeks. Local data show that due to strong global demand helping the country gradually recover from the coronavirus pandemic, the Reuters Tanken Index rose 1 point to 22 points from the previous month, the highest level in more than two years.
• REVIEWING ECONOMIC DATA:
Looking at the last economic data:
- RUB: In May 2021, the Russian producer price index rose by 35.3% year-on-year, higher than the 27.6% increase in the previous month. This is the largest increase in producer prices since the beginning of the series in 2005. The upward pressure comes from manufacturing (25.6%), raw material extraction (9.9%), electricity, gas, steam, and air-conditioning (5.3%), and water supply ( 3.8%). The producer price index rose by 2.3% on a monthly basis, following the 2.7% increase in April.
- USD: The Philadelphia Federal Reserve Manufacturing Index fell from 31.5 in May to 30.7 in June 2021 in the second month, compared with a market forecast of 31. Despite this, the index still shows that manufacturing activity in the region continues to grow. The indicators of new orders (22.2 to 32.5) and shipments (27.2 to 21) are still rising, despite mixed changes. In addition, the employment index rose (30.7 vs. 19.3), while the paid price index rose (80.7 vs. 76.8) and the acceptance price index rose (49.7 vs. 41). Most future indicators have improved, indicating that more companies expect overall growth in the next six months. The future diffusion index of general activities increased by 17 points from May, reaching 69.2, the highest level in the past 30 years.
- USD: In the week ending June 12, the number of new applications for unemployment benefits in the United States rose to 412,000, the first increase after six consecutive weeks of decline. Nevertheless, due to the wider economic reopening and the gradual cancellation of benefits, the total number of claimants is still close to last week’s pandemic lows. It is expected to decrease further in the coming weeks. This week’s report reflects that all states in the United States implemented comprehensive federal unemployment relief programs during the last investigation. Alaska, Iowa, Missouri, and Mississippi became the first to reduce federal support before the official deadline in September. State. Large and small businesses have been complaining about the difficulty of recruiting workers because the improvement in welfare has led to a continuous shortage of labor, and they are worried about contracting the COVID-19 virus and finding childcare.
- CAD: Foreign investors bought 10 billion Canadian dollars of Canadian securities in April 2021. This is their ninth consecutive month of net purchases. The withdrawal of private corporate bonds has eased investment in government bonds. After withdrawing 7.9 billion Canadian dollars in March, non-resident investors increased their holdings of Canadian bonds by 5.5 billion Canadian dollars in April. Foreign investment in federal government bonds reached 8.4 billion Canadian dollars, the largest investment in a year. The previous four consecutive months of withdrawals totaled 12.8 billion Canadian dollars. In addition, foreign investors purchased 3.9 billion Canadian dollars in provincial government bonds and issued new dollar-denominated instruments. In contrast, foreign holdings of private corporate bonds fell by 5.8 billion Canadian dollars in April. On the other hand, Canada’s total investment in foreign securities in April was 18.6 billion Canadian dollars, the 12th consecutive month of investment, mainly in the acquisition of US securities.
- EUR: In May 2021, the consumer price inflation rate in the Eurozone was confirmed to be 2.0%, the highest level since October 2018. The reason was that the base year was low, reflecting a sharp rebound in demand after the reopening of the economy. The upward pressure comes from energy (11.1% vs. 10.4% in April), service industry (1.1% vs. 0.9%) and non-energy industrial products (0.7% vs. 0.4%). On the other hand, the growth rate of food, alcohol, and tobacco costs was slightly slower (0.5% and 0.6%, respectively). At the same time, the annual core inflation rate after excluding fluctuations in energy, food, alcohol, and tobacco prices rose to 1.0% from 0.7% in April. On a monthly basis, consumer prices rose by 0.3%.
- EUR: Eurozone construction output jumped 42.3% in April 2021, after rising 20% in March, mainly due to the low base year effect. Construction activity began to shrink at a record rate a year ago when the pandemic crisis The impact of this is beginning to show. This is the largest increase in construction output since records began in January 1996.
- GBP: The FTSE 100 Index fell about 0.3% on Thursday from yesterday’s 16-month high. Mining companies performed the worst. The Federal Reserve’s unexpectedly tough tone hit commodity prices, and the U.S. dollar strengthened. The Fed has advanced its first interest rate hike expectations to 2023, and Fed Chairman Jerome Powell said it has also negotiated how to end bond purchases during the crisis. On the other hand, banks are rebounding due to improved profitability.
- EUR: In May 2021, the number of passenger car registrations in the EU increased by 53.4% year-on-year to 891,665, which is still far below the 1.2 million in May 2019. Sales in the national market grew strongly, with Spain increasing the most (+177.8%). The other three major EU automotive markets also performed well in May: France +46.4%, Italy +43.0%, and Germany +37.2%. From January to May 2021, the EU's demand for new cars increased by 29.5% to 4.3 million.
- NZD: The New Zealand dollar moved 0.0042 points or 0.6% to 0.70898 against the U.S. dollar on Thursday, rebounding from a 10-week low hit earlier this week. For the three months ending in March 2021, New Zealand’s GDP grew by 1.6% quarter-on-quarter, outpacing the market. Expected 0.5%. In the United States, officials from the Federal Reserve have sharply raised their inflation expectations for this year and brought interest rate hikes earlier. The local 10-year bond yield soared to a weekly high of 1.801%, while the U.S. 10-year bond yield was 1.575%.
- NZD: For the three months ending in March 2021, New Zealand's gross domestic product (GDP) increased by 1.6% month-on-month, which was revised to a contraction of 1.0% in the previous period, while the market expected a 0.5% increase. The service industry accounted for about two-thirds of New Zealand’s economy and grew by 1.1% after growing 0.2% in the previous quarter. In addition, primary industries (0.3% vs -0.8%) and commodity production (2.4% vs -3.1%) both rebounded. On an annual basis, GDP grew by 2.4% after shrinking by 0.8%.
- NZD: New Zealand’s economy in the first quarter of 2021 grew by 2.4% year-on-year, rebounding from the previously revised contraction of 0.8%, while the market is expected to grow by 0.9%. This is the strongest expansion since the third quarter of 2019.
- AUD: In May 2021, Australia’s seasonally adjusted unemployment rate unexpectedly reached 5.1%, while the market generally believes that the unemployment rate in the previous months was 5.5%. This is the lowest unemployment rate since February 2020, as the US economy has further recovered from the COVID-19 crisis.
- JPY: As strong global demand helped Japan gradually recover from the coronavirus pandemic, Japan's Reuters Tanken Index rose 1 point from the previous month to 22 points in June 2021, the highest level in more than two years.
• LOOKING AHEAD:
Today, investors will receive:
- JPY: National Core CPI y/y, Monetary Policy Statement, BOJ Policy Rate, and BOJ Press Conference.
- EUR: German PPI m/m, Current Account, and ECOFIN Meetings.
- GBP: Consumer Inflation Expectations, and Retail Sales m/m.
• KEY EQUITY MARKET DRIVERS:
- The U.S. 30 Index fell to a 4-week low of 33,780 points.
- HK$50 fell to a 4-week low of HK$28,195.
- US futures trading fell on Thursday, as investors digested the Fed’s tougher tone and higher-than-expected claims figures. The number of people applying for unemployment benefits for the first time rose to 412,000, the first increase in 7 weeks. Compared with the expected 359,000, this shows that the labor market still has a long way to go before it can recover from the coronavirus. The Fed will reduce its support for the stimulus plan slowly and cautiously. Policymakers now expect two interest rate hikes by the end of 2023, and discussions about curtailing bond purchases may begin soon. In addition, the central bank’s latest forecast shows that despite the slowdown in price pressures in 2022, the inflation rate will continue to soar this year. On Wednesday, the three major U.S. stock indexes fell further. The Dow Jones Index fell 266 points to 34034 points, a decrease of 0.8%; the S&P 500 Index fell 23 points to 4224 points, decreasing by 0.5%. The Nasdaq, which is dominated by technology stocks The index fell 33 points to close at 14,040 points, decreasing by 0.2%.
- The yield on the benchmark 10-year U.S. Treasury note fell slightly to 1.56% on Thursday, after data showed that the number of new jobless claims in the United States unexpectedly rose for the first time in seven weeks. Despite this, the yield was still much higher than the three-month low of 1.428% hit last Friday. After the Federal Reserve raised its PCE inflation forecast for this year by 1 percentage point to 3.4% and accelerated the pace of policy tightening expectations, the market Worries about uncontrolled inflation are growing. Nevertheless, as price pressures are expected to slow next year, the March yield is still well below the one-year high of 1.78%. The Fed expects PCE inflation rates to be 2.1% and 2.2% in 2022 and 2023, respectively.
- The yield on British 10-year government bonds soared to 0.81%, the highest level since June 7. The Federal Reserve has advanced the time frame for the first interest rate hike after the pandemic. Chairman Jerome Powell said Preliminary negotiations had been held to reduce bond purchases gradually. In other respects, economic data released earlier this week showed that the inflation rate in the UK rose more than expected in May, reaching the highest level since July 2019, higher than the Bank of England’s 2.0% target.
- The benchmark Japanese 10-year Treasury bond yield jumped to 0.064% in mid-June, which is much higher than the 5-month low of 0.024% hit earlier, and it follows the Federal Reserve's tougher tone and accelerated policy tightening expectations. After the pace, U.S. Treasury yields have risen. The Fed expects to raise interest rates twice by the end of 2023 and raise its inflation and growth expectations for this year. At the same time, the Bank of Japan expects to maintain the short-term interest rate target at -0.1% in June and the 10-year yield target at around 0%. In Japan, the macroeconomic situation is slightly different from that of the United States because inflation is falling, and GDP is struggling to recover from the impact of the coronavirus due to slow vaccine launches and the resurgence of infection.
- German 10-year government bond yields jumped to -0.15% on Thursday, the highest level since May 25, after the Federal Reserve hinted that its rate of interest rate increase might far exceed many people's expectations. The central bank’s forecast shows that 11 of the 18 officials will see interest rates rise in 2023, compared with only 6 before, and 7 others are expected to raise interest rates for the first time in 2022. In addition, Chairman Jerome Powell said at a press conference that he also initially discussed the gradual reduction of bond purchases.
• STOCK MARKET SECTORS:
- High: Information Technology, Communication Services, Utilities.
- Low: Financials, Materials, Industrials, Energy.
• TOP CURRENCY MARKET DRIVERS:
- CAD: The Canadian dollar against the U.S. dollar continued to fall to 1.23 yuan per U.S. dollar at the end of the third week of June, the lowest exchange rate since late April 2021. Traders believe that the Federal Reserve is announcing its plan to raise interest rates by 2023. After catching up with the hawkish stance of the Bank of Canada, the plan was at least one year ahead of the previous plan and began to discuss the gradual reduction of bond purchase plans. The Bank of Canada is the first central bank in an advanced economy to slow down the pace of weekly government bond purchases, and traders now expect the next reduction to take place at the next monetary policy meeting on July 14.
- USD: The Fed sharply raised its inflation expectations this year and advanced the timing of interest rate hikes. The US dollar index expanded its gains to an 8-week high of 91.8 on Thursday. This change in outlook benefits bullish investors, who expect the central bank to consider reducing quantitative easing policies to prevent the US economy from overheating. Nevertheless, the new economic data still requires caution. The number of first-time jobless claims rose to 412,000 for the first time in 7 weeks, retail sales fell by 1.3%, and both consumer and producer inflation showed that price pressures were increasing. The data shows that the economy is recovering, although a full rebound from the pandemic shock may take some time and will depend on monetary and financial support
- RUB: The Russian ruble exchange rate against the US dollar is 72.6, mainly due to the hawkish signal from the Federal Reserve that the US dollar strengthens. However, US President Biden and Russian President Vladimir Putin agreed to start cybersecurity and arms control negotiations at their first meeting in Geneva, highlighting the differences between the two sides on these issues, human rights, and Ukraine. The 71.5% that Zhou touched, the strongest since July 2020, is still not far away. The geopolitical discount of the ruble is still huge because in April 2019, the oil price, one of the main drivers of the ruble exchange rate, was close to the current level of around US$74.5 per barrel, and the ruble-to-dollar exchange rate was around US$65. Last week, the Russian Central Bank raised interest rates for the third time this year and said it would further tighten monetary policy at an upcoming meeting. After economic data showed that Russia’s annual consumer price inflation accelerated, policymakers expressed concern about increasing inflationary pressures
- GBP: The pound fell below the $1.40 mark, hitting its lowest level since May 9, as investors turned to the U.S. dollar after the Federal Reserve (Fed) signaled an interest rate hike earlier than expected. Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell said Negotiations have also been conducted on ending the emergency bond purchase. In other respects, investors digested key UK economic data, the UK-Australia trade agreement, and the postponement of the UK's plan to relax the blockade. The UK consumer price inflation rate jumped to 2.1% in May, higher than the Bank of England’s target of 2.0% and the highest level since July 2019. As the UK economy reopens from the lockdown caused by the coronavirus, inflationary pressures will increase. It will increase further in the coming months. The British labor market continues to consolidate the momentum of recovery. In May, the number of employees on the company's payroll increased at a record rate. In the year to April, wage growth reached the fastest level since 2007.
- AUD: In early trading in the Asia-Pacific region on Wednesday, the Australian dollar was quoted at 0.76131 against the US dollar, a 9-week low. Earlier, the Federal Reserve set a tougher tone and advanced the time frame for raising interest rates. At the same time, traders are also waiting for further signs of when the Bank of Australia and the Bank of New Zealand will withdraw from the stimulus plan. The minutes of the June meeting released by the Bank of Australia earlier this week showed that policymakers believed that the economic expansion was faster than previously expected while insisting that interest rates will remain at historical lows by 2024. Reserve Bank Governor Phil Lowe US lenders are warned to maintain lending standards because of the skyrocketing housing prices while suppressing expectations of strong wage growth after the coronavirus pandemic. The market predicts that the unemployment rate will stabilize at 5.5%, and employers will add 30,000 jobs.
• CHART OF THE DAY:
German benchmark DAX index was hovering near record levels. Investors' optimism in the region’s economic recovery contrasted with the hard-line comments of the US Federal Reserve. The Federal Reserve hinted that it might raise interest rates as early as 2023, faster than initially thought. Chairman Jerome Powell said that it has also had preliminary discussions on the gradual reduction of bond purchases. This change in outlook has triggered a sell-off on Wall Street, especially those economically sensitive industries that rebounded recently. However, in Europe, this statement is a bit different. The European Central Bank took a wait-and-see attitude after its June meeting. European Central Bank President Lagarde said that monetary and fiscal stimulus measures should remain unchanged until the economy recovers further.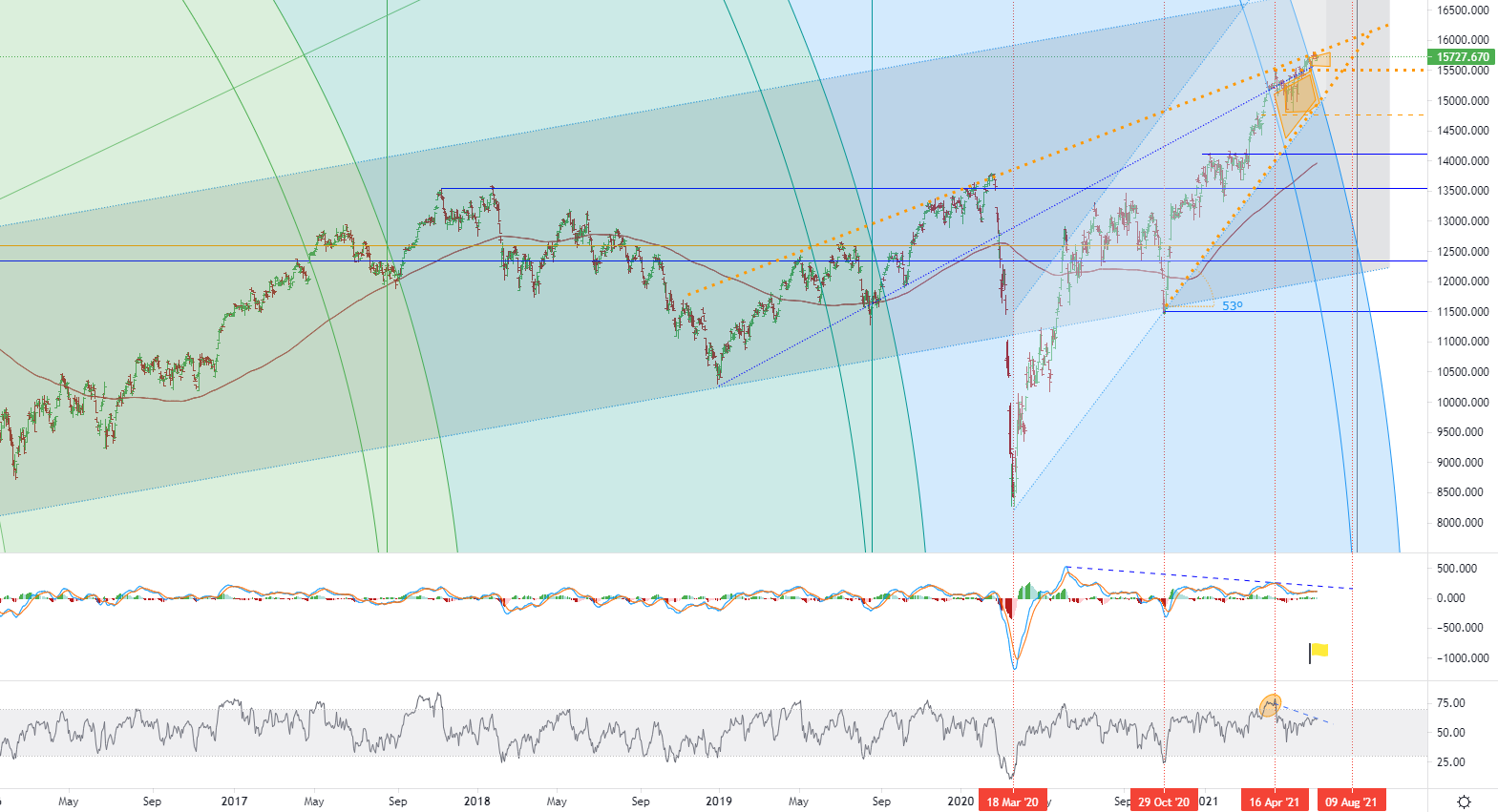
• German DAX index - D1, Resistance (target zone) around ~ 15900, Support (consolidation) around ~ 15538.
Demo account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account with virtual funds in a risk-free environment
Demo accountLive account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account in our transparent live model environment
Open an Account





