
The growth stocks up, energy sector pads big gain - treasuries finished on their highs
• CAPITAL MARKETS OVERVIEW:
Boosted by technology stocks, the three major U.S. stock indexes closed higher on Friday, ending a week of roller-coaster market. The lower-than-expected employment growth eased concerns about overheating the economy. The United States added 559,000 jobs in May, higher than the 278,000 jobs raised in April but lower than market expectations of 65,000. Earlier this week, the market worried that a strong economic rebound may lead to a longer duration of inflation and prompted the Fed to consider cutting crisis-level support, which caused investors to panic about the stock market. However, the latest interpretation of the job market reinforces the Fed’s statement that the Fed will continue to maintain an ultra-loose policy until the economy recovers further. Canada’s major stock indexes closed above 20,000 for the first time, and heavyweight commodity stocks pushed up the index. Denison Mines Corp. shares rose more than 6%, the largest gainer on the Toronto Stock Exchange, and the second-largest gainer was Nexgen Energy Ltd, which rose 5.2%. The risk of market sentiment is supported by another weaker-than-expected U.S. employment, which eases concerns about overheating the economy and leading to an early tightening of monetary policy. As a result, the S&P/TSX Composite Index rose nearly 1% this week, rising for the third consecutive week. European stock markets rose on Friday and reached a record level at the end of the week. The benchmark DAX index closed above 15,700 for the first time. The market is increasingly expecting that with the acceleration of vaccination, the eurozone economy will begin to improve in the coming months. Rebound at a fast speed. The data on the strong expansion of European factory activity in May, released earlier this week, provides more evidence that the block may be recovering from the second recession. In addition, new U.S. employment data showed that the number of U.S. employment growth last month was lower than expected, alleviating concerns that the Federal Reserve (fed) will reduce large-scale support earlier than expected. Last Friday, due to the slower-than-expected rate of job creation in the United States, inflation dilemmas, and concerns about the central bank’s early reduction of ultra-loose monetary policy eased, CAC successfully closed up 8 points or 0.1% to close at 6516 points, close to earlier this week. It hit a 21-year high at the time. The major French stock indexes traded near parity for most of the day, mainly due to the 2.4% drop of Air France-KLM after the UK withdrew Portugal from its safe destination and reduced the quarantine exemption list. In contrast, after the highly anticipated new product launch, Vallourec's share price rose by 8.9%. It increased its capital by 300 million, marking the final stage of its financial restructuring plan. At the same time, Vivendi said that it is negotiating with a US SPAC company to sell its 10% stake in Universal Music Group for €3.3 billion in about 10 years. On a weekly basis, the index rose 0.6%. The London stock market was basically in a rising range at the close of the market on Friday. The benchmark FTSE 100 index closed at around 7,070 points. Shares of Ocado Group PLC and Renishaw were among the top gainers, rising 2.9% and 2.7%, respectively. The market has benefited from the upward momentum that emerged earlier this week, and optimism about the reopening of the economy has increased risk appetite. Last Friday, the Shanghai Composite Index rose 7.63 points, or 0.21%, to close at 3,591.84 points, and fell 0.27% this week. Previously, there were reports that Beijing and Washington had "normal discussions" on trade and economics, and it was clear that they wanted to go beyond the target. The trade war to solve the problem. In terms of data, better-than-expected US May Employment Weekly Report and private sector salary data show that labor market conditions have improved, while service industry activities have increased to record highs. At the same time, in China, as price pressures increase, the growth of the service industry has slowed. In terms of policy, US President Joe Biden signed an executive order on Thursday prohibiting US entities from investing in dozens of Chinese companies that are said to be connected to the defense or surveillance technology sector. In Hong Kong, the Hang Seng Index fell 64.75 points, or 0.22%, to 28901.28, a weekly drop of 0.81%. The Nikkei 225 index fell 116.59 points or 0.4% on Friday to close at 28941.52 points. It was down 0.7% this week. After official data showed that Japan’s household spending increased by 13% year-on-year in April, it rose for two consecutive trading days. The largest increase since the data was released in January 2001 and affected by the sharp decline in 2020 due to the initial impact of the COVID-19 crisis. According to reports, the Japanese government is preparing to submit a fiscal blueprint on June 9 for cabinet approval. According to Reuters, in business news, Japan's steel company's exports and overseas operations have benefited from strong demand and strong steel prices. Japan's steel company may exceed its profit forecast for the year ending March 31, 2022. The European Council has officially included Japan on the EU’s so-called white list, allowing non-essential travel from countries outside the EU regarding the flu pandemic.
• REVIEWING ECONOMIC DATA:
Looking at the last economic data:
- USD: In April 2021, US factory orders fell by 0.6% month-on-month, the first decline in 12 months, and the decline exceeded market expectations by 0.2%. The largest decline in transportation equipment (-6.6%) was in ships (-62.8%), defense aircraft and parts (-8.5%), and motor vehicles (-1.8%). Orders for electrical equipment, appliances, and parts also fell (-0.7%). Excluding transportation, factory orders increased by 0.5%.
- USD: In May 2021, the U.S. economy added 559,000 jobs, which was higher than the 278,000 after the April upward adjustment but lower than the 65,000 expected by the market. This puts approximately 7.6 million jobs below the peak in February 2020. Employment in the leisure and hospitality industry (292K), public education (101K), private education (41K), and medical and social assistance (46K) have increased significantly. Nevertheless, because many workers (mainly women) still stay at home, and government subsidies may prevent some workers from finding jobs, tight supply, rising inflation, and labor shortages still pressure production capacity. Therefore, companies have been working hard to re-recruit employees to cope with the surge in demand, prompting them to raise wages to attract new employees. However, hourly income soared by 0.5%, higher than the 0.2% expected.
- USD: After an increase of 0.7% in April, exceeding market expectations of 0.2%, in May 2021, the average hourly earnings of all employees in private non-agricultural jobs increased by 15 cents, or 0.5%, to $30.33. After the average hourly wage of private-sector production and non-regulated employees increased by 19 cents in April, it rose by 14 cents to $25.60 in May. Compared with the same period last year, the average hourly income increased by 2%, which was revised by 0.4%, which was higher than the 1.6% expected by the market. The data of the past two months show that with the recovery of the influenza pandemic, the demand for labor continues to rise, which may put upward pressure on wages.
- CAD: The Canadian Ivey Purchasing Managers Index rose from 60.6 last month to 64.7 in May 2021, indicating that economic activity has grown rapidly. Job creation has accelerated (67 vs. 58 in April), and inventories have also risen (65.3 vs. 59.4). At the same time, prices fell (78.6 vs. 80), and supplier deliveries were slower than last month (34.8 vs. 37.8).
- CAD: Canada’s labor productivity fell by 1.7% in the first quarter, down by 2.1% in the previous quarter, and by a record 9.8% in the third quarter of 2020. This third consecutive quarter of decline continues to offset the strong productivity growth in the first two quarters of 2020.
- CAD: The Canadian economy lost 68,000 jobs in May 2021, surpassing the market’s expected reduction of 20,000 jobs, and added 207,000 jobs in the previous month. This month’s contraction reflects stricter public health restrictions since the last release, including the continued lockdown in Ontario, while Quebec and New Brunswick eased some restrictions in late May. Full-time (-13800) and part-time (-54200)-employment rate decreased by 1.6%.
- CAD: Canada’s unemployment rate rose from 8.1% last month to 8.2% in May 2021, in line with market expectations. The number of employed people fell by 68,000 (-0.4%), and almost all were working part-time (-5.4 million-1.6%). The unemployment rate of Canadian minorities between 15 and 69 years old rose by 1.5 percentage points to 11.4 % (Not seasonally adjusted). Long-term unemployment, that is, the number of people who have been unemployed for more than 27 weeks, is relatively stable at 478,000. The labor force participation rate fell to 64.6% from 64.9% last month, the lowest since August 2020. At the same time, in May, the youth unemployment rate fell to 15.9% from 16.1% in the previous month.
- EUR: In the eurozone, retail sales in April 2021 fell 3.1% from the previous month. In March, the growth rate was revised up by 3.3%, while market expectations were for a 1.2% decline. Non-food sales fell 5.1% (from 5.5% in March), and online transactions fell by 2.9% (from 2.0% in March). In addition, food sales fell 2.0% (1.4% in March), and fuel trade rose slightly by 0.4% (-1.9% in March).
- EUR: The IHS-Markit Eurozone construction industry PMI rose slightly from 50.1 in April to 50.3 in May 2021, indicating that economic activity will expand for the third time in a row. Although fragmented overall, the growth rate is the fastest since February 2020. The growth of residential construction activity peaked in 15 months, while commercial construction activity and civil engineering activity declined again. The increase in total construction activity in the Eurozone is driven by the substantial growth of Italian companies, which have expanded at the fastest rate since January 2007. In addition, production in France resumed growth, while construction activity in Germany continued to shrink. Due to the general shortage of suppliers, the prices of raw materials have risen in terms of prices. Since the data were available in January 2000, input costs have increased the most. Finally, Eurozone construction companies expressed optimism about the 12-month outlook in May for the fifth consecutive month.
- GBP: The IHS Markit/CIPS UK Construction PMI rose to 64.2 in May 2021, easily exceeding market expectations of 62.3, showing the strongest output growth rate since September 2014. In May, housing construction was the best-performing construction activity category, followed by commercial engineering. Civil engineering activities also increased sharply, but the rate of expansion slowed slightly from the previous month. Overall, the increase in new orders has been the largest since the survey began 24 years ago, and the rate of job creation has also been the fastest since July 2014. In terms of prices, input cost inflation has reached an all-time high. Finally, construction companies remain highly optimistic about their growth prospects in the next 12 months.
- GBP: In May 2021, the number of new car registrations in the UK reached 156,737, an increase of nearly 8 times over the same period last year, but still a 14.7% drop from May 2019 before the pandemic and a 13.2% drop from the 10-year average level in May. In a more positive economic context, the increase in fleet registrations in May was more than twice that of private purchases. Large fleets accounted for 50.7% of all new vehicles on the road, indicating that corporate confidence has improved compared with the same period last year. Nevertheless, the total number of registrations in 2021 is 296,448, 29.1% less than the average record from January to May of the past 10 years. Considering the impact of Covid on the market, evidence of the scale of recovery is still needed. The auto industry is expected to have about 1.86 million registered by the end of this year and 723,845 so far.
- SEK: Sweden’s current account surplus increased from SEK 77.9 billion in the same period of the previous year to SEK 78.3 billion in the first quarter of 2021. The service sector account recorded a surplus of SEK 5.8 billion, converted from a deficit of SEK 6.8 billion in the same period of the previous year to a major income surplus. As a result, it expanded from SEK 40.6 billion to SEK 43.2 billion. At the same time, the goods surplus narrowed to 69.1 billion Swedish kronor, and the secondary income gap widened from 33 billion Swedish kronor to 39.8 billion Swedish kronor.
• LOOKING AHEAD:
Today, investors will receive:
- USD: Consumer Credit m/m.
- EUR: Sentix Investor Confidence.
- AUD: AIG Services Index, and ANZ Job Advertisements m/m.
- CNY: Trade Balance and USD-Denominated Trade Balance.
- JPY: Leading Indicators.
- CHF: Unemployment Rate, CHF, CPI m/m, and Foreign Currency Reserves.
• KEY EQUITY MARKET DRIVERS:
- DE30 rose to a record high of 15687 points.
- Germany's 10-year government bond yield drops to a 4-week low of -0.217%.
- French 10-year government bond yield drops to a 4-week low of 0.148%.
- Italy's 10-year government bond yield drops to a 4-week low of 0.8758%.
- The benchmark 10-year Treasury bond yield fell back to 1.60% last Friday. The previous salary report showed that the US economy created fewer jobs than expected in May, alleviating concerns about the Federal Reserve (Fed) reducing large-scale support earlier than expected. In May 2021, the U.S. economy added 559,000 jobs, which was higher than the 278,000 after the April upward adjustment but lower than the 65,000 expected by the market. Earlier this week, a batch of latest data showed that continued economic growth, rising inflationary pressures, and tight supply might force the Fed to begin slowing negotiations soon. The comments of many Fed officials were mixed, showing that there is still no consensus within the Fed. St. Louis Fed President James Bullard said the labor market might be tenser than the current unemployment rate implies. New York Fed President John Williams pointed out that now is not the time to slow down asset purchases. In addition, Patrick Huck of the Philadelphia Fed noted that it might soon be time to consider cuts.
- US stock market futures rose on Friday as investors responded positively to the US non-agricultural employment report. In May 2021, the U.S. economy added 559,000 jobs, which was higher than the 278,000 after the April upward adjustment but lower than the 65,000 expected by the market. The latest interpretation of the job market eases concerns that the Federal Reserve will reduce its massive support earlier than expected.
• STOCK MARKET SECTORS:
- High: Technology, Health Care, Consumer Discretionary, Communication Services.
- Low: Financials, Energy, Materials, Real Estate
• TOP CURRENCY MARKET DRIVERS:
- GBP: The pound rebounded to $1.417 on Friday, still close to the three-year high of $1.425 hit earlier this week. The dollar weakened due to a weaker-than-expected US employment report and investors digesting optimistic British economic data. The Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) survey shows that the UK construction industry output increased the strongest in May since September 2014; although the number of new car registrations increased by 674.1%, it is still far below the level before the pandemic. In addition, the permanent placement index of KPMG and the Recruption&Employment Confederation shows that British companies hired permanent employees at the fastest rate in 23 years in May. In other respects, investors are concerned that the UK economy, which is scheduled to reopen on June 21, may be delayed due to the surge in cases of the COVID variant (now called Delta).
- EUR: The euro rebounded slightly above the US$1.21 on Friday, and the US employment report was weaker than expected to suppress the US dollar. In other economic news, the euro zone’s retail sales fell more than expected in April. However, construction output increased slightly in May, growth in Italy and France was offset by a sharp contraction in German activity. As a result, the euro hit a more than the four-month high of $1.2265 last week. Driven by accelerated vaccination and the gradual reopening of the eurozone economy, the market is hopeful for a strong recovery in the European economy. On Wednesday, European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen said that the EU is expected to achieve 70% of the adult population being vaccinated by the end of July.
- USD: The U.S. dollar index fell back to 90.3 from a 4-week high of 90.5 hits earlier in the session on Friday. Earlier, the U.S. employment report showed that the U.S. economy added fewer jobs than expected in May, alleviating the fear that the Fed will soon start to scale down. Expected. At the same time, the Federal Reserve announced on Wednesday that it would begin to liquidate its corporate bonds held last year by introducing an emergency loan mechanism to calm the credit market during the worst of the epidemic.
- CNY: The yuan fell by 0.00964 points, or 0.15%, to 6.40724 points against the U.S. dollar on Friday. The onshore exchange rate was previously set at 6.4072 points, the largest weekly decline in at least four months. The official issued a series of orders on the appreciation of the renminbi. Warn to bet. At the same time, after the US announced a better-than-expected weekly unemployment report, the U.S. dollar was bid for, and private sector wage data in May showed that labor market conditions strengthened. Service sector activity increased to record highs. At the same time, in China, as price pressures increase, the growth of the service industry has slowed. Traders are also paying attention to reports that Beijing and Washington are engaged in "normal discussions" on trade and economics, and it is clear that both sides are eager to get rid of the trade war aimed at solving the problem.
- RUB: The exchange rate of the Russian ruble against the US dollar was 73.2. Earlier in the session, it hit the highest level since March 17 of 72.8 US dollars. It was boosted by rising oil prices and the easing of geopolitical tensions. At the same time, investors continued to pay attention to Russia's main annual economic meeting. Oil prices have risen due to tighter market expectations. The benchmark Brent crude oil trading price is near a 15-month high of around $72 per barrel. In addition, the Kremlin confirmed that Russian President Putin and US President Biden would hold a summit in Switzerland on June 16 to discuss the future of bilateral relations, issues related to strategic nuclear stability, the Covid-19 pandemic, and regional conflicts. In addition, the United States also announced that it would not sanction the companies behind the Nord Stream 2 gas pipeline. In terms of monetary policy, the Central Bank of Russia raised interest rates by 50 basis points, which was more than expected. It opened the door for further interest rate hikes in the coming months to curb inflation.
- JPY: The yen rose 0.101 points or 0.09% against the dollar on Friday to close at 110.166 points, an 8-week low, as strong US data pushed the dollar to a 3-week high. The local 10-year bond yield was 0.086%, while the U.S. 10-year bond yield rose to 1.627%. In the United States, the ADP report shows that US companies have created the most jobs in 11 months, much higher than expected, while the number of first-time jobless claims has fallen more than expected, and the service industry PMI shows record growth in the service industry. Concerning the coronavirus, the Japanese government extended the COVID-19 emergency that it implemented in Tokyo, Osaka, and seven other prefectures last week. Furthermore, local data show that the actual household expenditure in April increased by 13% compared with the same period of the previous year, the highest increase in history. Earlier this week, the African Union Bank’s Japan Service Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) rose from an initial 45.7 to 46.5 in May, and the final value in April was 49.5.
- AUD: The Australian dollar was flat at a seven-week low of 0.76614 in early trading on Friday and stabilized after a 1.21% decline from the previous trading day, as strong US data pushed the dollar to a three-week high. The local 10-year bond yield was 1.645%, while the U.S. 10-year bond yield rose to 1.627%. In the United States, the ADP report shows that US companies have created the most jobs in 11 months, much higher than expected, while the number of first-time jobless claims has fallen more than expected, and the service industry PMI shows record growth in the service industry. In addition, local data show that retail sales in April increased by 1.1% month-on-month, the second consecutive month of growth; Australia’s trade surplus was the largest since January, with exports rising by 3%, a 13-month high, and imports falling by 3%.
• CHART OF THE DAY:
The FTSE MIB index rose for the fourth consecutive trading day. It closed on Friday at a nearly 11-year high of 25570 points, up 118 points or 0.5%, supported by cyclical stock gains. The central bank’s concerns about reducing ultra-loose monetary policy in advance have eased. As traders digested the news that the Italian drilling company signed an agreement with Naval Energy to acquire its offshore wind energy assets, Saipem rose to the rankings with a 2.7% increase. At the same time, Fitch Ratings Agency confirmed that GM's financial strength is "A-" and its credit rating remains unchanged at "BBB+." In terms of data, the Italian Institute of Statistics estimates that domestic demand and the economy will grow by 4.7% in 2021 and 4.4% in 2022. The index rose 1.7% last week.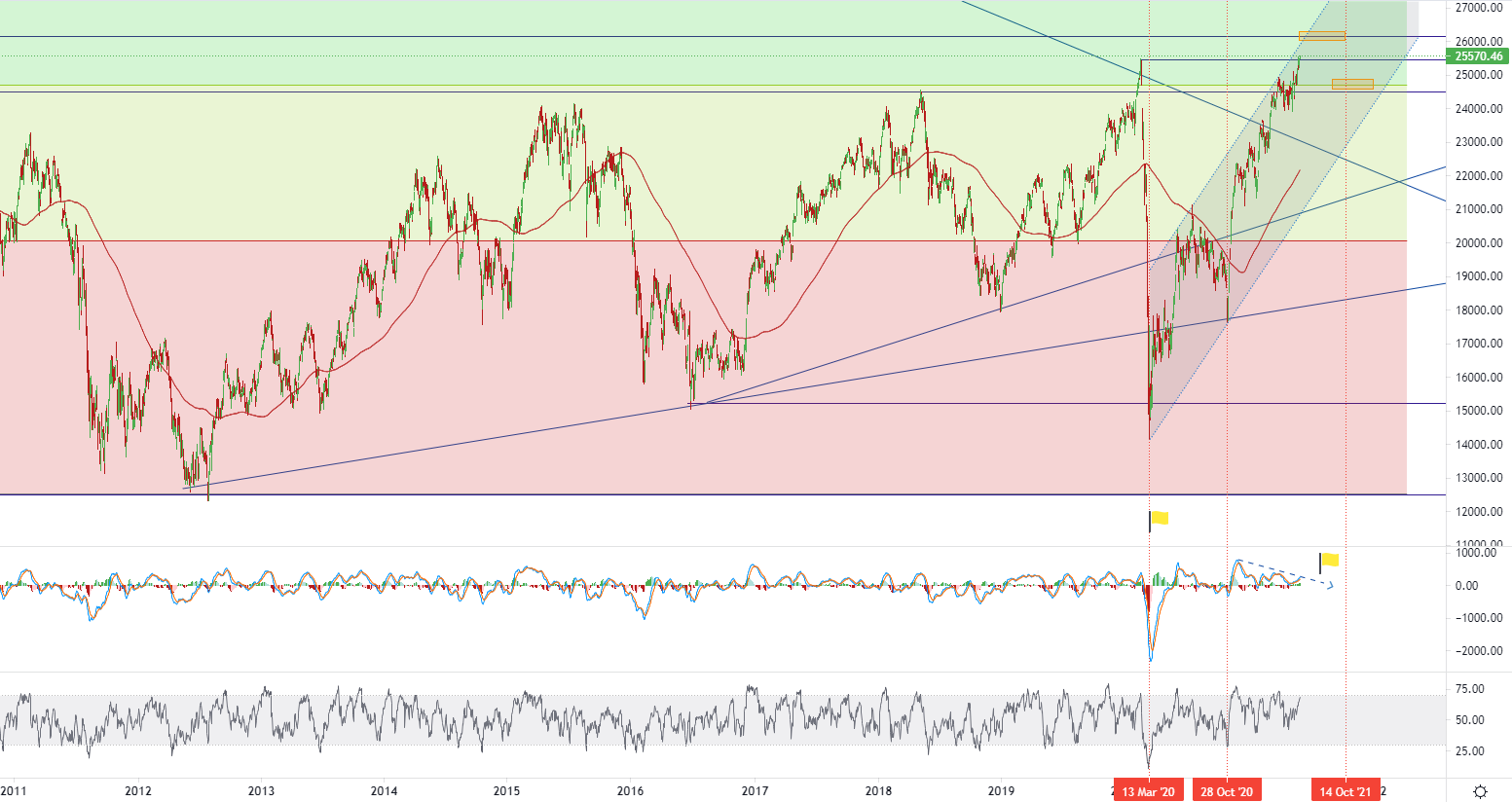 • Italian FTSE MIB index - D1, Resistance (target zone) around ~ 26178, Support (target zone) around ~ 24800.
• Italian FTSE MIB index - D1, Resistance (target zone) around ~ 26178, Support (target zone) around ~ 24800.
Demo account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account with virtual funds in a risk-free environment
Demo accountLive account
The Blue Suisse Trading Account in our transparent live model environment
Open an Account





