
S&P500 met with resistance at an all-time high, 10-y treasury yields edge lower, and lack of trading conviction at the large-cap level
• CAPITAL MARKETS OVERVIEW:
The US stock market fluctuated between a small decline and a rise on Tuesday. Investors are looking for new catalysts to push the stock index higher or justify the current valuation. Thanks to the successful launch of the vaccine and unprecedented monetary policy support, the economic outlook has improved, and the stock market has recently risen to historical highs. However, with this economic boom, people have been worried that rising inflation may force the Fed to tighten monetary policy faster and more suddenly than expected. Therefore, investors seem to be reluctant to Masukura before releasing the highly anticipated May U.S. Inflation Report on Thursday to guide stimulus policies during the crisis. Most European stock markets closed higher on Tuesday, with the benchmark DAX index hovering near records, as investors’ optimism about the region’s economic recovery and concerns about out-of-control inflation increased. The economic contraction in the Eurozone in the first quarter was lower than initially expected. The decline in household consumption was partially offset by growth in fixed investment and exports. There is evidence that the group is rebounding from the second recession caused by the influenza pandemic due to the delay in the start of vaccination work due to supply shortages, thereby boosting the spirit of the animals. However, with this economic boom, people have been worried that rising inflation may force the central bank to tighten monetary policy faster and more suddenly than expected. The CAC40 index rose for the third consecutive trading day. It closed on Tuesday at a nearly 21-year high of 6551 points, an increase of 0.1%. This is a calm day for the European market because investors are concerned about the ongoing economic recovery. Stay optimistic while facing the risk of the inflation outlook. In terms of the influenza pandemic, France entered the second phase of its reopening plan on June 9. The plan will allow customers to re-enter restaurants and bars. Still, it can only accommodate up to 50% of customers and postpone the mandatory curfew until the evening at 11 o'clock, and other measures. On the company side, the French anti-monopoly supervisory agency stated that it would decide to merge the two largest French broadcasters, TF1 and M6, before the summer of 2022. At the same time, Airbus said it delivered 50 aircraft in May, a slight increase from the 45 in April, and said it received 7 new orders. The FTSE MIB index closed 16 points or 0.1% lower on Tuesday at 25,809 points. It was flat with European counterparts for most of the session and was still close to the level at the end of 2008, as traders balanced the current economic recovery and rising inflation prospects. Italian payment company Nexi rose 1.9%, the second-largest increase on the trading day after Jefferies raised its target price to 1.9% before 25 and reiterated its "buy" recommendation. The Standard & Poor's/Toronto Stock Exchange struggled to hold 20,000 bar on Tuesday, pressured by weaker oil and gold stocks in energy and commodity prices. In terms of epidemics, Justin Trudeau is considering easing border restrictions on fully vaccinated travelers. At the same time, traders unexpectedly digested a trade surplus of 590 million Canadian dollars in May. Imports fell 4.7% from the previous month, while exports fell 1%. The global chip shortage affected Canada's foreign trade, which forced auto factories to suspend production, and imports of cars and parts plummeted by 22.1%. On Tuesday, the Shanghai Composite Index fell 19.43 points, or 0.54%, to close at 3,580.11 points, down from the 0.21% gain of the previous trading day, and fell from a 4-month high. It was previously reported that there were 33 new cases in mainland China on Monday. The number of COVID-19 cases was higher than the 19 cases the day before, and traders were depressed. It is reported that the Chinese government has stepped up its crackdown on Bitcoin trading and mining, which has also disrupted risk appetite. At the same time, there are reports that a large number of encryption-related accounts on China's Twitter-like Weibo platform have been blocked over the weekend. In terms of trade, due to the surge in demand for raw materials, China’s import growth in May hit its highest level in 10 years, while export growth slowed more than expected due to the disruption caused by COVID-19 cases in the country’s southern main ports. At the same time, the Hang Seng Index fell 47.63 points to close at 28739.65 points, a decrease of 0.17%. The index is expected to fall for the fifth consecutive trading day, tying the longest losing streak in 10 weeks. Nikkei 225 index fell 55.68 points, or 0.19%, to close at 28,963.56 points, which was lower than the 0.27% gain of the previous trading day. Market participants were cautious about their positions before the release of key US inflation data later this week. Among the local data, the Cabinet Office announced on Tuesday that the local gross domestic product (GDP) contracted by 3.9% from the last quarter of 2020, which exceeded the median forecast of economists and eased people’s concerns about the risk of a second recession. Because of another round of virus-related restrictions. The local 10-year bond yield fell to 0.074%, while the U.S. 10-year bond yield was 1.553%. US regulators approved a drug jointly developed by Eisai and Biogen to boost market sentiment on Monday as the first drug to treat Alzheimer's disease. Healthcare stocks performed well, with Daiichi Sankyo rising 4.58% and Astellas Pharma rising 1.83%.
• REVIEWING ECONOMIC DATA:
Looking at the last economic data:
- USD: The number of job vacancies in the United States increased by nearly 1 million from the previous month, setting a new high of 9.286 million in April 2021, easily exceeding market expectations of 8.3 million. Many industries have created job opportunities. Among them, the accommodation and food service industry (increased by 349,000), other service industries (increased by 115,000), and durable goods manufacturing (increased by 78,000) saw the largest increases. At the same time, education services fell by 23,000, and mining and logging fell by 8,000. Job vacancies in the four regions have increased.
- USD: The U.S. trade balance narrowed from a record of 75 billion U.S. dollars in March to 68.9 billion U.S. dollars in April 2021, in line with market expectations. Due to civil aircraft (US$1.4 billion), crude oil (US$1 billion), other petroleum products (US$600 million), and fuel oil (US$500 million), exports increased by 1.1%, reaching a 14-month high of US$205 billion. As a result of other textiles, clothing and household products (900 million US dollars), toys, games and sporting goods (700 million US dollars), household appliances (700 million US dollars), auto parts and accessories (700 million US dollars), and passenger cars (500 million US dollars) U.S. dollars), imports fell 1.4% to 273.9 billion U.S. dollars from a record level in March. Due to rising exports and falling imports, the trade deficit with China decreased by US$7.1 billion to US$32.4 billion.
- USD: In April 2021, imports to the United States fell by 3.8 billion U.S. dollars from the historical high of the previous month to 273.9 billion U.S. dollars.
- CAD: In April 2021, Canadian imports fell by 4.7% year-on-year to 49.6 billion Canadian dollars, mainly because the global semiconductor supply shortage forced the auto assembly industry to stop production and the foreign trade of automobiles and parts shrank sharply. Imports from the United States fell by 5.2% to 30.7 billion Canadian dollars, in line with other major trading partners, such as China (down 18.8% to 4.7 billion Canadian dollars) and Mexico (down 6.6% to 1.4 billion Canadian dollars).
- CAD: In April 2021, Canadian exports fell 1.0% month-on-month to 50.2 billion Canadian dollars, mainly due to the decline in sales of automobiles and parts (-4.7%). The global semiconductor supply shortage forced the automotive assembly industry to suspend production.
- CAD: Canada announced a trade surplus of 590 million Canadian dollars in April 2021. Last month’s deficit was revised upwards to 1.35 billion Canadian dollars, contrary to the market’s expected deficit of 700 million Canadian dollars. Total imports fell by 4.7% year-on-year to 49.6 billion Canadian dollars. The reason was that many auto and parts manufacturers in North America and overseas stopped or slowed down production due to semiconductor chip shortages. (-29.7%) and the purchase of engines and parts (-20.2%) decreased.
- EUR: In June 2021, due to a reassessment of the economic situation, the Eurozone’s ZEW Economic Confidence Index fell by 2.7 points to 81.3, returning to its pre-pandemic level. In June, inflation expectations rose by 2.0 percentage points to 79.6, and nearly 84% of the analysts surveyed expect the inflation rate to rise in the next six months. At the same time, the indicator of the current economic situation in the Eurozone increased by 27.0 percentage points to -24.4.
- EUR: The Eurozone economy shrank by 0.3% month-on-month in the first three months of 2021, revised from the initial estimate of a contraction of 0.6%. Activities and needs have been hit by new distance and lockdown measures implemented during that period to curb the spread of the coronavirus pandemic. Among the largest economies in the Eurozone, Germany, Italy, Spain, and the Netherlands fell into contraction again. In contrast, the French economy resumed growth due to the government’s postponement of the blockade. In the first quarter, GDP fell by 1.3% year-on-year, well below the 1.8% expected in the second quarter.
- EUR: In June 2021, Germany’s ZEW Economic Sentiment Index fell from a 21-year high of 84.4 in May to 79.8, which was far below market expectations of 86. At the same time, Germany's current economic situation index jumped from -40.1 to -9.1.
- EUR: In the first three months of 2021, the number of employed people in the Eurozone fell by 0.3% month-on-month, lower than the revised 0.4% in the previous period, which was in line with preliminary estimates. Compared with the same period last year, the employment rate fell 1.8%, which was the same as last year's, while the previously expected decline was 2.1%.
- SEK: In April 2021, Swedish industrial production increased by 26.4% year-on-year, after an increase of 5.6% in the previous month. This is the fastest increase in industrial activity since the start of the series in January 2021, mainly due to the significant impact of the COVID-19 outbreak on production in March 2020, so the base effect is low. The biggest positive contribution comes from the automotive industry, which has grown by 300%.
- SEK: In April 2021, Swedish household consumption fell 5.1% from the previous month, and the growth rate in March was revised to 0.7%. This is the biggest drop since a record drop in April last year due to coronavirus restrictions. On the other hand, household spending increased by 7.5% year on year, with transportation, automobile retail, and service industries contributing the most.
- CNY: The Chinese stock market fell 19 points. Kangmei Pharmaceutical (-4.39%), Kweichow Moutai (-3.52%), and Shanghai Pharmaceuticals (-3.23%) led to the decline. To offset the decline, the top gainers were AVIC Aviation Engine (5.96%), NARI Technology Development (4.48%), and Great Wall Motors (4.03%).
- RUB: In May 2021, consumer prices in Russia rose 6.0% after rising 5.5% last month, faster than market expectations of 5.8%. The latest data is still far higher than the central bank's 4% target, the highest inflation rate since October 2016, mainly driven by food prices (7.4%), non-food prices (6.7%), and service prices (3.3%). From a monthly point of view, the consumer price index rose 0.7%, following the 0.6% increase in April, compared with the expected increase of 0.6%.
• LOOKING AHEAD:
Today, investors will receive:
- USD: Final Wholesale Inventories m/m, Crude Oil Inventories, and 10-y Bond Auction.
- NZD: Manufacturing Sales q/q, and Prelim ANZ Business Confidence.
- AUD: RBA Assist Gov Kent Speaks and Westpac Consumer Sentiment.
- JPY: M2 Money Stock y/y.
- CNY: CPI y/y, and PPI y/y.
- EUR: German Trade Balance, and German 30-y Bond Auction.
- CAD: BOC Rate Statement and Overnight Rate.
• KEY EQUITY MARKET DRIVERS:
- CATSX rises to an all-time high in 20077.
- U.S. 10-year Treasury bond yield drops to a 4-week low of 1.5517%.
- AU200 rose to a record high of 7310 points.
- In the second week of June, the German 10-year bond yield was -0.2%, not far from the one-month low last Friday and lower than the two-year high in May. Investors await the European Central Bank (ECB) policy meeting on Thursday when officials will re-examine the pace of emergency bond purchases. However, the dovish comments of the European Central Bank and the latest money printing data show that under the PEPP framework, the European Central Bank is not in a hurry to slow down the pace of purchases. In other respects, we will pay close attention to key U.S. CPI inflation data later this week to further guide monetary policy. Higher-than-expected inflation figures may push the Federal Reserve (fed) to reduce the scale of negotiations.
- The UK 10-year government bond yield was almost unchanged in early June, at 0.8%. However, it hit one of the highest levels since June 2019 in May. Investors look forward to furthering guidance from the key US CPI inflation data released later this week. Monetary Policy. Higher-than-expected inflation figures may push the Federal Reserve (fed) to reduce the scale of negotiations. At the same time, due to the surge in cases of a new variant of the coronavirus, concerns about the possible delay of the reopening of the British economy on June 21 have intensified.
- As investors continue to evaluate the impact of global price pressures and the possibility of premature tightening by global central banks, the benchmark Japanese 10-year Japanese government bond yield fell to 0.07% in June, the lowest level since the close mid-April. Is consistent with the decline. However, in Japan, this situation is a bit different from Europe and the United States because the slow introduction of vaccines and the resurgence of the coronavirus infection have led to a decline in inflation. Japan’s GDP fell 1% from the previous quarter in the first quarter. Therefore, investors expect that the Bank of Japan will maintain its ultra-loose policy for longer than other central banks.
• STOCK MARKET SECTORS:
- High: Consumer Discretionary, Energy.
- Low: Utilities, Health Care, Consumer Staples.
• TOP CURRENCY MARKET DRIVERS:
- RUB: The Russian ruble climbed to 72.0 against the US dollar in the second week of June and hit its highest level since July 2020 on Tuesday. The market expects that the Russian Central Bank will implement a more aggressive rate hike when it meets on Friday. In addition, data released on Monday showed that China’s annual consumer inflation rate in May exceeded expectations, reaching 6.0%. As a result, the ruble-euro exchange rate hit its highest level in nearly three months.
- USD: The US dollar index rose slightly to 90.1 on Tuesday, as investors remained cautious before the announcement of the US CPI later this week and digested the possibility of an early reduction by the Fed. On the one hand, despite rising inflationary pressures, employment growth in May was not as strong as expected. On the other hand, the Federal Reserve (Fed) has been downplaying inflation risks, saying that inflation risks are temporary. Still, in recent weeks, several central bank officials have said that the Fed will soon start discussing inflation reduction. As a result, many investors now expect that the Fed will announce a plan to reduce bond purchases later this year, and the actual reduction will begin early next year.
- EUR: The euro fell from a more than the four-month high of US$1.2265 in May to US$1.217 in the second week of June. Earlier economic data was mixed. Investors waited for the ECB meeting on Thursday. The economic contraction in the Eurozone in the first quarter was lower than initially expected; despite the disappointing data in Germany, investor morale unexpectedly deteriorated in June, and both industrial production and factory orders fell in April. In addition, German Chancellor Angela Merkel warned on Monday that the global semiconductor shortage might last until at least the middle of 2022, making Germany's economic recovery more difficult.
- GBP: The pound fell slightly to US$1.415 in the second week of June, which is lower than the three-year high of US$1.425 hit last week. The market is concerned that the British economy will be affected by the surge in cases of the new coronavirus variant (now called Delta) detected in India for the first time. It may be postponed to reopen on June 21. British Health Secretary Matt Hancock said last weekend that it is too early to say whether restrictions will proceed as planned. In terms of economic data, the British Retail Consortium reported that in any month since the beginning of the pandemic, retail sales in the UK have increased the most compared to 2019, after the UK relaxed its lockdown measures. Compared with May 2020, due to a strict ban on sales, most of the non-essential businesses were closed, and total sales increased by 28.4%. Investors are currently waiting for the key GDP data to be released on Friday.
• CHART OF THE DAY:
The March rise in prices to the level of $ 71.38 per barrel ended in a correction, and by the beginning of April, the prices for Brent oil fell to almost $ 60.0 per barrel in anticipation of the expansion of OPEC + supply. At a meeting of OPEC + in April, it was decided to increase oil production by 350 thousand. Barrels in May, by 350 thousand. Barrels in June and 440 thousand barrels in July. Saudi Arabia has decided to gradually abandon the voluntary reduction of production, increasing the supply by 250 thousand barrels in May by 350 thousand barrels in June and 400 thousand barrels. The decision of OPEC + and Saudi Arabia was more balanced than the market expected, and prices began to recover, returning to early June at $ 70 per barrel against the background of overall growth in economic activity in the world. During the meeting on June 1, OPEC + again made a moderate decision, leaving the size of production quotas agreed at the April meeting unchanged, despite the likely increase in Iranian oil supplies to the world market. OPEC + clarified the importance of Iran's return to the world market, but judging by the decision, it does not expect a quick return of full supplies. It is estimated that additional Iranian oil exports to the world market by the end of 2021 could reach 0.5-1.5 million barrels per day. However, there is still a significant chance that a nuclear agreement with Iran will not be signed. The next OPEC + meeting is scheduled for July 1. During this meeting, according to the Ministry of Energy of the Russian Federation, production quotas will be discussed in August 2021, taking into account the expected seasonal growth in demand in the third quarter. There are already arguments in favor of extending the OPEC + agreement after April 2022. Leading industry agencies and OPEC + expect a steady increase in demand for oil and petroleum products in the second half of 2021, despite the continued spread of COVID-19 in some regions. This will reduce the accumulated level of oil reserves in the world to the long-term average in mid-2021. Against this background, Brent oil prices have fixed above $ 70 per barrel.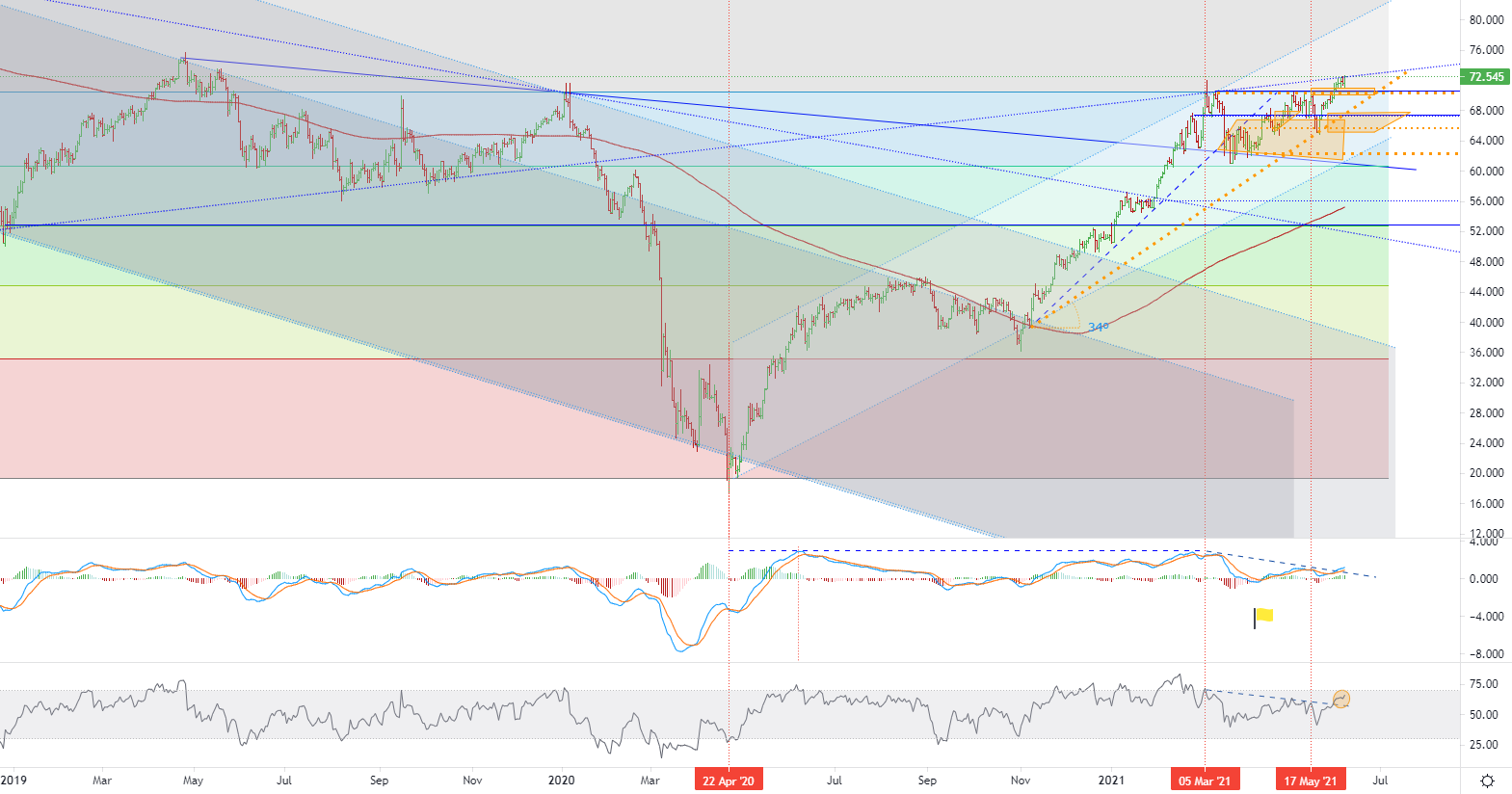
• Brent Crude oil - D1, Resistance (target zone) around ~ 72.77+, Support (consolidation) around ~ 70.48.
Demo account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account with virtual funds in a risk-free environment
Demo accountLive account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account in our transparent live model environment
Open an Account





