
European stock markets rose, S&P 500 and Nasdaq index fell from record highs, Asia - mixed
• CAPITAL MARKETS OVERVIEW:
European stock markets rose for the eighth consecutive trading day on Tuesday, and the Stoxx 600 Index closed at a record level, setting a record for the longest winning streak in more than two years. The market continues to benefit from the upward momentum in the past few weeks. Investors are optimistic about the euro zone’s economic recovery due to the latest reopening efforts and the rapid pace of coronavirus vaccination. Elsewhere, investors are waiting for hints from the Federal Reserve meeting this week on the outlook for inflation and bond purchases. Domestically, the benchmark DAX further marched towards green, setting a new historical high. The FTSE MIB index closed down 21 points or 0.1% on Tuesday to close at 25736 points, which is still close to the 13-year high reached last week. Market sentiment is cautious. The market expects Fed policymakers to comment on the outlook for tightening and consumer prices. In terms of data, supported by the cost of transportation, housing, and public utilities, consumer prices in Italy rose at the fastest rate in two and a half years in May. On the company side, Atlantia performed best, rising 3.6%. Traders welcomed its new dividend policy. The dividend distribution of the policy was 600 million shares for the 2021 fiscal year. At the same time, it plans to buy back up to 2 billion shares. On the other hand, Italgas has hardly changed after the release of its 2027 strategic plan. The plan is expected to invest USD 10 billion and €7.9 billion, of which €380 million will be used for mergers and acquisitions, and €1.4 billion will be used to digitize its network. The CAC40 index rose for the third consecutive trading day. On Tuesday, it closed at a nearly 21-year high of 6640 points, increasing 23 points or 0.4%. This was the most optimistic day for the European market, supported by the pace of economic recovery and vaccination efforts. At the same time, Airbus rose 0.7%. Investors welcomed the settlement of the 17-year dispute between the United States and the European Union. The two sides agreed to suspend five-year tariffs on Boeing and Airbus. At the same time, after HSBC upgraded the stock to "buy," Air Liquide surged 2.6%, becoming one of the best-performing companies in the index. The Dow Jones index set its lowest closing price in more than three weeks, while the S&P 500 and Nasdaq index fell from record highs as investors reacted negatively to retail sales reports and avoided taking them before the Fed’s two-day meeting in June. Major move. US retail sales fell 1.3% in May, faster than expected, as Americans shifted their consumption from automobiles, construction materials, and electronics to service industries, including food services, health, and clothing. In monetary policy, the Federal Reserve is expected to emphasize that the central bank will continue to maintain ultra-loose policies until the economy recovers further. Despite this, there are growing rumors that at some point, Jay Powell and his rate-setting colleagues will need to consider scaling back their quantitative easing policies. The Canadian stock market rose for the fourth consecutive trading day on Tuesday. Boosted by the rise of the heavyweight energy sector, the S&P/TSX Composite Index hit a new high near 20240. Oil prices have climbed to their highest level since 2018, and investors expect the introduction of vaccines and the reopening of the economy will help boost demand for crude oil. In terms of data, flash estimates show that the price index of industrial products rose 3.1% month-on-month in May, the sixth consecutive month of rising. The index rose 16.9% year on year, the largest increase since January 1975. On Tuesday, the Shanghai Composite Index fell 33.19 points to close at 3556.56 points, decreasing by 0.92%. It returned to the trading market after the public holiday of the previous trading day, after the Group of Seven (g7) and NATO accused China of its economic and military plans. , The buying support of mainland investors weakened, approaching a 3-week low. Market participants are also cautious when the US inflation spike may prompt the Federal Reserve to consider raising interest rates earlier than expected. The latest data shows that China's auto sales in May fell by 3% year-on-year, breaking the 13 consecutive months of growth since April 2020. Investors are currently waiting for a series of economic data from China for May later this week, including industrial output, retail sales, and unemployment. In Hong Kong, the Hang Seng Index fell by 182.96 points, or 0.63%, to 28,659.17. The Nikkei 225 index rose 279.5 points on Tuesday to close at 29441.3 points, an increase of 0.96%, continuing the 0.74% gain of the previous trading day and closing at a 5-week high. The Bank of Japan announced that it would extend the pandemic relief later this week. After planning to support a fragile economic recovery, investors showed optimism. After the Japanese government lifted Tokyo's COVID-19 emergency and reduced it to a quasi-emergency in three prefectures and prefectures, traders are also optimistic due to the steady decline in the number of infections. In terms of data, the month-on-month growth rate of Japanese industrial output was revised to 2.9%, the preliminary data was 2.5%, and the final data in March was 1.7%. Investors are also waiting for the Fed’s monetary policy decision and Japan’s May trade data to be released later this week.
• REVIEWING ECONOMIC DATA:
Looking at the last economic data:
- RUB: Russia's gross domestic product in the first quarter of 2021 shrank by 0.7% year-on-year, which has eased from the 1.8% contraction in the previous three months and is initially estimated to shrink by 1.0%.
- USD: According to data from the American Petroleum Institute, as of the week of June 11, 2021, US crude oil inventories plummeted by 8.537 million barrels after a decrease of 2.108 million barrels in the previous week. This is the largest draw since the week ending September 11, 2020.
- USD: In April 2021, the US capital and financial account surplus were 101.2 billion U.S. dollars, but it was lower than the 146.7 billion U.S. dollars in the previous month. Foreign investors bought 49.6 billion U.S. Treasury bonds in April, compared with 118.9 billion U.S. dollars in inflows last month. At the same time, the long-term transaction volume of Treasury International Capital (TIC) fell from US$224.9 billion in the previous period to US$59.3 billion in April.
- USD: In June 2021, the US NAHB housing market index fell to 81 from 83 in the previous two months, lower than market expectations of 83. With rising cost pressures, this is the lowest level in 10 months. The current single-family sub-index has dropped from 88 to 86, the house sales index in the next six months has dropped from 81 to 79, and the potential buyer sub-index has dropped from 73 to 71. “Rising costs and declining supply of cork timber and other building materials pushed down builders’ confidence in June. These rising costs pushed some new homes beyond the budgets of potential buyers, slowing down the strong pace of home construction”, NAHB Chairman Chuck Fox said.
- USD: In June 2021, the New York Empire Manufacturing Index fell 7 points to 17.4, which was lower than market expectations of 23. New orders (16.3 vs. 28.9) and shipments (14.2 vs. 29.7) increased moderately, while outstanding orders (7.9 vs. 21.4) increased. Delivery time has increased at a record rate (29.8 vs. 23.6), and inventory has fallen slightly (2.6 vs. 7.1). Employment levels (12.3 to 13.6) and average weekly working hours (15.1 to 18.7) continued to grow moderately, and input prices (79.8 to 83.5) and sales prices (33.3 to 37.1) continued to rise sharply. Looking to the future, companies are still optimistic that the employment situation will improve in the next six months, and the employment index will hit a record high in the future.
- USD: In May 2021, the US Producer Price Index (PPI) for final demand rose by 0.8% from the previous month, after rising by 0.6% in April, exceeding market expectations by 0.6%. The nearly 60% increase in the final demand index in May can be traced to a 1.5% increase in final demand commodity prices. The final demand service index rose by 0.6%.
- CAD: According to preliminary estimates, in May 2021, the Canadian Industrial Product Price Index rose 3.1% month-on-month, which was higher than the previous month's 1.6%. Excluding energy and petroleum products, producer prices rose by 2.8%. This is the sixth consecutive month of increase, mainly due to strong construction demand, tight supply and inventory, and a record monthly increase in softwood lumber prices (27.6%).- EUR: The Eurozone trade surplus widened from 2.3 billion euros in the same period last year to 10.9 billion euros in April 2021 due to the sharp recovery in global demand following the relaxation of coronavirus restrictions. Exports increased by 43.2%, and imports increased by 37.4%.
- GBP: British economic data showed that the British labor market continued to consolidate the recovery momentum. The pound remained stable at around $1.41 on Tuesday and hit a one-month low on Monday. The unemployment rate fell to 4.7% in February-April, the lowest level since June-August 2020. With the relaxation of epidemic restrictions, the number of employees on the company's payroll in May increased at a record rate. In addition, in the year ending in April, wage growth reached the fastest level since 2007. In addition, British Prime Minister Boris Johnson announced on Monday that the time for the full reopening of the British economy would be postponed by four weeks due to concerns about the rising number of COVID cases. Investors' attention is now shifting to the UK inflation report and Fed policy statement to be released on Wednesday.
- GBP: The number of people applying for unemployment benefits in the UK fell by 92,800 in May 2021, after falling by 55,800 in April. As the reopening of key parts of the economy has promoted employment and the government's wage subsidy program supports the labor market, the number of people applying for unemployment benefits has set a record monthly decline.
- NZD: In May 2021, New Zealand food prices rose 1.8% year-on-year, from 0.7% last month. This is the highest reading since May 2019. The prices of meat, poultry, and fish (0.2% vs. -2.2% in April) and non-alcoholic beverages (0.3% vs. -3.4%) rebounded, while the prices of groceries The price decline is relatively low (-0.1% versus -1.1%). On a monthly basis, food prices rose 0.4% after rising 1.1% in April.
- NZD: New Zealand's major stock indexes opened higher on Tuesday. The benchmark NZX 50 index climbed above 12,600 for the first time in more than a month. The rise in the healthcare sector offset the decline in consumer discretionary stocks. In the absence of a stronger catalyst, investors weighed optimism about the reopening of more economies and continued concerns about rising inflation. Fisher & Paykel Healthcare Corporation Ltd and A2 Milk Company Ltd were the companies with the largest gains in the index, rising 2% and 1%, respectively.
• LOOKING AHEAD:
Today, investors will receive:
- USD: Building Permits, Housing Starts, Import Prices m/m, Crude Oil Inventories, FOMC Economic Projections, FOMC Statement, Federal Funds Rate, and FOMC Press Conference.
- CAD: CPI m/m, Common CPI y/y, Median CPI y/y, Trimmed CPI y/y, Core CPI m/m, and Wholesale Sales m/m.
- GBP: CPI y/y, Core CPI y/y, PPI Input m/m, PPI Output m/m, and RPI y/y.
- CNY: Industrial Production y/y, Fixed Asset Investment ytd/y, Retail Sales y/y, and Unemployment Rate.
- JPY: Core Machinery Orders m/m, and Trade Balance.
- NZD: Current Account.
• KEY EQUITY MARKET DRIVERS:
- CATSX grows to an all-time high in 20222.
- GB100 rises to a 15-month high of 7188.
- The DXY index rose to a 4-week high of 90.627 points.
- AU200 rose to an all-time high of 7353 points.
- The yield on the 10-year British government bond has not changed much, at 0.75%, not far from the nearly three-month low of 0.69% hit last week. Investors are waiting for the outcome of the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy meeting on Wednesday. Policymakers are believed to have maintained the central bank's dovish stance because the market expects that the rise in inflation will be temporary. In other respects, investors digested news about the UK-Australia trade agreement and the postponement of the UK's easing blockade.
- The US benchmark 10-year Treasury bond yield rose to 1.50% on Tuesday, deviating from the 3-month low hit earlier this week. The latest data showed that US retail sales fell in May as Americans shifted their spending from goods to services. 1.1%, but the data for the first two months have been revised up. Investors continue to wait for the Federal Reserve's (Fed) monetary policy meeting later this week to wait for any updates on the reduction schedule. Traders will also expect policymakers to clarify their views on rising inflation further. As prices continue to soar, headline inflation will break through 13-year highs, and core inflation will soar to 1992 highs. At the same time, the producer price index of final demand increased more than expected. However, Fed officials have always reiterated that inflationary pressures are temporary, and the market seems to admit that the rise in inflation is mainly related to the flu pandemic.
- The yield on German 10-year government bonds remained almost unchanged in mid-June, at -0.26%, not far from a seven-week low. The market expects that the Federal Reserve may maintain a dovish stance at the two-day meeting. Elsewhere, the European Union received more than €76 billion in initial demand for bond issuance to support the European Union Recovery Fund; although ECB officials continue to reiterate that they are not in a hurry to cut the central bank's large-scale emergency stimulus plan. President Lagarde said Monday that monetary and fiscal stimulus measures should continue to be effective until there are clear signs that a "firm, solid and sustainable" economic recovery is underway. Last week, the People's Bank of China confirmed its very loose monetary policy stance and promised to continue emergency bond purchases at a "significantly higher rate" than at the beginning of this year.
- The benchmark Japanese 10-year Treasury bond yield was about 0.05% in mid-June, close to the highest level since late January. Tracking the general fall in US Treasury bond yields, investors wait for the monetary policy decisions of the Bank of Japan and the Federal Reserve. The Bank of Japan is expected to maintain its short-term interest rate target at -0.1% in June and the 10-year yield target at around 0%. The Fed is also expected to maintain monetary policy stability, but traders will look for clues about the reduction schedule and inflation forecasts. In Japan, the macroeconomic situation is slightly different from that of the United States because inflation is falling, and GDP is struggling to recover from the impact of the coronavirus due to slow vaccine launches and the resurgence of infections.
• STOCK MARKET SECTORS:
- High: Energy, Communication Services.
- Low: Materials, Real Estate, Consumer Discretionary.
• TOP CURRENCY MARKET DRIVERS:
- JPY: USD/JPY has broken through 110 points against the U.S. dollar, expanding its upward momentum to a level that has not been seen since June 6 because the two-day meeting of the Federal Reserve in June will provide clues to the path of stimulus measures during the crisis. The rate will pick up before the meeting. In Japan, Japan has extended the COVID-19 emergency in Tokyo and nine other regions until June 19, which is five weeks before the postponed 2020 Tokyo Olympics will begin.
- CNY: The offshore renminbi fell to 6.4 yuan against the US dollar in mid-June. The US dollar generally strengthened before the closely-watched Federal Reserve meeting. Driven by China's economic prospects and strong capital inflows, the yuan has strengthened since late March and hit a three-year high of 6.35 yuan per dollar on May 31. However, since late May, the rebound in the renminbi exchange rate has reversed. The People's Bank of China has raised the deposit reserve ratio of financial institutions from 5% to 7% for the first time since 2007 to curb the renminbi's appreciation. Although the People's Bank of China seems satisfied with the RMB exchange rate near its 3-year high, it seems unwilling to let the RMB appreciate more. Reuters reported that an article in "Financial News" supported by the People's Bank of China quoted analysts saying that the renminbi is approaching an inflection point of devaluation and may face greater pressure in the second half of the year.
- AUD: The Australian dollar exchange rate against the US dollar is about 0.77 yuan/US dollar, not far from the 7-week low of 76.5 yuan hit on June 3. Traders are waiting for the Reserve Bank of Australia (Reserve Bank of Australia) and New Zealand Reserve Bank a clue to withdraw from the stimulus plan. Investors are waiting for the central bank governor Philiplow's speech on Thursday and the employment data for May after the government ended wage subsidies for the unemployed at the end of March. The market predicts that the unemployment rate will remain at 5.5%, and employers will add 30,000 jobs.
- CAD: The Canadian dollar fell to a nearly six-week low of 1.22 yuan per US dollar in mid-June, and the decline in copper prices offset the rise in crude oil futures. As one of Canada’s main export commodities, gold traders are increasingly worried about China’s measures to combat speculative trading in the bulk commodity market. At the same time, preliminary estimates show that producer prices in Canada rose 3.1% in May compared to April, which is the sixth consecutive month of increase, mainly due to a record increase of 27.6% in softwood lumber prices.
- USD: The US dollar index held steady at 90.6 points, a more than one-month high on Tuesday. Traders await the outcome of the highly anticipated Federal Reserve meeting this week. The market expects that the Fed will continue to maintain ultra-loose policies until the economy recovers further. The 10-year U.S. Treasury bond yield is 1.48%, and investors’ concerns about inflation seem to have eased. Before this, US policymakers have repeatedly asserted that the rise in inflation will be temporary. In terms of economic data, US retail sales fell by 1.3% in May, while market expectations were for a 0.8% drop. The producer price index climbed more than expected. In addition, data released last week showed that the US consumer price inflation rate reached the highest level since 2008.
• CHART OF THE DAY:
On Tuesday, as investors digested news about the UK-Australia trade agreement and the postponement of the British blockade relaxation plan, the pound erased its early gains and hit a one-month low of $1.4071. The government stated that the agreement would eliminate tariffs on British cars, Scotch whiskey, and sweets, and British farmers would be protected by tariff-free import ceilings for 15 years. However, some officials estimate that this tariff-free agreement may increase £ In the long run, the UK’s economic output is 500 million pounds or 0.02% of GDP. At the same time, British Prime Minister Boris Johnson announced on Monday that the time for the full reopening of the British economy would be postponed by four weeks. The outside world is concerned about the rising number of COVID cases. In terms of economic data, the British labor market continued to consolidate the momentum of recovery. In May, the number of employees on the company's payroll increased at a record rate. In the year to April, wage growth reached the fastest level since 2007.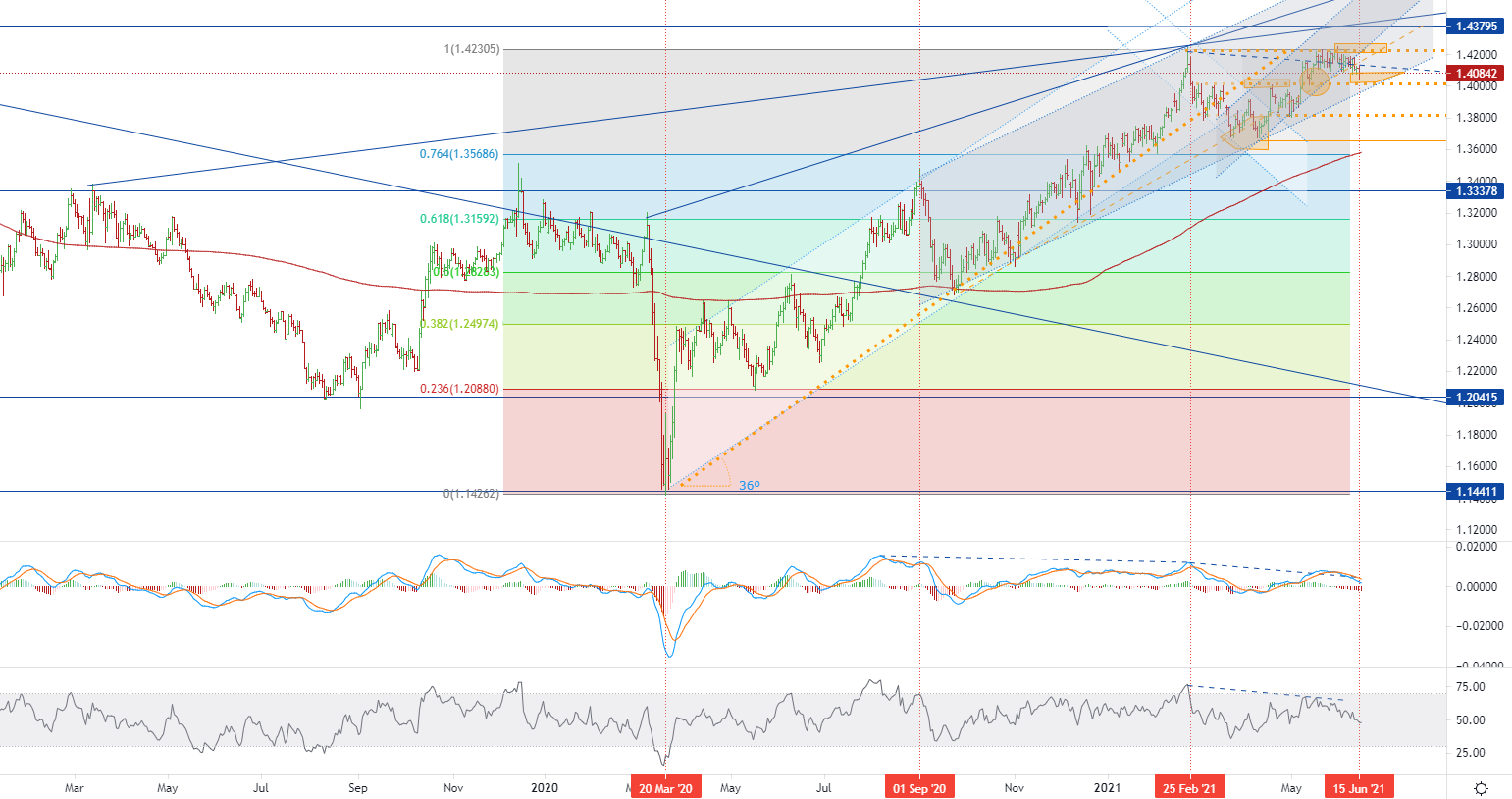
• GBPUSD - D1, Resistance (consolidation) around ~ 1.42, Support around (consolidation) ~ 1.40.
Demo account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account with virtual funds in a risk-free environment
Demo accountLive account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account in our transparent live model environment
Open an Account





