
CBOE Volatility Index closed at the lowest level since Feb.2020 - U.S. stock index almost flat, crude futures rise
• CAPITAL MARKETS OVERVIEW:
Last Friday, the U.S. stock index closed volatile, almost flat. Investors weighed the prospect of a strong economic recovery and growing inflationary pressures. Although the reopening of the economy has released pent-up demand, the supply side is struggling to meet demand, resulting in price pressures in recent data, especially since Thursday's inflation index was stronger than expected. However, investors have been digesting the Fed’s statement that the inflation spike is temporary because of an imbalance between supply and demand. Next week, everyone's eyes will turn to the Federal Reserve's (Fed) monetary policy announcement to seek guidance on the path of stimulus policy during the crisis. Canada's major stock indexes climbed for the second consecutive trading day on Friday, and the S&P/TSX Composite Index hit a new closing high above 20,100 points, rising for the third consecutive week. The market continues to benefit from last week’s upward momentum. Investors are optimistic about China’s economic recovery, while concerns about rising inflation have taken a back seat. Recent data shows that driven by growth in the construction and mining, quarrying, and oil and gas extraction industries, the Canadian industry’s production capacity in the first quarter of 2021 was 81.7%. European stock markets rose last Friday and reached a record level at the end of the week. The benchmark DAX index closed at around 15,700. Investors are increasingly optimistic about a strong economic recovery, thanks to the rapid promotion of vaccines, even in the face of inflation. Factor. The European Central Bank (ECB) raised its forecasts for economic growth and inflation in the eurozone in 2021 and 2022. It reassured investors that it supports the eurozone economy. The market has been digesting the central bank’s statement that the inflation spike is temporary and is due to an imbalance between supply and demand. The Federal Reserve, which will meet next week, also regards the strong inflation as temporary. It is studying investors’ reaction to Thursday’s stronger-than-expected U.S. inflation index. It seems that Wall Street is also satisfied with this view. CAC40 index rose 0.9% to 6,605 points, the highest closing point since September 2000, and outperformed its European counterparts. Investors bet that despite the signs of rising inflation, the major central banks will not cut monetary stimulus measures anytime soon. Renault’s share price rose more than 5%, and it is one of the best-performing automakers. This week, the company announced that it would merge its three plants in northern France to form a low-cost electric vehicle center that will create 700 jobs. Post. EssilorLuxottica rose nearly 2% after news that the Turkish competition regulator approved GrandVision's acquisition proposal after the French eyewear manufacturer promised to start a business in Turkey. As the inflation crisis subsides and the ECB’s monetary policy stance remains unchanged, the index will rise by 1.4% every week. The London stock market closed at its highest level since February 2020, achieving its third week of gains. Driven by the rebound in the materials and energy sectors, optimistic GDP data showed that the British economic recovery is accelerating. Output rose by 2.3% in April, slightly higher than expected, the fastest growth since July, and this increase reflects the recent reopening. The country's economic output has also increased by a record 27.6% from 12 months ago. Last Friday, the Shanghai Composite Index fell 21.11 points, or 0.58%, to close at 3,589.75. It fell for three consecutive trading days and closed down 0.2% this week. Previous data showed that China’s overall credit growth in May was due to the central bank seeking to curb the rise in debt. Continue to slow down. Investor sentiment was further depressed. Data showed that the US consumer price inflation rate jumped to 5% in May, the highest level since August 2008. Locally, as the economy rebounds from the epidemic, the People's Bank of China is trying to normalize policy by reducing stimulus measures and controlling debt. The latest data shows that in May, China’s new RMB loans increased from RMB 1.470 billion in April to RMB 150 billion, the M2 money supply increased by 8.3% year-on-year, and outstanding RMB loans increased by 12.2% year-on-year, lower than April’s 12.3%. In Hong Kong, the Hang Seng Index rose 95.49 points or 0.33% points to 28834.37 points, closing the market for 7 weeks, down 0.84% for the week. The Nikkei 225 index closed flat on Friday at 28948.73 points, down 0.93% this week. Investors weighed the fragile pace of domestic economic recovery and a sharp rise in an important US price indicator. At the same time, the Japanese government decided on Thursday to lift the COVID-19 quasi-emergency status in the three counties after this weekend because the infection rate has steadily declined, and the pressure on hospitals has eased. The local 10-year bond yield fell to a 5-month low of 0.029%, while the U.S. 10-year bond yield fell to a 3-month low of 1.37%. Local data show that in May 2021, Japan’s Producer Price Index (PPI) rose 4.9% year-on-year. The index rose 3.8% in the previous month, marking the third consecutive month of growth and the highest level since September 2008.
• REVIEWING ECONOMIC DATA:
Looking at the last economic data:
- USD: As investors continue to digest economic growth prospects, the latest U.S. CPI data, and the impact of CPI on the Fed’s monetary policy, US stocks barely changed on Friday. After the latest data showed that the U.S. inflation rate soared to a high of 5% in 2008, traders began to be optimistic that inflationary pressures will be temporary. This is consistent with the Fed’s position and increased people’s perception that the Fed will not be in the next year. Reduced bets earlier. However, this optimism faded on Friday. Without further catalysts, all eyes will be on the Federal Open Market Committee meeting next week. The quantitative easing policy is expected to be changed in August or September 2023. There will be no interest rate hikes before.
- USD: Preliminary estimates show that the University of Michigan’s consumer confidence in the United States in June rose from 82.9 in May to 86.4 in 2021, exceeding the market forecast of 84. Expectations soared (83.8 vs. 78.8), and the current conditions index also rose slightly (90.6 vs. 89.4). At the same time, the inflation expectations for the next year have dropped from 4.6% to 4%, and the five-year inflation expectations have dropped from 3% to 2.8%—consumers who expect stronger growth in the national economy and a net drop in unemployment the other hand, these number of people will hit a record high. According to a survey by consumer chief economist Richard Curtin, although the expected inflation rate has fallen in early June, rising inflation is still the most concerning issue.
- RUB: In April 2021, Russia's trade surplus expanded from 7.39 billion US dollars in the same period of the previous year to 10.59 billion US dollars. Exports increased by 47.6% year-on-year to US$36.86 billion, the highest level since December 2019, thanks to sales to non-CIS countries (45.9%) and CIS countries (58.1%). At the same time, due to purchases from non-CIS countries (50.3%) and CIS countries (42.0%), imports increased by 49.4% to US$26.27 billion, the highest level since October 2014.
- RUB: The Central Bank of Russia raised its benchmark policy rate by another 50 basis points to 5.5% at its June meeting, stating that the economic recovery is faster than expected and that inflation is higher than the central bank's target. Policymakers also stated that at the upcoming meeting, it is necessary to raise interest rates further because they fear that, with the completion of the economic recovery, inflationary pressures will increase, causing inflation to deviate from the target even more a longer period of time. Looking ahead, the Central Bank of Russia expects that the inflation rate will return to the target of the Central Bank of Russia in the second half of 2022 and will continue to stay close to 4%.
- CAD: Canadian industry operated at 81.7% production capacity in the first quarter of 2021. The 79.7% production capacity in the previous period was revised upwards, exceeding market expectations of 80.6%. This is the highest utilization rate of existing capacity in the Canadian economy since the fourth quarter of 2019. The main upward pressure comes from the construction industry (92.4% vs. 88.8% in the fourth quarter of 2020), mining, quarrying, oil and gas extraction (79.3% vs. 75.5%), and manufacturing (76.5% vs. 76.7%).
- EUR: As investors digested yesterday's ECB policy meeting, the euro erased the early gains on Friday and was reported at around $1.216. US data supports the Fed's view that current inflation will be temporary. The economic data released earlier this week were mixed. The European Central Bank (ECB) maintained its easing policy stance on Thursday and raised its forecasts for economic growth and inflation in the eurozone in 2021 and 2022. In other respects, investors continue to digest US data and support the Fed’s view that current inflation will be temporary. Earlier this week, mixed economic data showed that the euro zone’s economic contraction in the first quarter was lower than initially expected. However, disappointing data in Germany showed that investor morale unexpectedly deteriorated in June, industrial production and factory orders in April Both declined, and export growth was lower than expected.
- GBP: Affected by optimistic economic data and a general weakening of the U.S. dollar, the pound was almost unchanged on Friday, closing at $1.417. Britain’s GDP grew by 2.3% in April, slightly higher than expected and the fastest growth since July. This growth reflects the recent reopening. The country's economic output has also increased by a record 27.6% from 12 months ago. In other respects, some concerns persist, including the tension between Brussels and London, the rising number of COVID cases in the UK, and the possible delay in reopening the UK economy on June 21. In addition, the United Kingdom and the European Union failed to reach an agreement on a solution to the Northern Ireland trade issue after Brexit, and both sides accused each other of dishonesty.
- GBP: In April 2021, British manufacturing production surged 39.7% year-on-year, setting a record high growth rate. Last year, the coronavirus pandemic severely hit the British economy, and manufacturing production fell by 30.3% yearly, setting a record. This data is compared with the market forecast of 41.8%. As a result, the total industrial output value unexpectedly fell by 0.3% month-on-month, of which the essential medicine and preparation manufacturing industry fell by 16%.
- CNY: The Chinese stock market fell 21 points. AVIC Aviation Engine (-5.36%), Dalian Rubber (-4.99%) and Sanan Optoelectronics (-4.93%) led the decline. To offset the decline, the top gainers were PetroChina (6.52%), Xi'an Longji (5.23%), and Kangmei Pharmaceutical (5.08%).
- CNY: In May 2021, China's auto sales fell 3.1% year-on-year to 2.10 million vehicles, the first monthly decline in 14 months. New energy vehicles, including battery-powered electric vehicles, plug-in hybrid electric vehicles, and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, soared 160% from the same period last year to 217,000.
• LOOKING AHEAD:
Today, investors will receive:
- GBP: BOE Gov Bailey Speaks, and CB Leading Index m/m.
- EUR: Industrial Production m/m.
- NZD: Visitor Arrivals m/m.
- JPY: Revised Industrial Production m/m.
- CHF: PPI m/m.
• KEY EQUITY MARKET DRIVERS:
- CATSX rose to an all-time high in 20107.
- MOEX rises to an all-time high 3848.
- GB100 rises to a 4-week high of 7135.
- The benchmark 10-year U.S. Treasury yield on Friday extended its decline to a three-month low of 1.43%, despite recent data showing hot inflation in the United States. Investors clearly acknowledge that inflationary pressures are temporary, consistent with the Fed’s comments, and the labor market recovery is far from complete. For example, the number of people applying for unemployment benefits for the first time was 376,000, higher than expected. At the same time, the US Treasury auction held this week showed strong demand for 10-year and 3-year Treasury bonds and mixed demand for 30-year Treasury bonds. Attention is now turned to the Fed’s monetary policy meeting next week to get any clues about the cutback schedule.
- The yield on German 10-year government bonds fell below -0.27% for the first time since April 23 because investors were dismissive of inflation concerns. However, US data showed that the country’s consumer prices rose the most in the past 11 years, and the core inflation rate Reached a nearly 30-year high. At the same time, the European Central Bank (ECB) confirmed its very loose monetary policy stance and promised to continue to carry out emergency bond purchases at a "significantly higher rate" than at the beginning of this year in a generally expected manner.
- The 10-year government bond yield in the UK has not changed much, at 0.75%, not far from hitting a nearly three-month low this week. Investors welcome the optimistic UK GDP data, and concerns about global inflationary pressures have now eased. US consumer prices have risen the highest in nearly 13 years, and the annual core inflation rate has hit a new high in nearly 30 years. Still, investors believe that inflationary pressures are temporary. In other respects, investors are concerned about the tensions between Brussels and London, the rising COVID cases in the UK, and the possible delay of reopening the UK economy on June 21.
• STOCK MARKET SECTORS:
- High: Information Technology, Financials, Consumer Discretionary.
- Low: Health Care, Real Estate, Energy.
• TOP CURRENCY MARKET DRIVERS:
- USD: The dollar index regained lost ground on Friday and hit a one-week high of 91.60 points. Investors are pleased with new signs that the reopened economy is driving economic growth. Consumer confidence at the University of Michigan was higher than market expectations, and the number of unemployed fell to a new pre-pandemic low. In addition, the market dismissed the high US inflation data released on Thursday and digested the Federal Reserve's (Fed) statement that this is likely to be a temporary, temporary fluctuation, and it is due to an imbalance between supply and demand. Investors are now turning their attention to the Fed's monetary policy decision next week. It is expected that the Fed will continue to maintain its ultra-loose policy until the economy recovers further. As a result, the U.S. dollar rose nearly 0.5% this week and is expected to rise for the second consecutive week.
- RUB: The Russian ruble rose to 71.5 against the US dollar on Friday, the highest level since the end of July 2020, after the country’s central bank raised interest rates for the third time this year and said it would consider more monetary tightening measures at an upcoming meeting. Furthermore, after economic data showed that Russia’s annual consumer price inflation rate in May exceeded expectations, reaching 6.0%, policymakers expressed concern about increasing inflationary pressures. In other respects, rising oil prices have also provided some support, while investors are looking forward to talks between US President Biden and Russian President Putin next week.
- EUR: The euro rose slightly to US$1.218 on Friday, still close to the more than four-month high of US$1.2265 reached in May, supported by strong hopes for economic recovery and general weakness in the US dollar. The European Central Bank (ECB) maintained its easing policy stance on Thursday and raised its forecasts for economic growth and inflation in the eurozone in 2021 and 2022. In other respects, investors continue to digest US data and support the Fed’s view that current inflation will be temporary. Earlier this week, mixed economic data showed that the euro zone’s economic contraction in the first quarter was lower than initially expected. However, disappointing data in Germany showed that investor morale unexpectedly deteriorated in June, industrial production and factory orders in April Both declined, and export growth was lower than expected.
- CNY: The yuan was flat against the US dollar at 6.38565 on Friday, after the onshore exchange rate was previously set at 6.3856. As an important U.S. inflation report showed that the U.S. CPI jumped to 5% in May, the highest level since August 2008, the market’s confidence in the renminbi remains sluggish. The Central Bank of China is trying to achieve this by reducing stimulus measures and controlling debt. The policy is normalized because data on Wednesday showed that China’s ex-factory prices in May rose at the fastest annual growth rate in 12 years, and China’s economy rebounded as a result. In addition to other latest data, China’s new RMB loans increased from RMB 1.470 billion in April to RMB 150 billion in MaAs a result, these M2 money supply increased by 8.3% year-on-year, and outstanding RMB loans increased by 12.2% year-on-year, which was lower than 4. 12.3% of the month.
• CHART OF THE DAY:
At the end of Friday, the FTSE MIB index rebounded by 117 points or 0.5% to 25,760 points, close to the nearly 11-year high at the beginning of this week. As market concerns about the early tightening of monetary stimulus policies faded, investors were concerned about the strong economic recovery. The European Central Bank raised its economic growth forecasts for 2021 and 2022, and Italy's ongoing reopening plan has also raised expectations for a strong recovery in summer tourism. On the corporate side, DiaSorin led the rise by 2.8% after Bloomberg analysts raised its target price to 10% from €170 to €150 per share, and the stock was rated as "Buy." At the same time, as the Turkish competition watchdog approved GrandVision's acquisition proposal and the French Italo glasses manufacturer promised to start a business in Turkey, Essilor Luxottica rose nearly 2As a result, these indexes will rise 0.7% every week.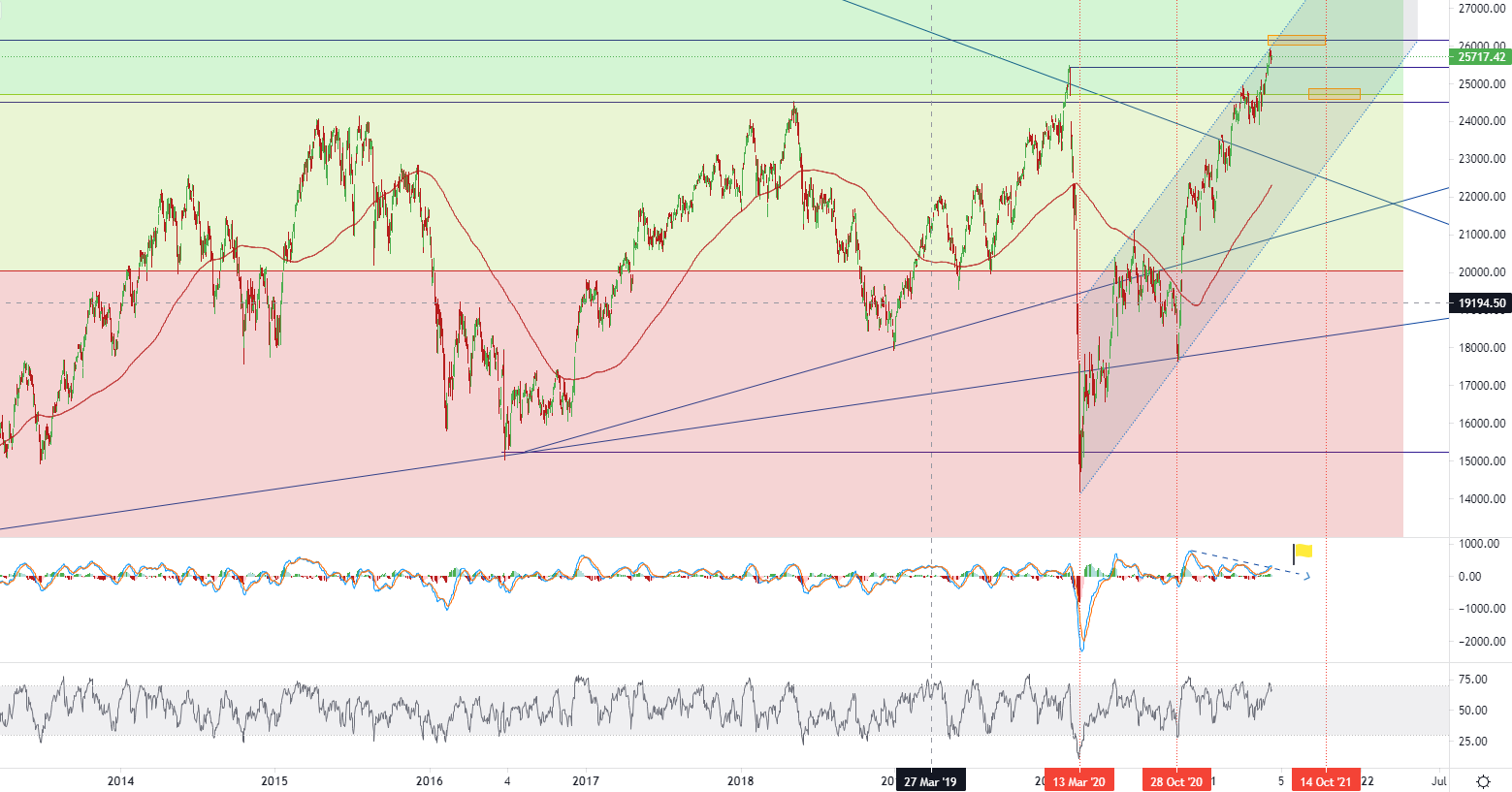
• Italian FTSE MIB index - D1, Resistance (target zone) around ~ 26178, Support (target zone) around ~ 24800.
Demo account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account with virtual funds in a risk-free environment
Demo accountLive account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account in our transparent live model environment
Open an Account





